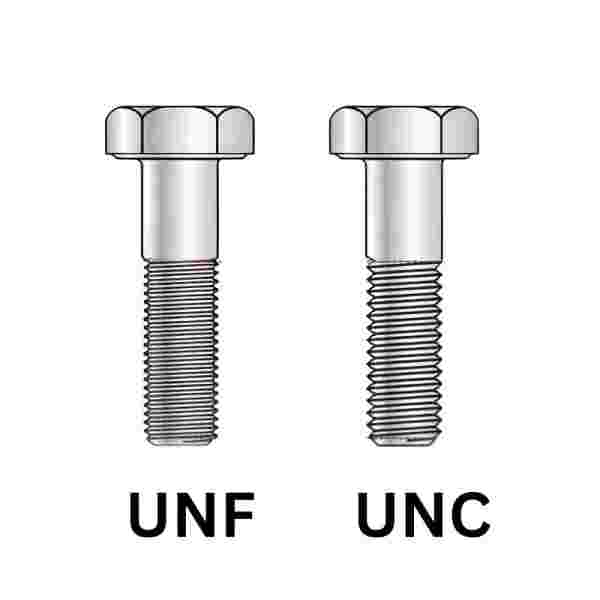
UNF vs UNC
Introduction
Selecting the most appropriate threading system is one of the critical steps in any design or application and may virtually make or mar the project. Of all thread systems, the two that are most frequently applied in thermoplastic mechanical and industrial applications are the “UNF” and “UNC”.
These thread systems differ in purpose, and by making a comparison, it should be easier to identify the most appropriate one based on its necessity in specific processes. In this article, the authors reveal what “UNF” and “UNC” are, how they work, and how to choose between them based on a range of important criteria like UNF colour or UNF size.
1、What is "UNF"?
If you want to know "what UNF means",First of all, we need to know “what is UNF thread”. UNF stands for Unified National Fine and refers to the threading system that is characterised by fine threads pitch. So, this is the exact word for UNF if we want to know what is UNF. The word “fine” here is used to denote the number of threads per inch, with “UNF” threads having more threads per inch than “UNC” (Unified National Coarse) threads. This fine pitch makes ‘UNF’ threads finer and more appropriate in cases where accuracy and stamina are considered crucial. The current threads produce a tighter compression than the previous threads, and this is especially important for high-accuracy applications such as aircraft or automotive industries. Here, we have understood what is UNF thread and what UNF means, and now let us discuss it in detail.
There might be confusion over what exactly “UNF” means, so it will be useful to explain the “UNF size” as well. The size of the thread is one of the most important aspects of any threading system because it indicates the diameter of the bolt or screw. The UNF size varies between small, such as 1/4 ”, to larger sizes for a certain application. UNf size is used to define the best size and shape of the fastener that is required for a particular application, which is important in industries where great accuracy is expected. There are also a variety of UNF colours. You can also choose UNF based on UNF colors and UNF size. In short, the UNF chart can be helpful in this regard. UNF size and UNF color are very essential factors in this regard.
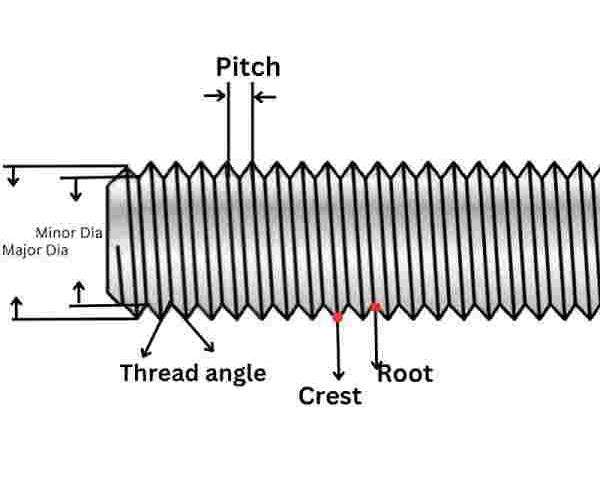
Yet another factor of the “UNF or UNF chart” is the “UNF thread”. The term “UNF thread” has a simple meaning of being the kind of thread which is produced on a screw or a bolt. This design enables the fastener to form a complementary shape with a nut or its intended hole so that when used, they are effective and very efficient. The UNF thread chart was created to withstand the loads and wear caused by the course of work, so it is suitable for problem-solving use.
