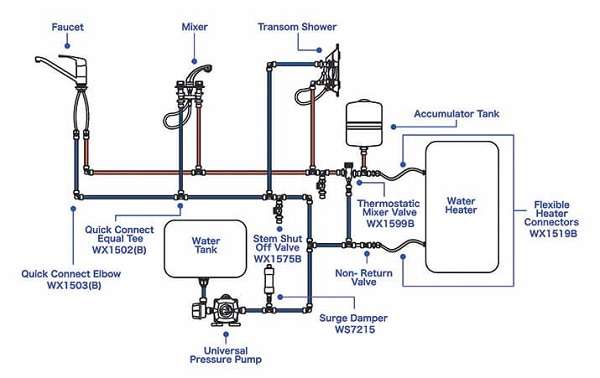
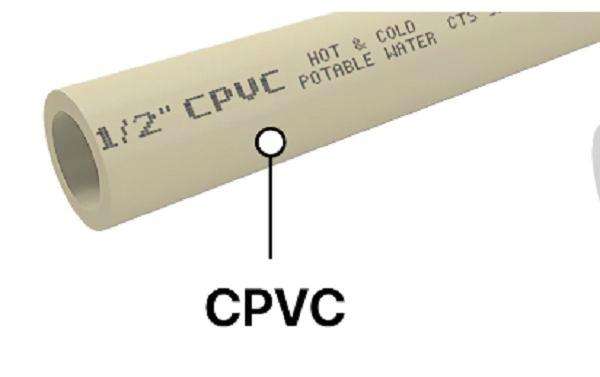
Find The Most Accurate PVC Pipe Sizing Chart
Introduction
The right size of PVC pipe must be selected to ensure effectiveness and durability in your plumbing, irrigation, or industrial systems.
A PVC pipe size chart shows the dimensions of the pipes, their wall thickness, and pressure ratings, which enables one to choose the best pipe for a specific application. Whether you're working on residential, commercial, or industrial projects, this chart will be very instrumental in achieving reliable and long-lasting results.
1. What is the PVC pipe?
Polyvinyl chloride, or PVC, pipe is a multipurpose plastic material with many uses in the plumbing, irrigation, and manufacturing industries. The strength, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation of PVC pipes are well-known.
The Complete Form of PVC Pipe
PVC means Polyvinyl Chloride. A synthetic plastic polymer is mainly used in construction and infrastructure.
Types of PVC Pipe
There are different types of PVC pipes, each designed for certain uses:
- UPVC (Unplasticized PVC):Rigid and used in water supply and drainage systems

- CPVC (Chlorinated PVC):Ideal for hot water applications due to its heat resistance
- PVC-U (Unplasticized PVC):Used in both pressure and non-pressure systems
- Foam Core PVC:Lightweight, used for drainage applications
What Are PVC Pipes Used for?
PVC pipes are incredibly versatile and widely used for:
- Plumbing:Both residential and commercial water supply systems.
- Irrigation:Watering systems for agriculture and landscapes.
- Drainage and Sewage:Treatment of wastewater and stormwater.
- Electrical Conduits:Protection of electrical cables.
- Industrial Applications:Handling of chemicals, gases, and other fluids
PVC Plastic Pipe
PVC plastic pipes are manufactured from polyvinyl chloride, which is light in weight, durable, and resistant to corrosion. In many instances, alternatives to metal pipes.

2. What materials are used for PVC pipe?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Resin
- PVC pipes are made up of polyvinyl chloride resin, which is a synthetic plastic polymer.
- The resin is the major constituent responsible for making PVC strong and resilient.

Stabilizers
- PVC requires the addition of stabilizers to protect it from the destructive effects of heat and UV light.
- The usual stabilizers added are lead salts, and calcium-zinc, among other non-toxic substances.
Plasticizers
- Phthalates are commonly added as plasticizers to make the PVC pipe less rigid.
- Flexible PVC pipes find applications in areas such as irrigation systems.
Lubricants
- Lubricants are added during manufacturing to facilitate the smooth extrusion of the PVC.
- Typical lubricants added include stearates, that prevent friction and blockages from occurring during production.
Impact Modifiers
- Impact modifiers are added to increase the pipe's toughness and resistance against impact.
- Impact modifiers improve the pipe's flexibility so that it can withstand mechanical stresses without breaking or cracking.
Fillers
- Fillers like calcium carbonate or glass fibers are typically added to the compound to reduce cost and improve some properties.
- The fillers can be used to increase the strength of the pipe or resistance to some environmental factors.
Colorants
- Colorants are mainly used for aesthetics or to differentiate between types of pipes, for example, water supply from drainage.
- Titanium dioxide is commonly used as a white pigment in PVC pipes.
3. What is the application of the PVC pipe?
Because of its long lifespan, low weight, and chemical and corrosion resistance, PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) pipes find extensive use in many different sectors. Some important uses for them are:
1. Plumbing and Water Supply:
Essential for water distribution systems at homes, commercial, and industrial levels.
2.Drainage and Sewage Systems:
Used in wastewater management, stormwater drainage, and underground sewage networks.

3. Irrigation and Agriculture:
Efficiently transports water for farming, gardening, and large-scale irrigation systems.
4.Electrical Conduits:
Gives a safe covering to electrical wiring in buildings and industrial setups.
5. HVAC and Ventilation:
Commonly used in heating, ventilation, and air condition ducting.
6. Chemical and Industrial Piping:
Used to transport chemicals, acids, and other industrial fluids due to its non-corrosive nature.
7. Construction and Infrastructure:
Used in water mains, scaffolding, and underground utilities.
8. Furniture, DIY, and Creative Projects:
Perfect for creating light frames, racks, storage units, and custom home improvements.

4. What are PVC pipe standards?
The PVC pipe standards are specifications and guidelines of organizations; these ensure that the pipes meet certain criteria in terms of quality, safety, and performance.
It will address issues such as composition, dimensions, pressure ratings, and methods for testing. Some of the key PVC pipe standards include:
1. ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials):
The standard of quality and performance in PVC pipes is developed here; for example, ASTM D1785 for Schedule 40, 80, and 120 pipes and ASTM D2665 for DWV pipes, which means drainage, waste, and vent.
2. ISO (International Organization for Standardization):
ISO 4422 specifies the requirements that a PVC pipe shall meet when used for potable water systems.
- EN (European Standards):
EN 1452 is a guide for plastic pipes used in water and gas applications throughout Europe.
4. AWWA (American Water Works Association):
AWWA C900 and C905 identify PVC pipes for use in potable water and waste water systems.
5. PVC Pressure Pipe Standards:
These standards represent requirements for PVC pipes in pressure systems, including ASTM D2241 on pressure pipes and ASTM F1483 on fittings.
Complete standardized guidelines establish PVC pipe safety levels and reliable performance within specified application conditions including plumbing systems and irrigation and industrial systems.
| Nom.Pipe Size (in) |
0.D. | Average 1.D. |
Min. Wall |
Nominal Wt./Ft. |
Maximum W.P.PSI* |
| 1/8 | 0.405 | 0.249 | 0.068 | 0.051 | 810 |
| 1/4 | 0.540 | 0.344 | 0.088 | 0.086 | 780 |
| 3/8 | 0.675 | 0.473 | 0.091 | 0.115 | 620 |
| 1/2 | 0.840 | 0.602 | 0.109 | 0.170 | 600 |
| 3/4 | 1.050 | 0.804 | 0.113 | 0.226 | 480 |
| 1 | 1.315 | 1.029 | 0.133 | 0.333 | 450 |
| 1-1/4 | 1.660 | 1.360 | 0.140 | 0.450 | 370 |
| 1-1/2 | 1.900 | 1.590 | 0.145 | 0.537 | 330 |
| 2 | 2.375 | 2.047 | 0.154 | 0.720 | 280 |
| 2-1/2 | 2875 | 2.445 | 0.203 | 1.136 | 300 |
| 3 | 3.500 | 3.042 | 0.216 | 1.488 | 260 |
| 3-1/2 | 4.000 | 3.521 | 0.226 | 1.789 | 240 |
| 4 | 4.500 | 3.998 | 0.237 | 2.118 | 220 |
| 5 | 5.563 | 5.016 | 0.258 | 2.874 | 190 |
| 6 | 6.625 | 6.031 | 0.280 | 3.733 | 180 |
| 8 | 8.625 | 7.942 | 0.322 | 5.619 | 160 |
| 10 | 10.750 | 9.976 | 0.365 | 7.966 | 140 |
| 12 | 12.750 | 11.889 | 0.406 | 10.534 | 130 |
| 14 | 14.000 | 13.073 | 0.437 | 12.462 | 130 |
| 16 | 16.000 | 14.940 | 0.500 | 16.286 | 130 |
| 18 | 18.000 | 16.809 | 0.562 | 20.587 | 130 |
| 20 | 20.000 | 18.743 | 0.593 | 24.183 | 120 |
| 24 | 24.000 | 22.544 | 0.687 | 33.652 | 120 |
5. How to choose the right PVC pipe?
PVC pipe selection follows vital factors that match the requirements of your particular application. Selection of the proper PVC pipe requires these steps:

Identify the Purpose and Application
- Water Supply:The selection of a PVC pipe for water supply requires materials that satisfy NSF National Sanitation Foundation criteria such as Standard ASTM D1785.
- Drainage and Sewage:Drainage systems and sewage pipelines need pipes that satisfy ASTM D2665 or comparable requirements for waste and vent (DWV) systems.
- Pressure Systems:Pipelines in pressure systems require high-pressure rating materials including ASTM D2241 along with ASTM D3034.
Determine the Pipe Size and Schedule
- Diameter:Calculate the diameter suitable to your application concerning water flow. PVC pipe diameters exist between ½ inch up to multiple-inch measurements.
- Schedule:The schedule number describes pipe wall thickness that indicates its strength capability for dealing with pressure forces.
The regular residential plumbing needs Schedule 40 but Schedule 80 serves when dealing with high-pressure systems.
Consider the Pipe’s Pressure and Rating
- Pick a pipe with the right pressure rating for your system; that is, ASTM D2241 pipes vary between a few to 400 psi, based on the size.
Assess Pipe Material and Durability
- Ensure that the PVC pipe is resistant to corrosion, chemicals, and UV exposure if used outdoors.
- Standard PVC pipes are durable, but for higher temperatures, specialty pipes such as CPVC—Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride—may prove even more effective.
Check the Pipe Standards
- Ensure that it meets the standard requirements of your locale or industry; in the case of materials, especially for potable water, many have to comply with ASTM, ISO, or AWWA.
Evaluate Temperature Tolerance
- PVC generally is good for cold-water service, but you will want CPVC pipes if you have any need to go to higher temperatures.
Assess Flexibility and Fittings
- Determine if you need rigid (standard PVC) or flexible (like PVC flex pipe) piping. Also, be sure to get the appropriate fittings to complete the installation (elbows, tees, couplings).
Location and Environment
- For outdoor applications, select pipes with UV-resistant coatings, or go with buried systems that are shaded from the sun.
Match these criteria to your project's requirements, and you can easily choose a PVC pipe that would deliver good performance.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the right size of PVC pipe is important to ensure effective flow and pressure resistance in the system.
A size chart helps you pick the right diameter and wall thickness of the pipe, considering the application for which it is intended—plumbing, drainage, or industrial uses.
Consider things like the requirements of water flow, pressure ratings, and local building codes.
Apply pipes that match project specifications to get maximum system performance. Understanding the PVC pipe size chart helps avoid system issues associated with clogging and leakage and decreases overall system inefficiency.
For detailed guidance and accurate pipe size tables, please visit Armpro Machine. Our range of accessories and expert advice ensures that you will find the perfect solution that meets your needs.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related Products
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and working details to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 159 27 555863

Want the best price & newest metal working machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Armpro's monthly newsletter,we're free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable working solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Tapping Machine: The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Electric Tapping Machines:the Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Drilling Machine: The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Drilling milling Machine:The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- CNC Tapping Machine :The Complete Buying Guide in 2024
- Pipe chafering Machine:The Complete Importing Guide in 2024
- Radial drilling Machine:The Complete Buying Guide in 2024
- Thread rolling Machine:The Complete Buying Guide In 2024
- Pillar Drilling Machine:The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
Most Popular

Tell us your material or budget,we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours