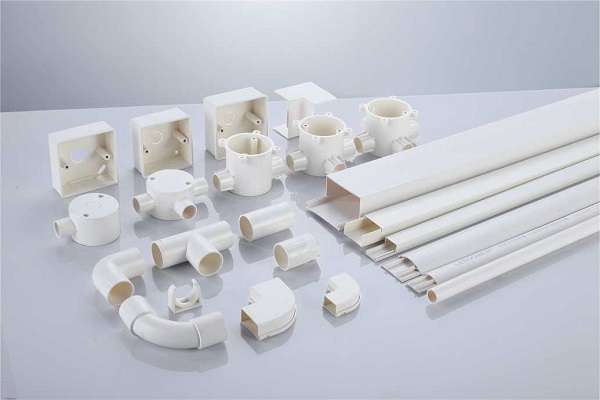
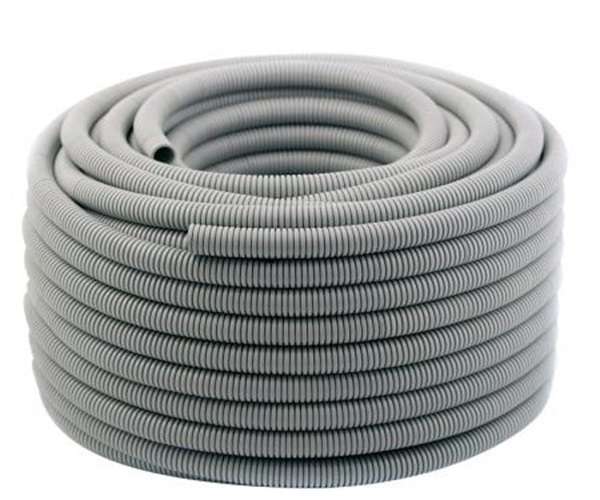
PVC Conduit Pipe Sizes Chart, Types, and Applications Explained!
Introduction
In residential, commercial, and industrial applications, PVC conduit acts as an essential safety measure for protecting and directing electrical wiring. It’s known for being lightweight, durable, and resistant to moisture, chemicals and corrosion. Most electricians prefer PVC conduit, as it is simpler to cut, bend, and install. Safety and organizational wire management depend on selecting the right cable size.
That's why a PVC conduit size chart is very helpful. It assists you in choosing the correct size of conduit in accordance with your wiring needs. This helps avoid things like overcrowding or overheating. In this article, we will explain what PVC conduit is, PVC conduit, and its applications. Keep reading to learn more.
1. What is the PVC Conduit?
What is PVC conduit? Essentially, it is a polyvinyl chloride (PVC) conduit for electrical wiring protection and routing. Because it is non-metallic and corrosion-resistant, it is a popular choice for both residential and commercial installations. In humid areas, it offers a cheaper and longer-lasting replacement for metal conduit.
Not only is PVC conduit lightweight, easy to install, and nonconductive, but it has other benefits as well. It is available in rigid and flexible form, providing more options depending on your project requirements. PVC conduit fittings, such as elbows, couplings, and connectors, are used to connect and route the conduit sections. These are the fittings that help keep the pathway of electricity secure.
PVC Conduit Types
There are two PVC conduit types and both of them are used in certain applications. Understanding these types help you choose the appropriate one for your project.
Rigid PVC Conduit
Rigid PVC Conduit is the most common type used in residential, commercial and industrial electrical systems. It offers a solid, durable structure, which makes it ideal for long, straight runs, as well as outdoor or underground installations. There are different thicknesses of rigid PVC, with Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 being the most common.
Schedule 80 is thicker and stronger than Schedule 40 in high-impact areas for extra strength and protection. This type of conduit can withstand moisture, corrosion, and chemicals, providing long-term durability. Also, it easily integrates with all types of PVC conduit fittings such as couplings, elbows, and junction boxes.

Flexible PVC Conduit
Flexible PVC conduit is useful in installations where it has to bend around an obstacle or parts located in a tight place. It’s more flexible than rigid conduit and requires no precise measurements or cuts.
This type of conduit is typically used in limited areas, such as under sinks, behind appliances, or in drop ceilings. While it is not as strong like rigid PVC, it is flexible and protects wires against moisture and abrasion. Also, it is compatible with PVC conduit fittings specifically made for flexible designs.
2. What is the PVC Conduit Size Chart?
A PVC conduit size chart is a tool used for reference of standard sizes of PVC Conduit pipes. It assists electricians, contractors, and DIYers in selecting the correct conduit size based on the quantity and size of wires. The sizing is important, as using an overly large size can result in too many wires crowded together while using an overly small size can lead to heating issues.
PVC conduit pipe sizes are typically between 16 mm and over 100 mm, with PVC conduit 20 mm and PVC conduit 25 mm being the most common for residential and light commercial applications.
The 20 mm conduit suits light-duty applications such as running multiple lighting wires, and 25 mm conduit is generally recommended for more wires or slightly heavier loads. This chart helps simplify conduit selection and make electrical installations safer and more efficient.
| Trade | PVC Conduit size | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| size in | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| inches | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 | 12 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1/00 | 2/00 | 3/00 | 4/00 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 750 | |||
| 1/2 | EMT | 12 | 9 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| IMC | 14 | 10 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| GALV | 13 | 9 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| 3/4 | EMT | 22 | 16 | 10 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| IMC | 24 | 17 | 11 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| GALV | 22 | 16 | 10 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| 1 | EMT | 35 | 29 | 16 | 9 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| IMC | 39 | 26 | 18 | 10 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| GALV | 36 | 29 | 17 | 9 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 1 | EMI | 61 | 45 | 28 | 16 | 12 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 1/4 | IMC | 68 | 49 | 31 | 18 | 13 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| GALV | 63 | 46 | 29 | 16 | 12 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 1 | EMT | 84 | 61 | 38 | 22 | 16 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 1/2 | IMC | 91 | 67 | 42 | 24 | 17 | 11 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| GALV | 85 | 62 | 39 | 22 | 16 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 2 | EMT | 138 | 101 | 63 | 36 | 26 | 16 | 13 | 11 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| IMC | 149 | 109 | 69 | 39 | 28 | 17 | 15 | 12 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| GALV | 140 | 102 | 64 | 37 | 27 | 16 | 14 | 11 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 2 | EMT | 241 | 176 | 111 | 64 | 46 | 28 | 24 | 20 | 15 | 12 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | |
| 1/2 | IMC | 211 | 154 | 97 | 56 | 40 | 25 | 21 | 17 | 13 | 11 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| GALV | 200 | 146 | 92 | 53 | 38 | 23 | 20 | 17 | 12 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 3 | EMT | 364 | 266 | 167 | 96 | 69 | 43 | 36 | 30 | 22 | 19 | 16 | 13 | 11 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| IMC | 326 | 238 | 150 | 86 | 62 | 38 | 32 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 12 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | |||
| GALV | 309 | 225 | 142 | 82 | 59 | 36 | 31 | 26 | 19 | 16 | 13 | 11 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | ||
| 3 | EMT | 476 | 347 | 219 | 126 | 91 | 56 | 47 | 40 | 29 | 25 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 4 | |
| 1/2 IMC | 436 | 318 | 200 | 115 | 83 | 51 | 43 | 36 | 27 | 23 | 19 | 16 | 13 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 4 | ||
| GALV | 412 | 301 | 189 | 109 | 79 | 48 | 41 | 34 | 25 | 21 | 18 | 15 | 12 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | ||
| 4 | EMT | 608 | 443 | 279 | 161 | 116 | 71 | 60 | 51 | 37 | 32 | 26 | 22 | 18 | 15 | 13 | 11 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | |
| IMC | 562 | 410 | 258 | 149 | 107 | 66 | 56 | 47 | 35 | 29 | 24 | 20 | 17 | 13 | 12 | 10 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | ||
| GALV | 531 | 387 | 244 | 140 | 101 | 62 | 53 | 44 | 33 | 27 | 23 | 19 | 16 | 13 | 11 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | ||
3. What Materials are Used for PVC Conduit?
PVC conduit is constructed of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a strong type of flexible plastic resistant to corrosion. The reason why this material is used commonly in the electrical industry because it does not conduct electricity and so it is a safe option to enclose and protect the wiring systems.
The base material–PVC resin, is blended with other additives during the manufacturing process to improve performance. These additives can be heat stabilizers, plasticizers for flexibility, UV inhibitors for outdoor use etc. So PVC conduit can endure extreme environmental conditions, threats such as moisture, chemical exposure and sunlight exposure.
4. What is the Application of the PVC Conduit?
Due to its durability, the non-conductive materials, and its resistance to corrosion, a PVC conduit is used in many electrical installations. Common applications include:
- Residential wiring:Installing electrical wires behind walls, ceilings and attics
- Underground installations:Safeguarding cables underneath gardens, driveways, and outdoor lighting.
- Commercial buildings:Establishing and protecting wiring in offices, retail stores, and schools.
- Industrial facilities:Protecting electrical systems in factories, warehouses, and processing plants
- Outdoor use:Weatherproof conduit for lighting poles, security systems, and signage
- Moist or corrosive environments:Pect for where you are exposed to water or chemicals or humidity.
- Temporary wiring configurations:Utilized on construction sites and event installations where rapid deployment and dismantling are essential.
These applications enable the use of PVC conduit in both permanent and flexible electrical systems.

