NPS vs NPT: Understanding the Differences and Applications
Introduction
To have proper functioning in threaded pipe systems and ensure compatibility, there is always a need to know the different types of threads that are used. Some of the popular threads include NPS (National Pipe Straight) and NPT (National Pipe Tapered).
While their external appearance resembles metal GDs, several aspects of their construction and installation make them different.
This guide will hold your hand through defining NPS and NPT threads and their applications, as well as educate you on NPS vs NPT and how to select the best one
1. What is NPS?
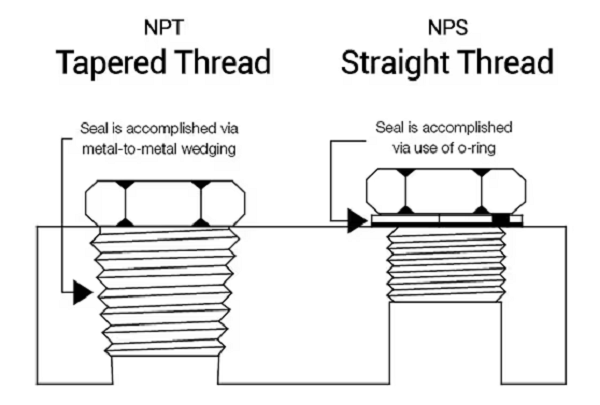
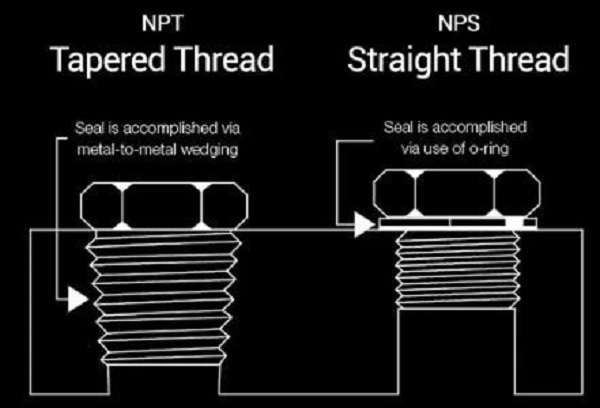
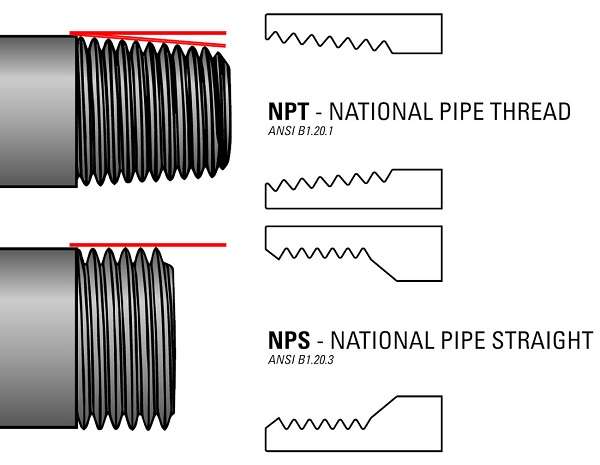
NPS stands for National Pipe Straight and is also called straight pipe threads. It is also important to note that when working with these threads, the diameter of the thread is constant along the thread length, and therefore, there is no taper.
Compared to tapered threads, NPS threads do not form a pressure seal. More frequently, they are used in conjunction with an O-ring or gasket to achieve the desired sealing performance.
NPS threads are expendable and set to the ‘‘ANSI/ASME B1.20.1’’ standard and are required on parts where alignment is very important.
Since such valves do not depend on thread interference to develop the seal, they are applied in connection with mechanical joint systems as opposed to pressurized sealing.
Such categories include members and plates used structurally, hanger supports, and threaded products employed in non-pressurized applications.
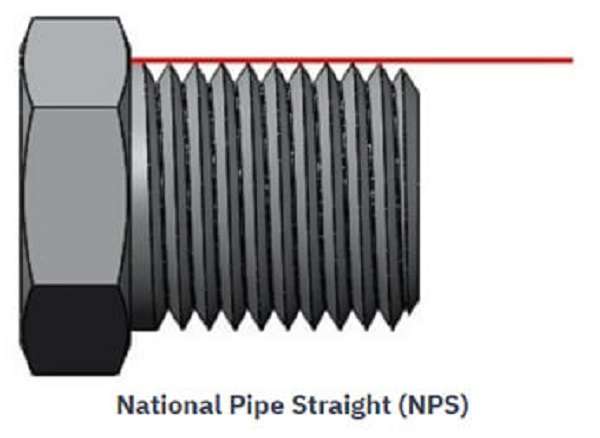
2. NPS Applications
The uniform diameter of NPS threads makes them ideal for situations where accurate alignment is crucial.
For instance, the common NPS applications are:
- Structural Applications: NPS threads are often employed in pipes used as structural elements, where precise alignment and assembly are more critical than a pressure-tight seal.
- Fittings with Gaskets: In systems where a gasket or O-ring is used to create a seal, NPS threads ensure easy installation without the need for tapering.
- Low-Pressure Systems: NPS threads are suitable for applications with low or no pressure, such as decorative or mechanical pipe fittings.

- Electrical Conduits: NPS threads are commonly used in conduit systems for protecting electrical wiring, ensuring proper alignment of fittings and connections.
- Food and Beverage Industry: In applications where cleanliness and alignment are essential, such as in stainless steel piping systems for food processing.
- Automotive Applications: NPS threads are utilized in fuel lines or exhaust systems where alignment is more critical than sealing.