In other words, the “UNF thread chart” provides a threading system that highlights aspects such as precision, strength, and durability. It is highly suitable where close tolerance is called for and where the strength of the fastener is a consideration. We can use those standards in machinery, automotive parts, aerospace equipment, and so on. The “UNF chart” and UNF thread chart offer information about the kind of performance expected in demanding situations.
2、"UNF" Application
The “UNF application” is primarily used in industries that require the efficiency of the product’s strength and accuracy. Aerospace production is perhaps the most well-known application of “UNF.” The fasteners used in aircraft need to be capable of withstanding high stress, resisting vibration loads and being durable to a large degree for extended periods. They are particularly suitable for this purpose, as the given UNF threads’ pitch is fine, thus providing good contact and clamp load even when the equipment is exposed to heat.
Secondly, apart from aerospace engineering, “UNF” is widely applied in the automobile industry. Cars and especially racing cars need high-quality car screws and bolts that guarantee great performance. For instance, “UNF” bolts and screws are applied in the construction of engine parts where threads are subjected to tension that cannot cause the fastened parts to come loose. The “UNF application” in automotive manufacturing ensures that the engine and other parts are shaped to be high-strength.
The final sector where the application of the “UNF thread chart” is very important is in the manufacturing of industrial plants. The industrial applications of heavy machinery manufacturing, construction, and many others make use of the “UNF” thread system to maximise the holding power of the parts subjected to high loads. This is because “UNF” threads are very accurate and long-lasting for such uses, and any failure here could be disastrous.
However, apart from these industries, it is also crucial in medicine where “UNF” threads are utilised. For instance, surgical tools and medical equipment need a “UNF” thread because such a thread profile is crucial in guaranteeing how safe and effective the surgical tool or equipment would be in serving its intended function. Depending on the application of UNF application in medical devices ensures that the fasteners are highly usable, especially under the various uses that they are subjected to; thus, they are highly durable.
Specifically in the “UNF application”, the detailed narrow threads and high strength of “UNF” are especially suitable to use in applications where high precision along with stress and vibration resistance is essential.
3、What is "UNC"?
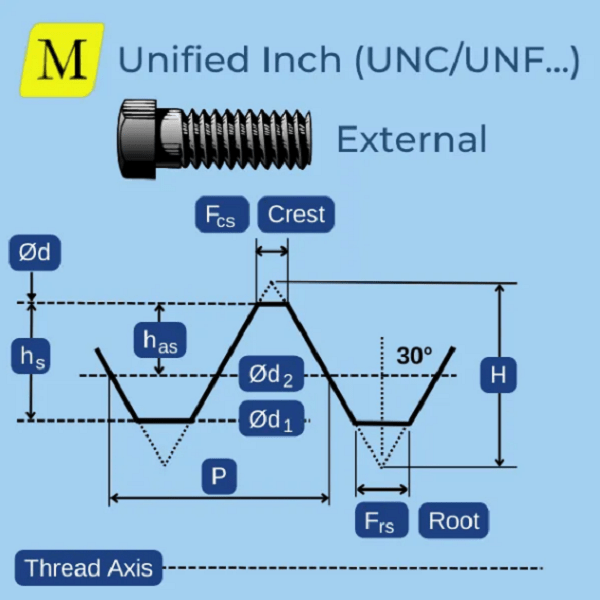
Now, we need to know what is UNC and what does UNC mean. The “UNC”, also known as Unified National Coarse, is a thread system that has slight differences from the “UNF” thread system. So, this is exactly what you want to know, “what does UNC mean.” The main difference comes down to the depth of the threads that are cut on the shafts’ surfaces. As for the manufacturer’s threading standards, “UNC” threads are comparatively coarser than “UNF” threads due to the fact that the number of threads per one inch is relatively less for “UNC” than for “UNF ‘threaded fasteners’. This results in making “UNC” threads heavier or provided with a greater load-carrying capacity and better ability to resist wear than “UNF” threads in some circumstances.
Have you learned “what does UNC stand for”? We have already discussed “what does UNC stand for” or what does UNC mean and what is UNC. Now, we will discuss the UNC thread. The “UNC thread” is mainly applied in cases where strength wear resistance is a priority over accuracy. For instance, and as discussed earlier, in construction and heavy machinery equipment, the “UNC” threads are often used because the threaded members have rough cooperative threads that are more appropriate for withstanding rigorous loads and harshest working conditions. The design of the “UNC thread” is also more convenient for production, as the large thread sizes are not susceptible to breakages throughout the manufacturing process.
Another essential aspect of discussion along with “what is UNC or what does UNC stand for” is its great flexibility. Applications for “UNC” threads include automotive products, industrial machinery and so on. Their capability to deliver secure connectivity for the demands, whereby accuracy is not a consideration, makes them worthwhile in applications whereby strength and astoundingly stability are paramount.