How to Choose the Right PVC Conduit?
Choosing the right PVC conduit is crucial to ensure safety and efficiency in electrical installations. Here are some critical factors to consider when making your choice:
- Application type:Identify where you’ll put in the conduit—inside, outside, underground, or in a high-moisture area. Rigid PVC works well outside and underground, while flexible PVC is good for tight or flexible spaces.
- Conduit size:Use a PVC conduit sizes chart to select the correct diameter based on the number and sizes of wires. Standard choices such as PVC conduit 20mm and PVC conduit 25mm can be sufficient for light to moderate projects.
- Wire capacity:Ensure the conduit can hold all the wires without overcrowding to prevent overheating and maintain compliance with electrical codes.
- Environmental considerations:If the environment will expose the conduits to sun, chemicals, moisture, ensure the conduits are rated for that environment.
- Local codes and regulations:Refer to your local electrical codes to make sure that the type of conduit and installation method is approved.
These factors will allow you to choose the optimal and right type and size of PVC conduit for your work.

Conclusion
PVC conduit is a proven solution for protecting electrical wiring in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Each application may require specific types of PVC conduit, so knowing the various options facilitates choosing between rigid and flexible types. Use a PVC conduit size chart for accuracy. Pairing the conduit with cthe orrect fittings and following local codes can ensure a safe, durable electrical installation.
For detailed guidance and accurate conduit size, please visit Armpro Machine. Our range of accessories and expert advice ensure that you will find the perfect solution for your needs.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related Products
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and working details to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 159 27 555863

Want the best price & newest metal working machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Armpro's monthly newsletter,we're free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable working solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Tapping Machine: The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Electric Tapping Machines:the Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Drilling Machine: The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Drilling milling Machine:The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- CNC Tapping Machine :The Complete Buying Guide in 2024
- Pipe chafering Machine:The Complete Importing Guide in 2024
- Radial drilling Machine:The Complete Buying Guide in 2024
- Thread rolling Machine:The Complete Buying Guide In 2024
- Pillar Drilling Machine:The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
Most Popular

Tell us your material or budget,we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours