NPT Thread vs BSP Thread
Introduction
NPT (National Pipe Thread) and BSP (British Standard Pipe) are two of the more well-known types of threading standards used in sealing pipe connections. NPT is commonly applied in North America and has a 60-thread angle; BSP is utilized in Europe and Asia and uses a 55-degree angle.
It is crucial to distinguish between connecting parts to prevent cases where different pieces of piping equipment do not fit well together and leaking occurs. The differences between NPT and BSP threads and their usage are explained in this article.
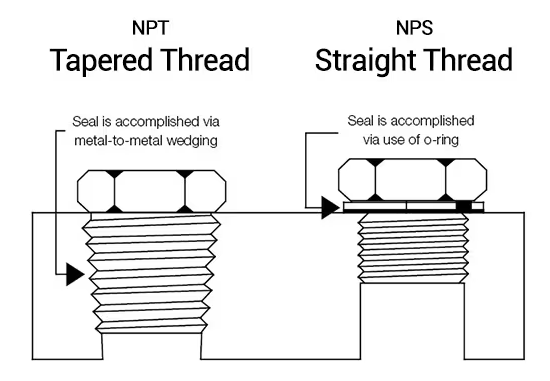
1. What is npt thread?
NPT thread, or National Pipe Thread, is a commonly used threading system regarding pipe connections, or pipe taps in certain specialties of North America.
With a narrowing structure, NPT thread is known to fit tightly to provide leak-tight sealing in Irrigation pipes, LPG cylinders, hoses, and natural gas systems among others.
A slender taper along with cut threads provides better and tighter coupling as pressure is applied when the connection is tightened which makes it perfect for application with high pressure.
NPT Thread Types
Several NPT thread types are used in different industries since they offer different specifications for various purposes. The most common NPT thread types include:
- NPT (National Pipe Taper):Also known as the acute taper thread and is commonly used for normal usage in its host industry.
- NPTF (National Pipe Taper Fuel):A thread that does not require a user to use other sealing material to cover the last thread of the smooth flow.
- NPS (National Pipe Straight):A standard used as a parallel-thread type where a straight-thread design is appropriate.
NPT threads can be classified into three types and it is crucial to note them so that one can be able to choose the type that is suitable for a particular project. Each type is intended to meet the most efficient for the specific use that it is put in.
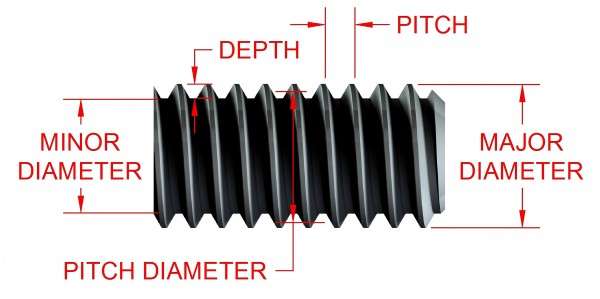
NPT Thread Dimensions
The dimensions of the nuclear piping system NPT thread are developed without tolerance to facilitate and enable a perfect fit of pipes and pipe fittings.
Thread data which refers to specifications shared by NT & P that come under the general NPT thread dimensions consists of attributes like the pitch, thread count, and taper angle. For example, 1 2NPT thread dimensions are for the 1/2-inch nominal pipe size used in domestic water supply systems and industrial practice.
Similarly, 1 8 NPT thread dimensions are created for a 1/8-inch nominal Pipe Size, which has a small application in applications such as air tools and instrumentation.
These include 1 2 NPT thread dimensions and 1 8 NPT thread dimensions Some of the parts of the move towards standardization are part of this area of the industry. Knowledge of these NPT thread dimensions is important to achieve a high degree of interference and thus have a good seal.
| Trade Size | Threads per inch | Pitch | Major Diameter (O.D) | ||
| Inch | mm | Inch | mm | ||
| 1/8 | 27 | 0.03704 | 0.94082 | 0.405 | 10.29 |
| 1/8 | 18 | 0.05556 | 1.41122 | 0.54 | 13.72 |
| 1/8 | 18 | 0.05556 | 1.41122 | 0.675 | 17.15 |
| 1/8 | 14 | 0.07143 | 1.81432 | 0.84 | 21.34 |
| 1/8 | 14 | 0.07143 | 1.81432 | 1.05 | 26.67 |
| 1 | 11 陆 | 0.08696 | 2.20878 | 1.315 | 33.4 |
| 1 录 | 11 陆 | 0.08696 | 2.20878 | 1.66 | 42.16 |
| 1 陆 | 11 陆 | 0.08696 | 2.20878 | 1.9 | 48.26 |
| 2 | 11 陆 | 0.08696 | 2.20878 | 2.375 | 60.33 |
| 2 陆 | 8 | 0.125 | 3.175 | 2.875 | 73.03 |
| 3 | 8 | 0.125 | 3.175 | 3.5 | 88.9 |
| 4 | 8 | 0.125 | 3.175 | 4.5 | 114.3 |
2. NPT applications:
NPT fittings:
NPT fittings are used in various industrial as well as domestic fields to ensure mechanical interconnection for joining pipes in a piped system for perfect sealing. These fittings are highly demanded especially in the plumbing, oil and gas sector, manufacturing sectors, HVAC, etc.
It eliminates leakage and generally makes the connection as efficient as intended by creating impeccable NPT fitting sizes to properly fit into the connection system.
NPT fitting sizes:
NPT Fitting sizes available in NPT form are crucial to the development of effective piping systems. Standard fitting sizes for NPT include 1/8 inch through to 2 inches, suitable for low and high pressure respectively.
For instance, a 1/8 NPT coupling or thread is appropriate for applications that require accuracies, such as piggyback equipment and small pipes, whereas larger NPT couplings or threads, 1” or 2,” are fit for large and high-flow industry pipes.
When choosing the right sizes of the NPT, you get an ideal match, and this improves the safety of the system and reliability.
BSP to NPT adaptor:
A BSP to NPT adaptor is very important especially when fitting two components with different thread standards.
In BSP (British Standard Pipe) thread predominant in European and Asian systems, PLL is employed; while in NPT fittings used in North America, PLL is absent. An adapter from BSP to NPT is in this case favorable as it would provide a direct interface of these components, especially for industries that require cross-system compatibility.
These adapters facilitate discontinuity since they enable constant and, at the same time, secure connections.
NPT Adapter:
Another important element of the piping system is an NPT adapter. This one connects pipes or fittings of different NPT fitting sizes or configurations, which is a good thing regarding the scalability of the system.
There is no way you can avoid the use of an NPT adapter especially if you are adding length to a pipeline or if you want to modify a fitting to fit in a particular system. If there are BSP threads in the operation, an NPT adapter may combine with a BSP to NPT adapter to support even more configurations of your system.
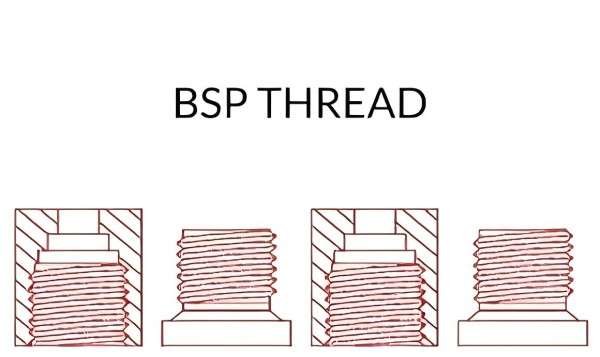
3. What is BSP Thread?
Before understanding ‘what are bsp threads’, let's first get to know ‘what is bsp’.The full name of BSP is British Standard Pipe. As the name suggests, BSP thread is one of the commonly used types of threaded connections in various pipeline systems both domestically and internationally.
This thread standard is common in the UK, Europe, and the world over as it provides safe and drip-tight connections across sectors that deal with water and gas supply, manufacturing, and automotive, amongst others.
BSP threads provide cost-effective solutions due to safe interconnection and a standard fit that provides a wide acceptance of BSP threads in numerous piping systems.
The threads on the pipe are such that any fluid, when the pipe is tightened, will lock in place to avoid any leakage when in use in handling either fluids or gases.
BSP Thread Dimensions and Specifications
The dimensions of the BSP thread depend on the size and the type of the BSP thread that is required for the particular application. BSP threads come in two main types: BSPP British Standard Parallel and BSPT British Standard Tapered.
Each thread of the BSP is dimensionally important for fitting applications; the sizes vary in the market. For instance, the BSP 1/4 thread dimensions are utilized in thin pipelines that are installed in the plumbing systems or equipment.
These BSP dimensions are very influential as they determine how closely the threads engage with the fittings and connectors to give a leak-proof and tight connection.
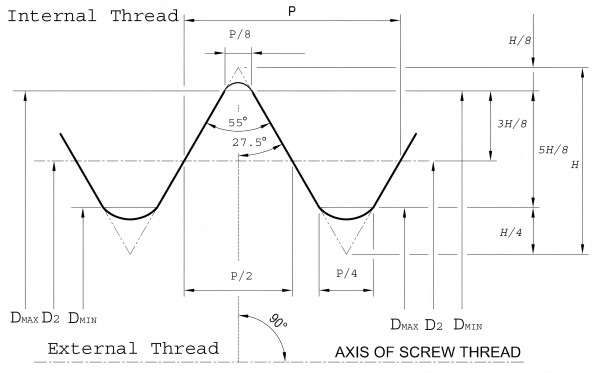
BSP Thread Angle: 55°
The BSP thread angle is 55° – this is the angle between the sides of the thread. This must be a standard angle for the satisfactory positive engagement of the threaded parts.
This ensures that the threaded sections interconnect perfectly thanks to the 55° angle – the setup is strong and relatively free from leakage in diverse pipeline applications.
As to the second parameter, the BSP thread angle is 55 degrees, which has to be considered when the thread is produced or assembled – otherwise, it will be impossible to avoid leaks and other system failures.
BSP Thread Chart in mm:
Moving down the right-hand vertical scale in mm gives a BSP thread chart with measurements in millimeters which are more helpful when selecting a fitting to be used in a certain application.
This chart also offers the related sizes, diameters, and thread pitches to allow professionals to decide on the appropriate fittings and connectors in piping services.
The BSP thread chart in mm is useful when using BSP threads as it provides a reliable reference when choosing the right size to use to have a leak-proof system.
BSP 1/4 Thread Dimensions:
BSP 1/4 thread dimensions are one of the widely used thread sizes within the BSP systems. It is little used for small uses such as air compressors, water pumps, and plumbing among others.
The actual dimension of BSP 1/4 thread fittings and connectors guarantees that they interconnect effectively to prevent leakage.
When it comes to a BSP 1/4 thread dimensions, one should be very careful in ensuring that the right type of BSP thread is used either it be BSPP or BSPT to get the right seal on the product and prevent leakage.
| Trade Size | Threads per inch | Pitch | Major Diameter | Minor Diameter | Gage Length | ||||
| Inch | mm | Inch | mm | Inch | Mm | Inch | mm | ||
| 1/8 | 28 | 0.0357 | 0.907 | 0.383 | 9.728 | 0.3372 | 8.565 | 0.1563 | 3.97 |
| 1/8 | 19 | 0.0526 | 1.337 | 0.518 | 13.157 | 0.4506 | 11.445 | 0.2367 | 6.012 |
| 1/8 | 19 | 0.0526 | 1.337 | 0.656 | 16.662 | 0.5886 | 14.95 | 0.25 | 6.35 |
| 1/8 | 14 | 0.0714 | 1.814 | 0.825 | 20.955 | 0.7336 | 18.633 | 0.3214 | 8.164 |
| 1/8 | 14 | 0.0714 | 1.814 | 1.041 | 26.441 | 0.9496 | 24.12 | 0.375 | 9.525 |
| 1 | 11 | 0.0909 | 2.309 | 1.309 | 33.249 | 1.1926 | 30.292 | 0.4091 | 10.391 |
| 1 1/4 | 11 | 0.0909 | 2.309 | 1.65 | 41.91 | 1.5336 | 38.953 | 0.5 | 12.7 |
| 1 1/2 | 11 | 0.0909 | 2.309 | 1.882 | 47.803 | 1.7656 | 44.846 | 0.5 | 12.7 |
| 2 | 11 | 0.0909 | 2.309 | 2.347 | 59.614 | 2.2306 | 56.657 | 0.625 | 15.875 |
| 2 1/2 | 11 | 0.0909 | 2.309 | 2.96 | 75.184 | 2.8436 | 72.227 | 0.6875 | 17.463 |
| 3 | 11 | 0.0909 | 2.309 | 3.46 | 87.884 | 3.3436 | 84.927 | 0.8125 | 20.638 |
| 4 | 11 | 0.0909 | 2.309 | 4.45 | 113.03 | 4.3336 | 110.073 | / | / |
4. BSP thread applications:
BSP threads or British Standard Pipe threads are used in plumbing, gas, oil, construction, and manufacturing industries to join pipes and fitting. Because these pipes are piped in standard sizes, their connection is leak-proof and applicable in both domestic and industrial use in piping systems.
A well-developed BSP thread chart enables professionals to know the right size to fit a specific application so that thread compatibility can be observed.
In general, it is vital to comprehend how to measure threads accurately as part of system integrity and reliably performing secure connections.Role of BSP Thread Chart in Applications
A BSP thread chart is an important reference material when discussing the size, pitch, and type of thread used in piping systems.
It also provides outlines of BSPP (parallel) threads and BSPT (tapered) threads, where they are needed. From the BSP thread chart, it is made easier for the professionals to determine the ideal thread to fit the job depending on whether it is going to be used to transport water, air, or gases.
This chart saves time and does not allow for mismatches on a lot of fittings, which would slow the process down.
For instance, in the case of the BSP thread chart, sizes that include 1/8”, 1/4”, 1/2”, and other bigger sizes are shown together with their respective measurements. It is important to match thread sizes more accurately to avoid leakage and serve system efficiency.
How to Measure Threads for BSP Applications?
Learning to identify threads is important in BSP fittings and there is a need to learn how to measure threads. Correct measurements including the thread pitch, diameter, and the type help the fittings to be a perfect fit. To measure threads:
- To determine the thread pitch, use the thread gauge.
- Using the calibrated, calipers, measure the outer diameter of the thread.
- Check the size and type of thread from the BSP thread chart.
- Explaining how to calculate threads enables the experts to choose the correct fittings hence avoiding system failures and too much downtime.
Applications of BSP Threads
Now you know “what are bsp threads”, then you can further understand their applications
- Plumbing Systems:
These BSP threads are widely used in systems that involve water supply and even water drainage systems because of the tight seal that cannot leak.
By using the BSP thread chart, a particular thread size for fitting the residential or commercial plumbing system can be chosen easily.
- Gas Pipelines:
In gas systems, the main challenge is to guarantee the connections are well-fixed. Accurate measurements of the threads and the proper execution of the BSP thread chart guarantee safe pipelines.
- Industrial Machinery:
These types of threads are usually used in the manufacturing of equipment as well as hydraulic systems. It also enables understanding how to measure threads and select the right sizes improving the durability of industrial piping connections.
- Global Projects:
BSP is globally used in Europe and other parts of the world hence using the BSP thread chart is crucial for projects that need compatibility with the British or European standards.