But let me also remind you that it is also important to mention the sizing when speaking of the “UNC”. Similar to “UNF”, “UNC” threads are of different sizes, and they are mostly used for bolts from small size to large-sized fasteners. Superficially threaded parts with a coarser percentage of thread are designated as “UNC” threaded parts because of their ability to engage the threads more initially and their ability to withstand larger forces,such as the common UNC screw, which is a type of threaded part.
Thus, “UNC” is a threading system that proposes strength and durability instead of accuracy, including the UNC screw we mentioned earlier. It is composed of extra coarse threads and is therefore suitable for uses where the linking has to endure a burden and rough environment. In the construction of all forms of infrastructure, automotive applications, and industrial machinery, “UNC” threads are crucial in creating perpendicular to the main plane threads that compliment the parallel ones by giving support and safety to the components they are used in.
4、"UNC" Application
The “UNC application” phenomenon is untypical and exists in various fields which demand strength and durability. A primary use of the “UNC” is in the construction industry, where pipes are used to transport different commodities such as oil. In this sector, fasteners are demanded to join large and heavy parts, most frequently in rather severe climate conditions. Due to the composition of “UNC” threads, these fasteners have adequate tensile strength to enable them to achieve excellent performance under pressure, particularly in equipment used in construction and structures.
Apart from construction, the “UNC thread chart and UNC application” are widely used in the automotive industry. “UNC” thread chart is normally used when some of the vehicle components need to be assembled with strong threaded joints, though not very accurate in terms of the nature of the application needed. Thus, we have “UNC” bolts used in engine blocks and chassis wherein the threads need to be hard-wearing but do not require the close tolerance of “UNF” threads.
The “UNC application” also stands for the industrial sector of enterprises where machine tools and equipment are often operating at high loads and stress. In these applications, the “UNC” thread chart guarantees information about the fact that the fasteners can take these forces without yielding. The threads created by ‘UNC threads are also easy to assemble, especially when there is a need to assemble products in industries.
Therefore, the “UNC application and UNC thread chart” suit the structure best whenever strength, durability, and minimum time for assembly are rated among the top priorities. By design, whether in construction, automotive or industrial applications, “UNC” threads offer the durability and workmanship that comes with applications of higher levels of viscosity.
| Thread Designation | UNF / UNC | Threads per Inch | Basic Major Diameter | Basic Minor Diameter |
| 0-80 | UNF | 80 | 0.06 | 0.047 |
| 1-64 | UNC | 64 | 0.073 | 0.056 |
| 2-56 | UNC | 56 | 0.086 | 0.067 |
| 2-64 | UNF | 64 | 0.086 | 0.069 |
| 4-40 | UNC | 40 | 0.112 | 0.085 |
| 5-40 | UNC | 40 | 0.125 | 0.098 |
| 5-44 | UNF | 44 | 0.125 | 0.1 |
| 6-32 | UNC | 32 | 0.136 | 0.104 |
| 6-40 | UNF | 40 | 0.136 | 0.111 |
| 8-32 | UNC | 32 | 0.164 | 0.13 |
| 8-36 | UNF | 36 | 0.164 | 0.134 |
| 10-24 | UNC | 24 | 0.19 | 0.145 |
| 10-32 | UNF | 32 | 0.19 | 0.156 |
| 1/4-20 | UNC | 20 | 0.25 | 0.196 |
| 1/4-28 | UNF | 28 | 0.25 | 0.211 |
| 5/16-18 | UNC | 18 | 0.313 | 0.252 |
| 5/16-24 | UNF | 24 | 0.313 | 0.267 |
| 3/8-16 | UNC | 16 | 0.375 | 0.307 |
| 3/8-24 | UNF | 24 | 0.375 | 0.33 |
| 7/16-14 | UNC | 14 | 0.438 | 0.36 |
| 7/16-20 | UNF | 20 | 0.438 | 0.383 |
| 1/2-13 | UNC | 13 | 0.5 | 0.417 |
| 1/2-20 | UNF | 20 | 0.5 | 0.446 |
| 9/16-12 | UNC | 12 | 0.563 | 0.472 |
| 9/16-18 | UNF | 18 | 0.563 | 0.502 |
| 5/8-11 | UNC | 11 | 0.625 | 0.527 |
| 5/8-18 | UNF | 18 | 0.625 | 0.565 |
| 3/4-10 | UNC | 10 | 0.75 | 0.642 |
| 3/4-16 | UNF | 16 | 0.75 | 0.682 |
| 7/8-9 | UNC | 9 | 0.875 | 0.755 |
| 7/8-14 | UNF | 14 | 0.875 | 0.798 |
| 1-8 | UNC | 8 | 1 | 0.865 |
| 1-14 | UNF | 14 | 1 | 0.91 |
| 1 1/8-7 | UNC | 7 | 1.125 | 0.97 |
| 1 1/8-12 | UNF | 12 | 1.125 | 1.035 |
| 1 1/4-7 | UNC | 7 | 1.25 | 1.095 |
| 1 3/8-6 | UNC | 6 | 1.375 | 1.195 |
| 1 1/2-6 | UNC | 6 | 1.5 | 1.32 |
| 1 3/4-5 | UNC | 5 | 1.75 | 1.534 |
| 2-4.5 | UNC | 4 1/2 | 2 | 1.759 |
| 1 1/4-7 | UNC | 7 | 1.25 | 1.095 |
| 1 3/8-6 | UNC | 6 | 1.375 | 1.195 |
| 1 1/2-6 | UNC | 6 | 1.5 | 1.32 |
| 1 3/4-5 | UNC | 5 | 1.75 | 1.534 |
| 2-4.5 | UNC | 4 1/2 | 2 | 1.759 |
5、How do you choose "UNF" or "UNC" for your application?
