Your Guide to Mastering Sheet Metal Fabrication and Growing Your Business
Introduction
Sheet metal is a vital raw material in various industrial fields: construction, automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.
Although definitionally a transformation of raw metal sheets into functional products, sheet metal fabrication helps industries create custom parts production or meet large-scale industrial needs.
Knowledge of sheet metal fabrication helps industries to become competent in making good production decisions, thereby increasing product quality while optimizing their manufacturing processes.
The following guide teaches business owners essential features about sheet metal production alongside key properties to maximize output quality.
1. The Sheet Metal Fabrication Process
A sheet metal fabrication procedure includes multiple essential steps that help manufacturers create desired metal products.
The fabricator selects project-appropriate metals, such as steel, aluminum, brass, and copper, for material specification.
The metal undergoes shape transformation using laser cutting, plasma cutting, and water jet cutting processes.
Pressing of brakes together with rollers enables metal parts to learn their intended form.
Welding and assembly function as the process of uniting various pieces through welding techniques or fastener applications.
Importance of Sheet Metal Manufacturing
The production of sheet metal components proves essential for businesses that need affordable manufacturing of high-quality metal elements.
Through sheet metal production, companies receive flexibility for design work while achieving large-volume manufacturing and delivering strong results across multiple uses.
Businesses that grasp sheet metal manufacturing methods can lower waste while building efficient production lines that make high-performing product solutions for their specific needs.

2. Sheet Metal Properties
When selecting materials for your project, you must understand how different sheet metals behave due to their properties. Sheet metal properties decide how strong or flexible a sheet will be and how suitable it is for particular applications.
What is Sheet Metal?
Sheet metal represents a flat thin metal piece that produces numerous shapes after easy shaping or cutting. This material finds widespread applications in construction together with automotive and aerospace sectors for building components, enclosures, and structures.
Sheet Metal Gauge Chart
A sheet metal gauge chart determines sheet metal thickness by displaying metal thickness amounts for various gauge levels. The lower the gauge number, the thicker the metal. A 10-gauge steel sheet exceeds the thickness of a 20-gauge steel sheet in dimension.
| Gauge | Thickness | |
| inch | mm | |
| 7 | 0.1443 | 3.665 |
| 8 | 0.1285 | 3.264 |
| 9 | 0.1144 | 2.906 |
| 10 | 0.1019 | 2.588 |
| 11 | 0.09074 | 2.305 |
| 12 | 0.08081 | 2.053 |
| 14 | 0.06408 | 1.628 |
| 16 | 0.05082 | 1.291 |
| 18 | 0.04030 | 1.024 |
| 20 | 0.03196 | 0.812 |
| 22 | 0.02535 | 0.644 |
| 24 | 0.02010 | 0.511 |
| 26 | 0.01594 | 0.405 |
| 28 | 0.01264 | 0.321 |
| 30 | 0.01003 | 0.255 |
Sheet Metal Grade
The market provides sheet metals with different grades that vary by their chemical compositions and material properties. Some common grades include:
- The resistance of stainless steel (304, 316)in food processing and medical industries against corrosion is shown through its application.
- Aluminum (5052, 6061) – Light in weight and therefore suitable for use in aerospace and automotive sectors.
- Carbon Steel (A36, A1011)is employed in structural applications due to its strength and toughness properties.
The distinction between metal materials and sheet metal products exists regarding their form characteristics.
The primary distinction emerges through the different forms between regular and sheet metals.
Base materials comprising iron and aluminum alongside copper in the forms of ingots and bars and rods constitute metal.
A processed metal product called sheet metal appears as a thin, flat material that enables easy fabrication of various shapes.
