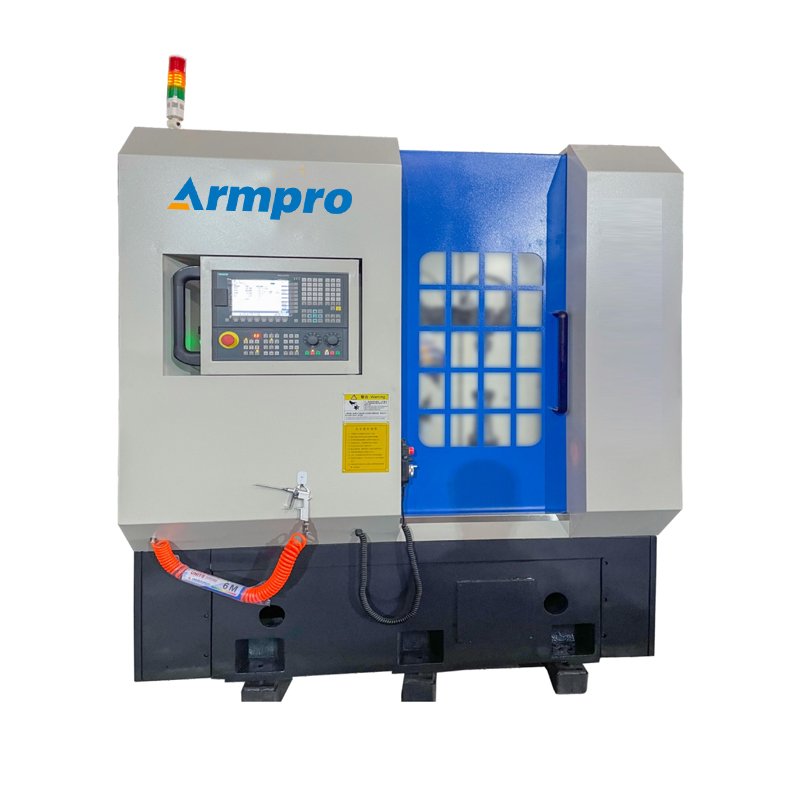
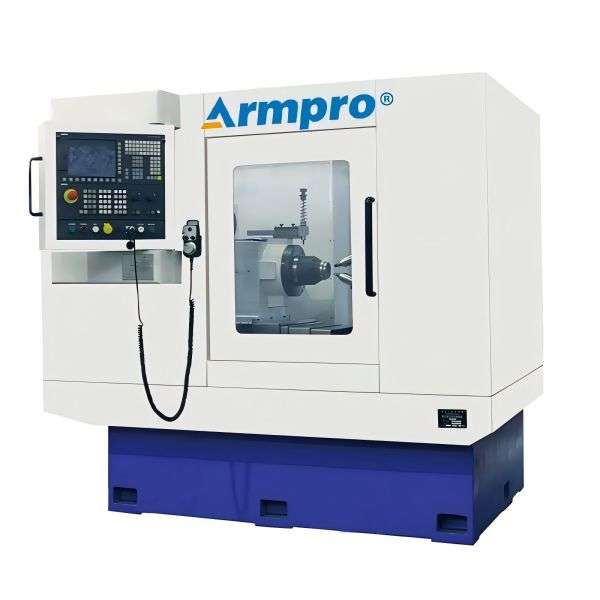
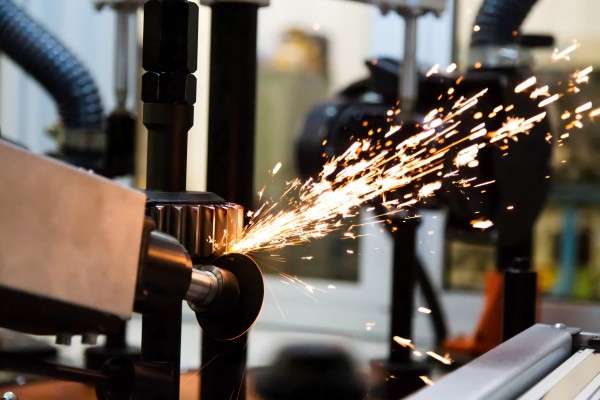
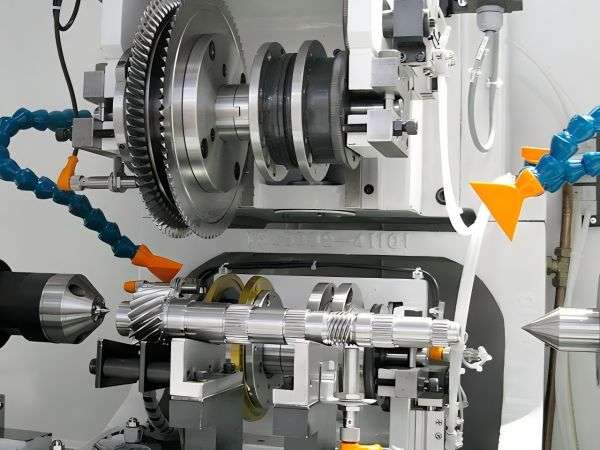
Why Armpre Machinery is Trusted
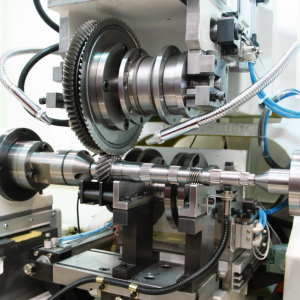
Welcome to Visist Our Gear Chamfering Machine Factory
Welcome customers from all over the world to come to visit our gear chamfering machine factry, we can show you our Gear Chamfering Machine workshop, and also Gear Chamfering Machine production site.
The Buyer's Guide
Gear Chamfering Machine: The Complete Buying Guide in 2024
Gear chamfering machine provides unique chamfering work in the gear manufacturing process
Gear deburring and chamfering process is more and more applied in Gear industry, client not only satisfied with just deburring
the also required angle chamfering
In this article,we will explain to you how to select suitable gear chamfering machine for your gear manufacturing
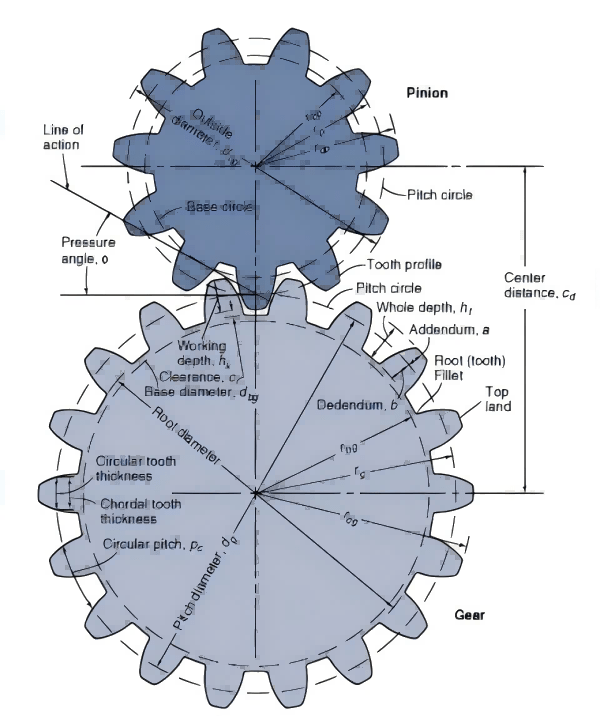
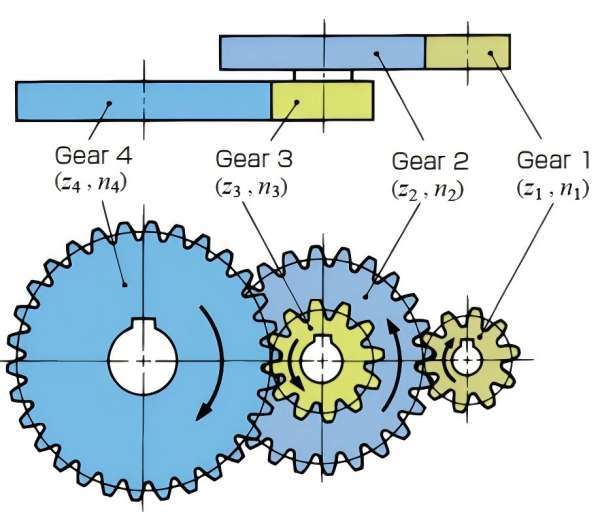
1. Overview of Gear
Gear is commonly interlinked in mechanical operations through effectively passing torque and motion among apparatus parts. They date back to the ancient Greeks; Archimedes describes the first-gear trains.
Gears have developed over time, especially during the age of the Industrial Revolution when there were enhanced and innovative engine and fine machining practices. Gears function based on the meshing of the two gears, transmitting energy with very little wastage of energy, and hence they are very efficient.