Now you know the unf means and what does UNC mean. Therefore, when one is choosing between “UNF” and “UNC”, then he has to take into consideration the nature of the application in the project. If you require accuracy, fine thread, or the trait that can minimise the impacts of vibration, then go for “UNF”. The fine threads of “UNF” are suitable for use in high performance where precision is highly desirable, for instance, in aircraft and instrument fabrication industries.
On the flip side, the kind of strength and endurance needed rather than accuracy makes the “UNC” the best choice for the application. For those applications where high force and wear and tear are likely to be exerted on the fastener, “UNC” threaded bolts are a good fit for machinery, autos, and construction equipment.
The use of “UNF” and “UNC” can be limited by the type of material that is to be applied and by the environmental conditions of the threads. For instance, it is easier to notice that “UNF” may be more applicable for instances where the material used needs to have a running fit, while “UNC” is better for situations where threads have to offer more force.
Only the application has to specify the need so as to be supported by either the “UNF” or the “UNC”. When you look at the mechanical requirements, the level of precision required, and the conditions of use, you will be able to determine the best thread system to use.
Conclusion
It is important that one has prior knowledge of UNF and UNC threads to make the best decision on which to use. Self-locking ‘UNF’ threads have low pitch values along with high accuracy and strength needed for high-end domains such as aviation and car manufacturing. UNC threads have a larger size and larger pitch to provide extra strength for construction industries, four-wheelers, and other heavy industries.
Being a product of Tennenson Metals, each thread system should be selected based on the type of operation, precision, strength, and environment to which the fastener will be exposed. Thus, both “UNF” and “UNC” exist for good reasons, and knowing when to use each will prevent you from facing project failure or later round-offs.
Related Reading
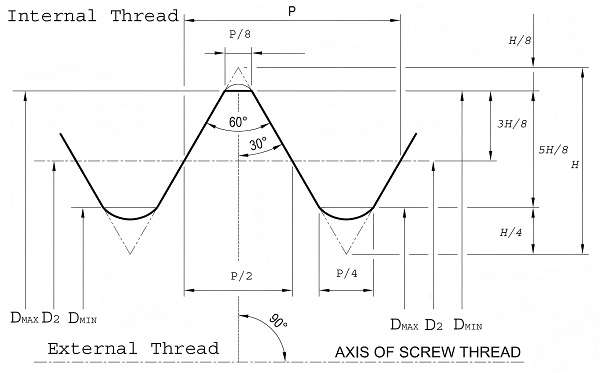
What's the unc thread angle?
The standard angle for UNC (Unified Coarse Thread) threads is 60 degrees.
Here is an unc-thread-chart. I hope it will help you.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related Products
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and working details to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 159 27 555863

Want the best price & newest metal working machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Armpro's monthly newsletter,we're free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable working solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Tapping Machine: The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Electric Tapping Machines:the Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Drilling Machine: The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Drilling milling Machine:The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- CNC Tapping Machine :The Complete Buying Guide in 2024
- Pipe chafering Machine:The Complete Importing Guide in 2024
- Radial drilling Machine:The Complete Buying Guide in 2024
- Thread rolling Machine:The Complete Buying Guide In 2024
- Pillar Drilling Machine:The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024