Understanding sheet metal properties enables businesses to pick suitable materials and improve their production approaches. Manufacturing projects benefit from efficiency together with durability and cost-effectiveness when producers use the sheet metal gauge chart to select appropriate sheet metal grades and thicknesses.
| AISI/ASTM | EN | Weight% | ||
| Cr | Other elements | Melts at | ||
| 405 | 1.4000 | 12.0-14.0 | ||
| 409L | 1.4512 | 10.5-12.5 | 6(C+N)<Ti<0.65 | |
| 410L | 1.4003 | 10.5-12.5 | 0.3<Ni<1.0 | |
| 430 | 1.4016 | 16.0-18.0 | 1510[9] | |
| 439 | 1.4510 | 16.0-18.0 | 0.15+4(C+N)<Ti<0.8 | |
| 430T | 1.4511 | 16.0-18.0 | Ti:0.6 | |
| 441 | 1.4509 | 17.5-18.5 | 0.1<Ti<0.6
0.3+3C<Nb<1.0 |
|
| 434 | 1.4113 | 16.0-18.0 | 0.9<Mo<1.4 | |
| 436 | 1.4513 | 16.0-18.0 | 0.9<Mo<1.4
0.3<Ti<0.6 |
|
| 444 | 1.4521 | 17.0-20.0 | 1.8<Mo<2.5
0.15+4(C+N)<Ti+Nb<0.8 |
|
| 447 | 1.4592 | 28-30.0 | 3.5<Mo<4.5
0.15+4(C+N)<Ti<0.8 |
|
Sheet Metal Advantages and Disadvantages
The evaluation of sheet metal benefits and drawbacks serves businesses in their project decisions because, like all materials, it offers both positive and negative features.
Sheet Metal Advantages
- The strength of sheet metal allows it to operate successfully under high pressure in addition to enduring extreme environmental conditions.
- This material maintains flexible properties that enable both cutting operations and bending tasks and the formation of different shapes.
- The economy benefits from mass production since it leads to reduced product expenses.
- The weight of sheet metal becomes reasonable while preserving its structural integrity because of material selection.
Sheet Metal Disadvantages
- Tablet setup expenses, including machine and instrument costs, start off at a high level.
- The process of rust requires some metals to be protected with coatings or unique surface treatments.
- The manufacturing process and exact cutting operations need professional workers along with specialized manufacturing technologies.
Sheet Metal Designing
Sheet metal part designers need to plan thoroughly before production so the created part meets operational standards.
Material Selection – Choosing the right metal for strength and durability.
Selecting the appropriate material thickness requires the use of a sheet metal gauge chart as a design reference.
The prediction of material deformation during bending requires a calculation of Bend Allowance.
Sheet Metal Design Software
Multidimensional models with precise accuracy result from the use of advanced sheet metal design software. Popular tools include:
The CAD Modeling and sheet metal design suite includes SolidWorks as one of its main features.
AutoCAD – Ideal for 2D and 3D designs.
Fusion 360 enables users to model and manufacture through its internet-based platform.
Sheet Metal Application
Sheet metal serves numerous industries throughout the market.
Automotive Industry
The automotive and other industries use this material to build their car frames as well as panels and exhaust systems.
Provides lightweight yet strong components.
Aerospace Industry
Aircraft bodies, together with wings and engine parts, depend on it for construction.
Offers a high strength-to-weight ratio.
Construction Industry
This material serves multiple purposes because it enables roofing applications and cladding operations as well as structural building components.
Provides weather resistance and durability.
Energy Industry
Photovoltaic energy facilities use this material, as do turbines and solar panel structures, in wind power applications.
Offers corrosion resistance for long-term applications.
Sheet Metal Material
The performance of every project depends on selecting an appropriate sheet metal. Strength, durability, weight and environmental resistance (inclusive of corrosion and temperature changes) are all affected by the material chosen.
For this reason, industries apply different kinds of sheet metals for their projects.

Types of Sheet Metal
It should be noted that there exist various types of sheet metals which serve different functions due to their unique properties.
Stainless Steel Sheet Metal
- Resistance to rust and corrosion is very high in this case.
- This type of sheet is commonly found in the food industry, hospitals (for tools), etc., and it is also used at sea for many applications.
- Stainless steel can come in several grades e. g. 304 or 316 each offering varying degrees of strength and resistance level.
Galvanized Steel Sheet Metal
- In galvanized steel, there is a preventive layer made up of zinc or oxide, which stops corrosion from developing.
- It is used mainly for external constructions, roofing, and several automotive components.
- Galvanized steel has a reasonable degree of durability and weather resistance.
Aluminum Sheet Metal
- Very corrosion-resistant and highly malleable.
- Best suited for aerospace, automotive, and electronic applications.
- Has excellent thermal and electrical conductivity.
Carbon Steel Sheet Metals
- Strong and cheap.
- Used for construction, machines, and industrial purposes.
- Works well for protective coatings against the onset of corrosion.
Copper and Brass Sheet Metal
- Excellent electrical and thermal conductivity.
- Used in electrical components, roofing, and decorations.
- Brass is particularly well known for making musical instruments and plumbing fittings.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Sheet Metal
For one to decide on the right kind of sheet metal, he or she should think about its:
- Strength and Durability: These are the types of metals that have high strength e. g. stainless and carbon steel, which are very suitable when working with strong structures.
- Corrosion Resistance: If the surface may come into contact with moisture or chemicals in any environment, it is recommended that stainless steel or galvanized sheets be used.
- Weight Considerations: The best option for applications where weight is of concern is aluminum because it is light in weight but still strong enough.
- Cost Efficiency: On a side note, carbon steel is cheaper, but most of the time, it has to be coated for additional protection.
- Aesthetic Value: Copper and brass are fashionable options that give ornamental appeal to architectural and artistic elements.
Therefore, one needs to be very keen while selecting the most appropriate sheet metal since this will determine if the project will succeed in the long run.
Companies must understand the types of sheet metals that exist and their properties to improve their manufacturing processes and produce stronger products. This is vitally important because it contributes to meeting the sector's requirements.
3. Different Types of Sheet Metal Fabrication
The various industries, such as automotive and aerospace, together with construction and electronics, heavily depend on sheet metal fabrication procedures. The procedure combines diverse technological methods for modifying metal sheets before assembling them into operational end products.
Modern industry utilizes multiple sheet metal fabrication techniques as described in this list:
Sheet Metal Bending
Sheet metal bending constitutes an essential production technique for creating specific angular and shaped modifications in metal sheets that preserve their original volume. Different equipment, such as press brakes along with rollers and manual bending tools, execute this bending technique. Industrial manufacturing needs bending operations to fabricate enclosures and produce brackets together with structural components.
Sheet Metal Cutting
The removal of excessive metal material from sheet forms the basis of sheet metal cutting which creates products with specific dimensions and shapes. Laser cutting performs together with plasma cutting and water jet cutting and shearing represent different cutting techniques for sheet metal applications. The selection of tooling methods depends specifically on the material type as well as sheet thickness and necessary accuracy standards.
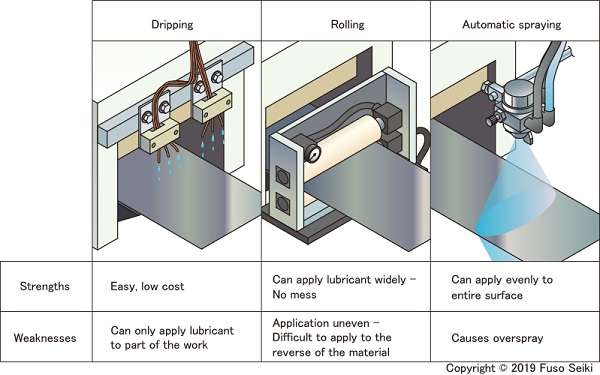
Sheet Metal Coating
The protective treatment of sheet metal uses protective layers that prevent corrosion and improve its visual appeal. The three main coating techniques used are powder coating, galvanization, and anodizing. Coatings play a vital role when metal materials operate outside where they need protection from extreme environmental elements.
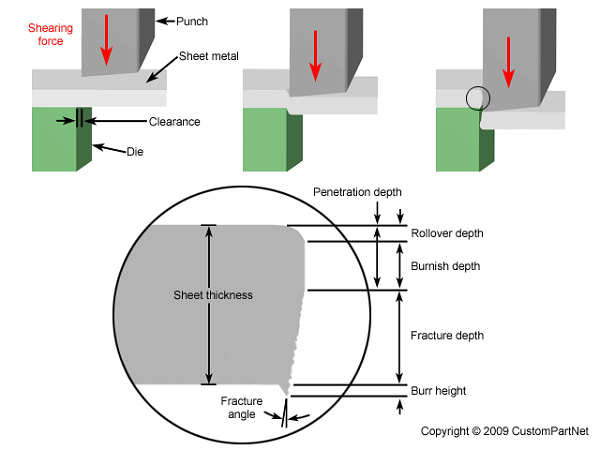
Sheet Metal Deburring
The fabrication process creates various sharp edges together with burrs on metal components. The removal process, which achieves safety, operational enhancement, and better looks, is known as sheet metal deburring. Manual operations apply deburring through files alongside abrasive pads, while automated equipment operates deburring machines.
Sheet Metal Stamping
The fabrication process called sheet metal stamping allows high-speed formation of metal sheets into specific shapes through the use of dies operated by presses. The sheet metal manufacturing process using this method produces numerous identical components of excellent quality, such as automotive panels alongside electronic enclosures and metal brackets.
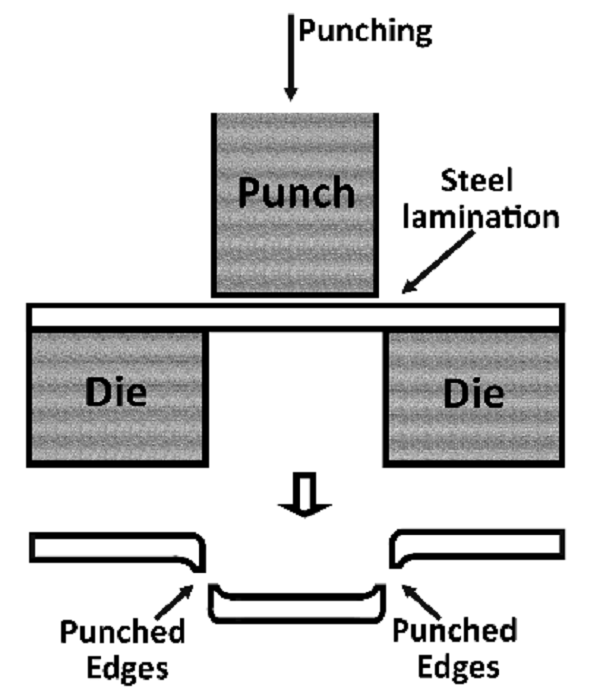
Sheet Metal Punching
A punch press directs its operations towards creating holes and slots along with intricate cutouts within metal sheets. High efficiency marks this process when building ventilation panels as well as mounting brackets and custom enclosures.
Sheet Metal Assembly
The end purpose of fabrication includes joining various metal pieces for final manufacturing by sheet metal assembly. The application requirements determine which joining methods will be used, such as welding, riveting, fastening, or adhesive bonding.
The various sheet metal fabrication techniques are necessary steps to create high-quality metal products. The knowledge about these operations enables manufacturers to optimize their manufacturing approach for better outcomes.
Sheet Metal Welding
For manufacturing operations, the combination of different metal pieces through welding becomes a fundamental requirement. Any procedure among MIG, along with TIG and spot welding can be used according to the metal thickness together with the material type. The structural integrity of objects results from welding processes that appear in automotive frames as well as machinery components and industrial equipment.
4. Why Sheet Metal Deburring is Becoming Increasingly Important in the Sheet Metal Fabrication Process
Manufacturing sheet metal pieces demands both exceptional precision and top-quality standards in every stage of the production process. The process of sheet metal deburring has become increasingly important for manufacturers during the last few years.
The manufacturing industry now requires metal parts with higher accuracy standards, which makes deburring a vital requirement for fabrication production. The increasing demand for sheet metal deburring arises from the following reasons:
Improved Safety
Sheet metal deburring serves primarily as a method to protect workplace environments better. Metal components pose significant safety hazards because they contain burrs as well as sharp edges. The removal of these imperfections decreases the chance of work-related injuries because it establishes better workplace safety.
Enhanced Aesthetics
Visual aesthetics of fabricated metal components remain crucial to various business sectors that depend on the appearance and quality of their products. The final product acquires a professional finished appearance when sheet metal deburring rounds off its harsh edges. The process of removing imperfections is essential for consumer goods, together with decorative metal products and high-end industrial components.
Better Fit and Assembly
Manufacturing applications require precise fabrication since it determines the successful assembly of machine parts. The presence of burrs creates obstacles for precise assemblies because they weaken the alignment between components. The correct application of a sheet metal deburring process enables perfect component placement, which enhances both product performance and simplifies the assembly work.
Increased Durability
Unsmooth metal edges produce weak structural points, which shorten the lifespan of metal components and cause their premature breakdown. Sheets that undergo treatment by a sheet metal deburring machine develop enhanced durability through the removal of imperfections. Longevity of products along with decreased maintenance expense becomes possible when manufacturers use sheet metal deburring.
Improved Coating Adhesion
The success of protective coatings such as paint and powder coating requires surface smoothness as well as galvanization, depending on a smooth substrate. The application of coating becomes irregular and leads to peeling and chipping, which later results in corrosion because of burrs and sharp edges. A uniform surface produced by sheet metal deburring operation leads to better protective coating adhesion and extended coating life.
Reduced Wear on Tools
The tool and equipment wear rate increases when burrs and rough edges exist because they create friction during subsequent production stages. A sheet metal deburring machine eliminates imperfections, which extends tool and drill life as well as machine press longevity, thus cutting production expenses.
Sheet metal deburring is still a critical process of contemporary fabrication, given that there is an increasing need for high-quality and precisely engineered metallic products. To make sure that everything is done well and that the machines are safe, one should invest in the right deburring methodologies as well as equipment which also serve to improve the appearance of the products and their safety; this will increase their lifespan and how they work at large.
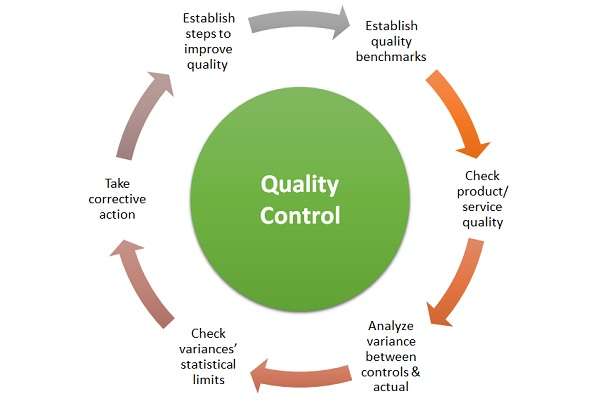
5. Sheet Metal Fabrication Inspection and Quality Control
Maintain high standards of fabricated sheet metal components since quality assurance leads to both precision and durability, as well as functional performance. The fabrication process uses different inspection methods and quality control procedures to detect flaws and uphold outstanding quality. The following are significant inspection procedures:
Visual Inspection
Inspection through visual examination works as an essential quality control approach by letting inspectors view metal parts for their external flaws and marks together with their non-uniformities. The identification of visible imperfections using these methods happens before proceeding with more complex testing methods.
CMM Inspection
The Coordinate Measuring Machine, known as CMM Inspection, provides manufacturers with an exceptional measurement capability to evaluate intricate geometries precisely. Manufacturers in the aerospace and medical device sectors depend on this method to achieve their required tight tolerances.

Bend and Form Inspection
The accuracy of sheet metal bends and formed shapes go through evaluation during bend and form inspection. The evaluation method confirms that bent parts and shapes align with engineering drawings from specifications.
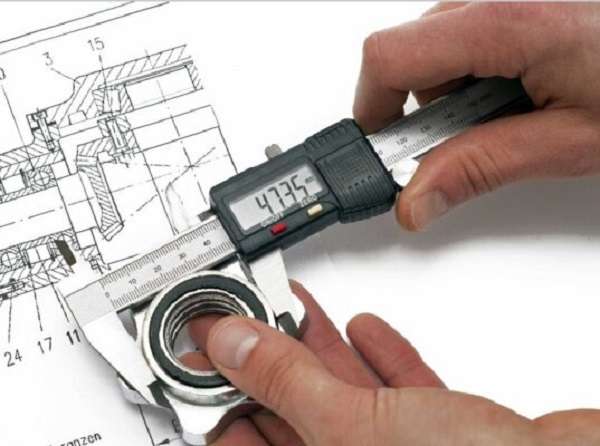
Dimensional Inspection
Dimensional Inspection validates that produced metal components stay within their defined dimensional requirements. Manufacturers use Kleiss, micrometers, and Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) to verify the precision of each manufactured component.
Weld Inspection
Technicians look for weld defects like cracks and both inward and outward defects during Weld Inspection to prevent NBC bulges. If welding standards are not kept, then the strength and overall integrity of the commodity will be reduced.
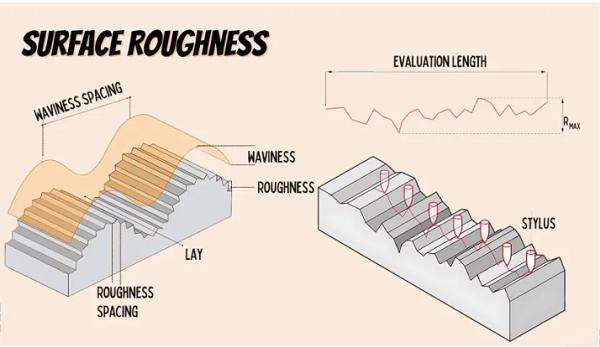
Surface Roughness Measurement
Surface Roughness Measurement provides an assessment of metal surface texture together with finish quality. High aesthetic requirements and proper coating binding need a smooth surface.
Gauge Inspection
The procedure of gauge inspection necessitates using specific measuring tools to confirm part dimensions and fit quality. Manufacturers depend on this method to verify component alignment with design requirements while maintaining correct functioning inside their assembled systems.
Non-Destructive Testing
The non-destructive testing comprises ultrasonic testing and x-ray inspection that reveal e any damage that exists inside without causing any harm to the part under test. Such tests carried out by NDT play a critical role in ensuring that products remain dependable within sensitive application areas e. g., aerospace manufacturing or the automobile industry.
Through such forms of examining and monitoring quality control, the manufacturer can uphold high levels of quality to reduce flaws thereby increasing durability as well as performance of sheet metal components.

Conclusion
In summary, sheet metal fabrication is a fundamental stage in contemporary manufacturing processes because it offers precision, strength, and adaptability applicable across all industries.
Knowledge of the properties of sheet metals, various fabrication methods, as well as deburring’s role, is crucial since it leads to effective, secure, and durable fabrications.
These include but are not limited to deburring machines and other advanced equipment employed for improving products’ aesthetics while also increasing their resistance and strength.
Sheet metal remains crucial in the future of creative thinking and industrial growth, being used in automotive, aerospace, construction, and energy sectors among others.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related Products
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and working details to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 159 27 555863

Want the best price & newest metal working machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Armpro's monthly newsletter,we're free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable working solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Tapping Machine: The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Electric Tapping Machines:the Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Drilling Machine: The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Drilling milling Machine:The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- CNC Tapping Machine :The Complete Buying Guide in 2024
- Pipe chafering Machine:The Complete Importing Guide in 2024
- Radial drilling Machine:The Complete Buying Guide in 2024
- Thread rolling Machine:The Complete Buying Guide In 2024
- Pillar Drilling Machine:The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024