5. BSP vs NPT thread chart
Here is the BSP vs NPT thread chart. I hope it can help you.
| Size | BSP | NPT |
| 1/8” | 28 27 | |
| 1/4” | 19 | 18 |
| 3/8” | 14 18 | |
| 1/2” | 14 | 14 |
| 3/4” | 11 | 14 |
| 1” | 11 | 111/2" |
| 11/4” | 11 111/2" | |
| 11/2” | 11 | 111/2" |
| 2” | 11 111/2” | |
| 21/2” | 11 | 8 |
| 3” | 11 | 8 |
| 4” | 11 | 8 |
6.How to choose the NPT thread or BSP thread for Your Application?
So, after understanding the difference between NPT and BSP threads, you need to consider several factors when choosing NPT threads and BSP threads, such as the BSP vs NPT thread chart, application type, regional specifications, and compatibility with existing systems. Here is a guide to help you make a decision:
1. Understand Regional Standards
- NPT threads are mostly used in the United States, Canada, and some other parts of America.
- Self-tapping screws belong to the thread of BSP type which is commonly used in European, Asian, and Australian countries.
Choose a type of thread that corresponds to the standard of production from the region of manufacture of equipment or its components.
2. Application Requirements
- PTFE polymer threads are tapered and therefore give a close fit to prevent leakage which makes it suitable for use in pressure applications such as; gases, oil, and hydraulic applications.
- These threads come in parallel known as BSPP and tapering known as BSPT. These are preferred in plumbing, water supply, and low-pressure systems.
Find out if your implementation should have the thread parallel or tapers and if the sealing has to occur with the aid of tape or gaskets.
3. Compatibility with existing components
When building in an existing system, verify the type of thread used in current fittings into consideration. When BSP and NPT threads are used together there are high chances of leaks or damages if BSP to NPT adapter is not used.
It is ideal to ensure that you use a thread type that is constant to give the system a perfect workflow.
4. Measure and Verify Thread Type
Accurately measuring thread pitch, angle, and diameter helps identify whether you need NPT threads or BSP threads:
- NPT uses 60 degrees for the thread or lead whereas the BSP uses 55 degrees for thread or lead.
- Thread check by using a thread gauge and to ensure the dimensions of the workpiece use calipers.
5. Consider Adaptability
If the change between these systems does occur, then BSP to NPT adapters will help with the transition. These adapters are used for the connection of NPT with those fittings that have BSP threads or on the contrary.
As such, ensure that the adapter will fit the pressure and sealing needs of your application.
6. Pressure and leak considerations:
NPT threads are used for pressure higher than 1.5MPa where a tighter thread tolerance is needed to ensure a correct seal. For less demanding pressure applications BSP threads might be an option given that they could follow the local standards.
Conclusion
The local standard, usage needs, and system compatibility determine whether to use NPT or BSP threads.
Due to their superior strength and largest pitch, these threads are better for high-pressure pipelines in the Americas, while BSP is used in plumbing and low-pressure applications in Europe/Asia and Australia due to its small pitch.
To avoid connection failures, thread dimensions and angles must be measured consistently and accurately. An adapter can ensure that BSP and NPT threads are compatible and connect well.
Our Armpre Machinery can provide customized thread rolling machines and electric tapping machines to meet your NPT or BSP Threads product requirements
Don't forget to share this post!
Related Products
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and working details to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 159 27 555863
Want the best price & newest metal working machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Armpro's monthly newsletter,we're free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable working solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Tapping Machine: The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Electric Tapping Machines:the Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Drilling Machine: The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Drilling milling Machine:The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- CNC Tapping Machine :The Complete Buying Guide in 2024
- Pipe chafering Machine:The Complete Importing Guide in 2024
- Radial drilling Machine:The Complete Buying Guide in 2024
- Thread rolling Machine:The Complete Buying Guide In 2024
- Pillar Drilling Machine:The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024