There are many types of gears for instance spur, helical, bevel, and the like all of which are designed on the type of motion required. Even today, gears can hardly be called a specialized component; instead, they are one of the most fundamental elements of motion transmission, and therefore engineers and designers need to understand their basics to the smallest detail.
2. How many different gear products are in the industry?
In the industry, there are almost all types of gears and the basic function of gears is dependent on the design and the application of the gear.
· Spur Gears:
The first and the most general type of spur gears transmit motion and power between parallel shafts and are considered in most elementary machines.
· Helical Gears:
These gears have their teeth set at an angle to each other and are much smoother in operation than the spur types and will take the loads up to a certain point better.
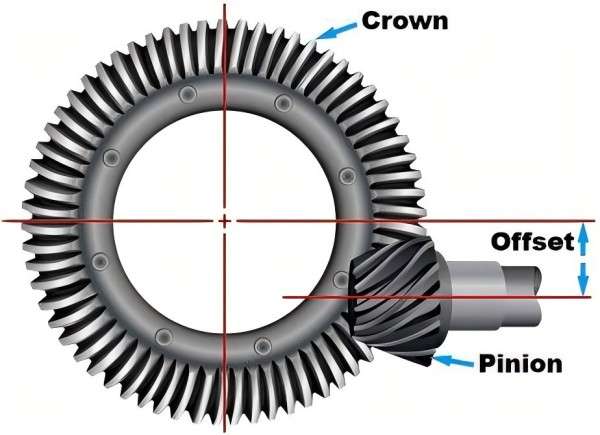
· Bevel Gears:
Normally employed to transmit motion from one shaft to another in a perpendicular direction and most vehicle differential systems.
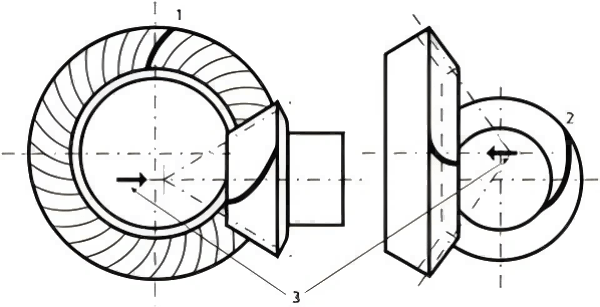
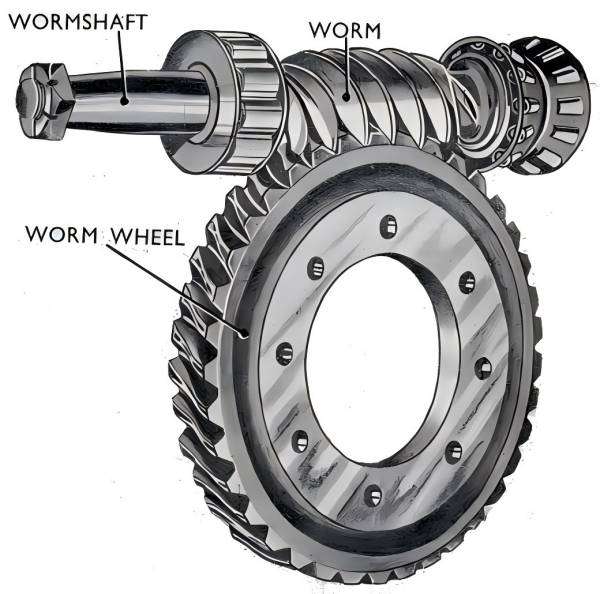
· Worm Gears:
These include worm and worm wheels which are very suitable in situations where they are to slow down the rate as well as tremendously increase the amount of turning force.
· Rack and Pinion:
Transforms rotational movement into straight-line movement and is commonly applied in car steering systems.
Planetary Gears: Including the sun gear, planet gears, as well as an outer ring gear, these are heralded for their high torque in small places.
· Hypoid Gears:
Different from bevel gears, they have an offset axis, thus offering improved operation and higher torque output.
Some of the other types of gears are Herringbone gears (double helical for heavy machinery); Crown gears (right angle bevel gears); and last is Internal gears (Turbine gears for Planet gears with teeth on the inside). These diversified designs reveal how gears are used in virtually all industries to serve various purposes.
3. What is gear production technology
Gear production technology embraces several processes, which ensures the development of gears with accurate size, and strength besides being strong. It starts with the design of the gears and choice of material with steel and other exotic alloys used for fabrication to ensure the best output.
Some of the conventional processes used in manufacturing gears include the hoboing technique where a cutter rotary forms the teeth, shaping technique where a reciprocating cutter forms the profile of the gear.
For improved quality finishes of the teeth surface, there are grinding and honing which aids in improving the accurateness of the teeth.
Hence, heat treatment is used to strengthen the gear and gain the wear-resisting properties of the gear material. Contemporary gear manufacturing is more and more reliant on the use of computer numerical control (CNC) technology that lets the user have centralized control over the material removal process.
The integration of CNC makes production more consistent, and efficient and requires enhancing the ability to meet certain specifications necessary in the production of gears suitable for high-performance industries engagements.
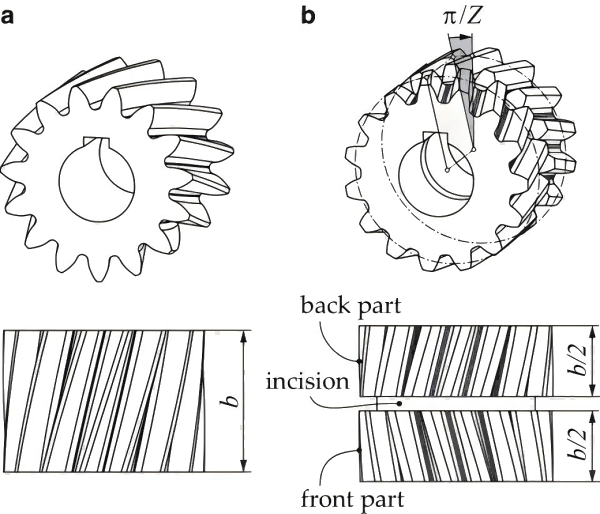
4. What is a Gear Chamfering Machine?
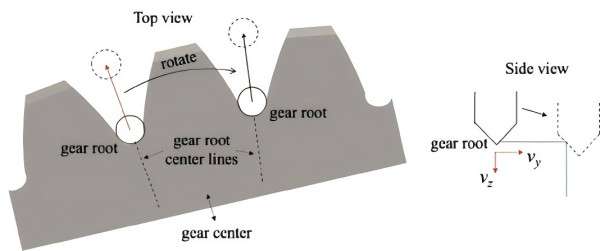
A gear chamfering machine is a tool used to produce a chamfer on the gear teeth, that is, a beveled edge. Chamfering reduces a small amount of material off the tooth profile edges and their edges are inclined rather than straight.
This machine always cuts or grinds with high accuracy making it appropriate to be a finishing machine for producing gears. Chamfer gives aesthetics to the gears and it has a direct relation to gears performance because it relieves stress concentrations at the corners of gear teeth.
These machines bring efficiency, accuracy, and standardization in chamfering which is hard to attain manually. They are especially used in applications that need high-performing geared systems such as automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery.
5.What are the Benefits of a Gear Chamfering Machine in Gear Manufacturing?
Investing in a gear chamfering machine can have numerous benefits, impacting both the quality and longevity of the gears produced:
· Improving Gear Mesh:
Chamfering improves the engagement of the mating features of a gear because sharp edges are eliminated. This leads to smoother operation and helps eliminate the potential for bending or warping between components during the assembly or use of gears.
· Enhancing Durability and Longevity:
Chamfering helps to counteract stress concentration on each gear tooth, as a result, they form an elongated period of wear resistance. This is most useful in high torque operations where it is very easy for a small irregularity to bring about a failure of the gears.
· Reducing Stress Concentration:
Gear chamfering minimizes the risks of obtaining fractures because it redistributes the pressure all over the various facets of the gear teeth. This is quite beneficial to prevent gear tooth damage and this is essential to ensure higher reliability of the system.
· Achieving Smoother Operation:
The finest and systematically cut gear teeth, requiring less noise and vibrations, enhance the ability to function in the entire gear setup.
A gear chamfering machine is a perfect tool to purchase for gear manufacturers as they strive to offer better gears that are stronger and have better performance. By allowing gears to have better endurance and by preventing gear damage it allows for gears to perform more effectively and to also have longer service lives which finally results in happy customers and better value in the long haul.
6. What industry applications need gear chamfering machine
Gears chamfering machines are essential in applications in which gears are vital to the motion systems since chamfering aids in improving gear durability, efficiency, and ease of connection. Here are some of the main industry applications that benefit from gear-chamfering machines:
· Automotive Industry:
In cars and trucks, chamfered gears in transmissions, differentials, and engine components increase the product endurance and decrease the noise. High-accuracy chamfering can also optimize gears’ load-carrying capacity and reduce wear, a critical function for vehicles’ durability and dependability.
· Aerospace Industry:
Communication systems rely on highly accurate gears for engines, actuators, and landing gear in aerospace systems.
Chamfering helps share load on such gears and thus they do not get damaged easily by fatigue and wear which is important in performance vehicles and those that are used in safety-critical applications.
· Industrial Machinery:
Used in manufacturing conveyors, mixers, heavy-duty pumps, and other equipment that develops high torque and stress concentrations chamfered gears are used. Chamfering makes the gear engagement smooth, and reduction of any chances of chipping or cracking of the gear Teeth.
· Robotics:
In robots, gears are most of the time subjected to cyclic motion under different loads. Chamfered gears support precise motion transfer, minimize noise, and extend the durability of the gears which requires precision as well as reliability of the robotic systems.
· Wind Energy:
Wind turbines involve a high-stress large gear system as part of their gearbox. Chamfering eliminates stress concentrations and makes the assembly easier so maintenance becomes easier and the efficiency of turbines increases in the long run.
· Heavy Equipment and Construction:
Chamfered gears are applied in harsh surroundings in heavy machinery equipment such as excavators and bulldozers. Chamfering improves the service life as well as minimizing wear on gears, particularly in severe applications where gear failure could prove very expensive in terms of lost time.
Gear chamfering machines are thus very useful in the retention of gear characteristics in various industries, which require high levels of precision, durability, and smooth functioning of gears.
7. What are the different Types of Gear Chamfering Machines?
There are different types of gear chamfering machines depending on the application and nature of the job, precision level, and production requirements. Here are some of the main types:
· Manual Gear Chamfering Machines:
These are, however, operated through manual means, which effectively reduces the costs involved and is ideal for low-volume or custom gears. In particular, they are used in workshops whenever flexibility is dominant but the requirement for precision may be less than those offered to automated solutions.
· CNC Gear Chamfering Machines:
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are completely controlled; thus, chamfering has very close tolerance and repeatability.
This method of chamfering is preferred in high production lines since most of the work is done by machines and the precision is first-rate because of the programmability and repeatability of the CNC chamfering machines, especially for the complex chamfer designs.
· Bevel Gear Chamfering Machines:
Used particularly for bevel gears these machines fit the geometries and angles necessary for chamfering bevel gears while creating smooth finishes on edges. It is widely in car manufacturing industries as well as airplane industries.
· Double-Sided Chamfering Machines:
The machinery used here is of a kind that is most suitable for production lines since it can chamfer both sides of a gear at once. The dual-sided chamfering machines are used in many applications in mass production to enhance efficiency and minimize working time.
· Deburring and Chamfering Machines:
The machines perform both deburring and chamfering operations on the gears eliminating sharp edges and gears burrs while chamfering the teeth. Doubled utilization of the tool makes it very important in cases where fine finishes and accurate chamfers are desirable as in the automotive and aerospace gears.
· Robotic Chamfering Systems:
These systems utilize robotic arms with chamfering tools because the tasks of chamfering are versatile and can be done flexibly by these tools. Robotic systems are employed in the automated product manufacturing lines where they are capable of working with diverse types and sizes of gears particularly where complexity or scale is involved.
Every type of chamfering machine is effective according to the production demands, accuracy level, and kinds of gears and thus, manufacturers/technicians can choose the appropriate solution to implement in their applications.
8. How does the Gear Chamfering Machine Work?
A gear chamfering machine uses cutting tools to bevel or chamfer gear teeth. The goal is to smooth off tiny spurs from the teeth to improve gear fit and reduce gear failure during assembly and operation. The standard process is as follows:
· Positioning and Clamping
The gear is firmly placed and held by a clamp on the machine so that it will not move.
· Chamfering Tool Alignment
A chamfering tool most often a rotary cutter is oriented in position to match the intended chamfer angle on the edges of the gear teeth.
- Material Removal (Chamfer Cutting)
The tool cuts an inclined plane or beveled edge or chamfer, a small portion of material from each tooth edge.
· Automatic or Manual Gear Rotation
To set each tooth’s cutting point, the gear may be repositioned by the machine, or this has to be done manually.
· Quality Control and Inspection
Every tooth is thoroughly examined to make sure it has chamfers of the required standard and within tolerable limits.
9. What are Materials Compatible with the Gear Chamfering machine?
· Steel
Used for mass production of high-strength gears, including carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel.
· Cast Iron
Resistant to wear and strong and is often used for manufacturing heavy-duty gears.
· Aluminum
Light may be applied for gears where the weight is critical.
· Brass and Bronze
Gears where there is a requirement of low coefficients of friction and corrosion resistance.
· Plastic and Composites
Used for light load gears in industries such as robotics or electronics.
· Hardened Materials
Gears that are made from hardened steel or any other strong material mean that special chamfering tools are necessary.
These materials can easily be worked on in gear chamfering machines to provide the necessary accuracy and strength in a variety of uses.
10. What is gear chamfering cycle time
Cycle time means the time required to perform one operation for individual parts, while gear chamfering cycle time means the time it takes to chamfer the edges of a gear during production.
Chamfering is the removal of sharp edges on the gear teeth by cutting or grinding, which enhances the effectiveness of the gear, reduces concentrate stresses, and increases the general endurance of the gear.
The cycle time for gear chamfering can vary depending on several factors, including:
· Gear Size and Complexity:
Chamfering large gears or gears with intricate tooth profiles may take longer compared to chamfering small gears with simple profiles.
· Material Type:
The material of gear will have an impact on cutting speed and tool wear affecting the cycle time of the whole process.
· Chamfering Method:
Cycle times may also vary depending on other machining operations that may be performed such as mill, grinding, or through the use of a chamfering machine.
· Machine Setup:
The equipment used in the operation, whether it is computer numerically controlled machines or specialized chamfering machines, has a role to play.
· Cutting Tool Efficiency:
Properties of the tool such as its type (rotary tool, abrasive disc, and the like) as well as sharpness define the cutting speed and therefore the cycle time.
By these factors, it is usually possible to achieve a cycle time starting from a few seconds up to a few minutes per gear. The sources of cycle-time reduction include optimizing machine settings, using high-speed cutters, and identifying the best methods for chamfering gears.
11. Manual vs. Automatic Gear Chamfering Machines
Manual Gear Chamfering Machines:
- Operation:
Demands the operator to supervise the process of feeding the gear and manage the settings on his own.
- Flexibility:
Provides the ability for more control over the process and should be used for shorter production runs, or custom parts.
- Speed:
Taking a slightly longer time compared to fully automatic machines since human interference is required.
- Skill Requirement:
Experience in culture and settings is dependent on the operators that are handling them.
- Cost:
Usually costs less at the initial stages but needs more effort and time for the execution.
Automatic Gear Chamfering Machines:
- Operation:
Completely automated where the machine takes care of feeding the gears, chamfering them, and often even changing the tools.
- Efficiency:
Faster and of uniform quality, recommended where little manual control is needed and large numbers are required.
- Accuracy:
The precision that comes with it since automation eliminates one source of error – humans.
- Cost:
High initial investment but low cost is incurred on the labor since the equipment will be autonomous.
- Flexibility:
Usually, there is less versatility compared to manual machines due to the fact they are designed for certain operations and configurations.
Manual machines are suitable for any small or custom project as the operation is more controllable and flexible, whereas automatic machines are better suited to high-volume production, as the components that make up the project are economically assembled with higher speed, precision, and quality.
12. Key Features to Consider when buying gear chamfering machine
When buying a gear chamfering machine, consider these key features:
· Chamfering Capacity:
Check that any sizes of gear required need to be adjusted and that angles are adjustable.
· Automation Level:
They come in three options depending on the level of automation required; Manual, Semi-Auto, and Fully Auto.
· Precision and Accuracy:
High precision with good repeatability should define the characteristics of the process.
· Tooling Compatibility:
It should be compatible with other tools and also be quickly changeable between the tools when necessary.
· Material Compatibility:
Ensure that the machine is appropriate to the kind of material used in your gear.
· Cycle Time and Productivity:
Choose machines with a short cycle time if the production process involves a large number of units.
· Machine Stability:
Select a rigid, stable machine design if you are concerned with the performance and long life of the machine.
· Maintenance and Support:
Consider ease of maintenance and high backup from the manufacturer.
· Energy Efficiency:
Notice energy performance and motor power.
· Cost of Ownership:
Consider the first cost, cost of operation, and other costs of maintenance.
These features will assist you in making the right buying decision as far as the machine you need is concerned.
13. How to Choose the Right Chamfer Angle for gear chamfering machine?
To choose the right chamfer angle for a gear chamfering machine, consider the following:
· Gear Type:
Conventional standards range between 15°- 45° with 30° - 45° generally used in most gear designs.
· Material Hardness:
Hard materials will require large angles usually between 30° – 45° while soft materials will require smaller angles or as low as 10°.
· Load and Application:
Larger angles are termed preferable where loading is high since it exerts stress.
· Tolerance and Finish:
Sharping smaller angles leaves a better finish while the large angles are relatively easier to shape.
· Gear Size:
The circumference` of large gears is larger than that of small gears, hence, require larger chamfer angles in comparison with the small gears require small angles.
Choose the angle according to these factors to optimize the performance together with the resilience and ease of machining.
14. How to do gear chamfering in the industry automation
To perform gear chamfering in an automated line, follow these general steps:
Automated Gear Feeding
- To feed gears into the chamfering station it is advisable to adopt conveyor systems or robotic arms.
- Make sure that the gears are correctly positioned to avoid losing the oriented angles of each gear.
Automated Chamfering Machine setup
- When it comes to material and gear specifications, be sure to specify the angle of chamfering as well as cutting factors like speed and depth.
CNC and Robotic Systems: - Use computer numerical control (CNC) or robotic systems to achieve complete command over the motion of the tools.
Tools Selection and Setup
- The automatic tool changers will choose the appropriate chamfering tool—a single or double chamfer cutter—according to the task at hand and the procedure followed.
- Machines designed for high-volume automation must be able to use carbide or high-speed steel tools, which can endure the extreme wear and tear that comes from cutting tougher materials.
Chamfering Process
- The chamfer is formed on the edges of the gear when the chamfering tool contacts it at this angle of setting.
- With a computer numerical control (CNC) system, the chamfer can be executed with minimal human intervention as the operation is set to follow the gear profile.
Quality Control and Inspection
- To ensure the chamfer dimensions and surface smoothness are verified, set up vision systems or sensors for automatic in-process inspection.
- A reject conveyor or robotic arm removes the gear from the production line if its quality is not up to par.
Automated Gear Discharge
- Following chamfering, gears are sent, via robotic arms or conveyors, to the subsequent processing or packing stage.
Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment
- To keep the chamfering quality constant throughout the manufacturing cycle, the settings are adjusted by real-time systems that monitor the process.
- With these processes integrated into a single automated line, gear chamfering may be done more precisely and efficiently with far less human involvement.
15. What are Safety Tips When Operating Gear Chamfering Machines?
It is critical to follow all safety protocols while operating the gears chamfering machine to prevent any mishaps that could lead to injuries sustained on the job. As a result, please adhere to the safety procedures described below.
· Wear Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Always wear protective gear, such as goggles, gloves, and earplugs, to shield yourself from sparks, flying debris, and loud environments.
- Machine Inspection
Check the machine for any damage or wear before turning it on. Make sure the tools and the machine are both securely fastened.
· Proper Training
Instruct your employees on how to use the machine, including all safety features and what to do in the event of an emergency.
· Use Machine Guards
To protect yourself from moving parts and flying debris, make sure to wear the necessary safety gear during the procedure.
· Avoid Loose Clothing or Jewelry
Remove any jewelry or loose clothing that could become stuck in the running gear.
· Follow the Manufacturer's Instructions
In regards to machine adjustments, tool swaps, and general operation, always refer to the manufacturer's instructions.
· Keep the Work Area Clean
To prevent trips, slips, and falls, the work environment should be kept clean at all times and free of chips, trash, clutter, etc.
· Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) Procedures
Whether the power is off and the machine cannot be accidentally turned on, lockout/tagout must be followed at all times whether doing maintenance or changing tools.
· Monitor Machine Operation
Keep an eye on the machine at all times. Keep an ear out for any unusual sensations, sounds, or malfunctions.
· Proper Handling of Tools
Handle chamfering tools with the utmost care at all times. Do not attempt to use a broken instrument without first following the correct lifting techniques.
A person operating gear chamfering equipment can lessen the likelihood of injury and maximize productivity by remembering these safety precautions.
16. Maintenance Tips for Longevity for gear chamfering machine
The gear chamfering machine will require the following maintenance to prolong its service life and maintain its performance:
- Routine Cleaning:
Every day, you should clean the machine by removing dust, metal shavings, and any other debris. These will accumulate over time and impact the accuracy and durability of components.
· Lubrication:
Gears, bearings, and guide rails are just a few examples of moving components that need regular lubrication using the manufacturer-recommended lubricant. The result will be less wear and friction.
· Tool Inspection and Replacement:
To keep chamfer quality and prevent machine over-strain, inspect cutting tools for damage and wear and replace them as needed.
· Calibration:
Regularly re-calibrate the machine, usually after repairs or adjustments, to make sure cuts are produced precisely and in alignment.
· Coolant and Fluid Levels:
Keep the hydraulic fluid and coolant at the correct levels and refill them occasionally to keep the engine from overheating and keep it running smoothly.
· Electrical Components Check:
It is important to periodically inspect the electrical components, such as the wiring, connectors, and circuit breakers, for any defects, particularly in CNC versions.
· Scheduled Servicing:
Having your equipment serviced by experts regularly is a great way to prevent problems from getting worse and to ensure that it lasts longer.
Regular maintenance on the gear chamfering machine extends its life, improves its performance, and guarantees precision.
17. What are common Issues and Troubleshooting on gear chamfering machine
Gear chamfering machines often have the following issues, and here are some ways to fix them:
· Misalignment and Positioning Errors:
An uneven chamfer is the result of a misalignment or placement issue. Make sure everything is set up correctly on the machine, and then adjust the alignment of the workpiece and the tools.
· Tool Wear or Damage:
Damage to or dullness of the chamfering tool might result in subpar edge quality. To keep precision, check the tools often and sharpen or replace them as necessary.
· Burr Formation:
When there is an excessive amount of burr creation, it could be a sign that the feed rate or tool angle is inappropriate. Change the tool for one that is better suited to the task at hand, or alter the feed rate or tool placement.
· Vibration and Noise:
The presence of excessive vibration or noise might hurt precision, suggesting potential mechanical problems. Tighten all nuts and components to the correct torques, and maintain all machine parts regularly.
· Software and Automation Errors:
Chamfering machines that are fully automated can experience operational problems due to software issues. Try resetting the control settings, installing software updates, or recalibrating any automatic systems that aren't working properly.
· Poor Surface Finish:
Inadequate tool speed or feed rate causes surfaces to have poor finishes. Get these settings just right for a little chamfer.
With regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting of the mentioned common faults, the gear chamfering machines will run more efficiently and sustainably.
18. What is the leading Brand of gear chamfering machines in the world?
Gear chamfering machines made by some of the most prestigious companies in the world are:
- Gleason
Gleason is well-known for their cutting-edge deburring and chamfering equipment. When it comes to gear systems, no one does it better than Gleason's high-precision machines.
· Höfler:
Höfler is a Klingelnberg citizen. For many years, it has been a go-to name for gear chamfering and high-precision finishing in the aerospace, automotive, and industrial industries, among others.
- Liebherr:
Chamfering machines from Liebherr are adaptable and feature cutting-edge automation and integration choices, which are essential for high-volume manufacturing.
· EMAG
Innovative and effective chamfering solutions that cater to the demands of the automotive and industrial gear production industries while maintaining a high level of flexibility.
- FFG Werke:
Superior gear chamfering machines are long-lasting, precise, and ideal for situations where the workpiece is subjected to high levels of stress.
· Koepfer (part of EMAG):
Its forte is gear-cutting technology, particularly chamfering procedures. Its compact, high-quality gear sizes are a major selling point.
Because of their reliability, accuracy, and cutting-edge technology, these select brands have become household names in their respective fields.
19. What are the future trends in Gear Chamfering machines?
A look at what's to come in gear-chamfering machines:
· Advanced Automation:
Increased reliance on robots to facilitate error-free, high-speed manufacturing.
· AI and Machine Learning:
Predictive maintenance, and optimizing the chamfering process in real-time.
· Adaptive Technology:
These machines are designed to automatically adjust to various part sizes and materials.
- High-Precision Chamfering:
The aerospace and electronics sectors rely on our ultra-precision micro-chamfering services.
· Energy Efficiency:
Designing for sustainability means reducing energy and lubricant needs.
· Integrated Quality Monitoring:
Real-time consistency in quality control is ensured by on-machine sensors.
Gear chamfering is one area where these trends are aiming to improve accuracy, productivity, and environmental friendliness.
20. Conclusion
In 2024, the needed precision, automation capability, and type of gear being processed will determine which gear chamfering machine is best for you.
Emphasize some of the cutting-edge capabilities that boost efficiency, quality, and productivity through AI-driven process optimization, low energy use, and simple maintenance.