- Fire Protection Systems: Certain sprinkler systems use NPS threads in non-sealing applications where gaskets provide the primary seal.
- International Standards Applications: Industries requiring adherence to international threading standards often prefer NPS for compatibility and standardization.
Their compatibility with certain international standards also makes them a preferred choice in industries where standardization is essential.
3. What is NPT?
National Pipe Tapered threads are abbreviated as NPT and constitute one of the most common thread forms embraced in the piping industry.
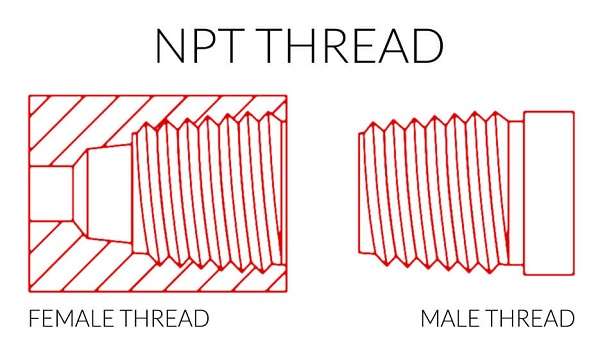
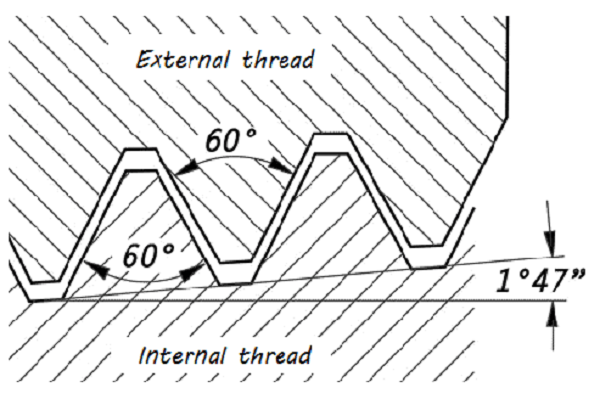
In the case of NPT threads, the other common characteristic is that the diameter of the thread reduces along the length of the particular thread. This tapering results in a tight, pressure-proof screw fit when two NPT threads are screwed together because the threads fade when tightened, leading to metal-to-metal contact.
NPT threads also conform to the ANSI/ASME B1.20.1 code and are intended for high-pressure applications.
They especially find applications in plumbing, oil, and gas, as well as many manufacturing industries where tight and leak-proof connections are required.
4. NPT Applications
NPT threads are rather universal and can be effectively used for sealing owing to their tapering shape. Common uses include:
- Plumbing Systems: NPT threads are used in water, gas, and steam pipeline connections to provide secure, pressure-tight joints.
- Hydraulic Systems: General accessories used in hydraulic circuits—NPT threads are employed in joining equipment like valves, pumps, and cylinders.
- Industrial Equipment: These threads are ideal for uses where press-fit connections are useful, for instance, in compressors and chemical processes.
- Seepage Prevention: Since NPT threads lock themselves upon use, they are ideal for applications where leakages must be prevented.
- General Accessories: The general-purpose thread is NPT, which is commonly used in couplings, adapters, and plugs in systems.
- Oil and Gas Applications: It is actively used in pipes and vessels for the conveyance of oil and natural gas, with sealants designed to prevent leakage under pressure.
- HVAC Systems: Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning systems employ NPT threads for joining purposes, such as pipes and valves.
- Fire Sprinkler Systems: Because of their secure sealing ability, they are mostly used in fire safety equipment such as sprinklers and control valves.
- Chemical and Process Industries: NPT threads are used in managing chemicals because, in such applications, a tight connection and mechanical integrity of the joint are crucial.
- Marine Applications: Applied in ships and offshore platforms for piping that operates under conditions causing considerable pressure changes.
5. Selection Criteria for NPT or NPS Threads
The decision of which thread to use for your application depends on the specific application's needs. Here are some factors to consider before NPS vs NPT thought.
- Sealing Requirements: If the application using the threaded connection is expected to operate under conditions of relatively high pressure, then NPT threads are to be preferred. For non-sealing applications or gasket-dependent products, NPS threads may be acceptable.
- Alignment Needs: To have extremely precise parallel dimensions that are unencumbered by any taper requirements, NPS threads are proper, especially in applications that include structures and accents.
- Pressure Levels: NPT threads are created for use where high pressure is likely to be encountered, while NPS threads are more suited for applications where pressure could be low or absent.
- Compatibility: Verify adaptation with the current gear or standard. NPT threads are more commonly used in North America, while NPS threads are used internationally.
Conclusion
These differences are essential for choosing the right type of threads for a certain application when debating NPS vs NPT.
Whereas NPS threads are optimized for alignment and non-full-pressure applications, NPT threads deliver a tighter seal for high-pressure systems.
Through the assessment of sealing systems, alignment, and pressure ratings, the right thread type can be selected accurately and without doubt, ensuring safety, efficiency, and compatibility.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related Products
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and working details to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 159 27 555863

Want the best price & newest metal working machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Armpro's monthly newsletter,we're free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable working solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Tapping Machine: The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Electric Tapping Machines:the Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Drilling Machine: The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Drilling milling Machine:The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- CNC Tapping Machine :The Complete Buying Guide in 2024
- Pipe chafering Machine:The Complete Importing Guide in 2024
- Radial drilling Machine:The Complete Buying Guide in 2024
- Thread rolling Machine:The Complete Buying Guide In 2024
- Pillar Drilling Machine:The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024