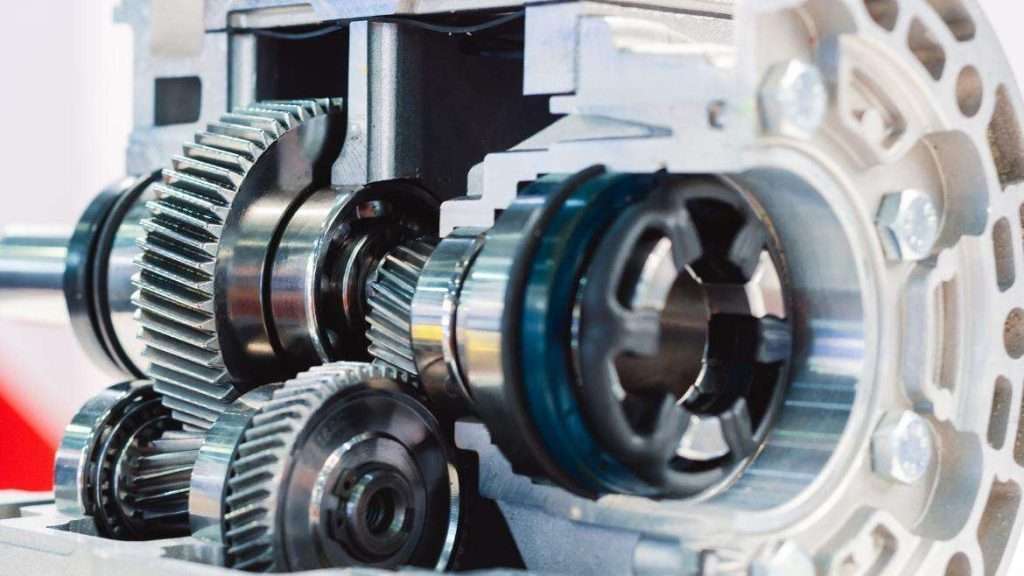
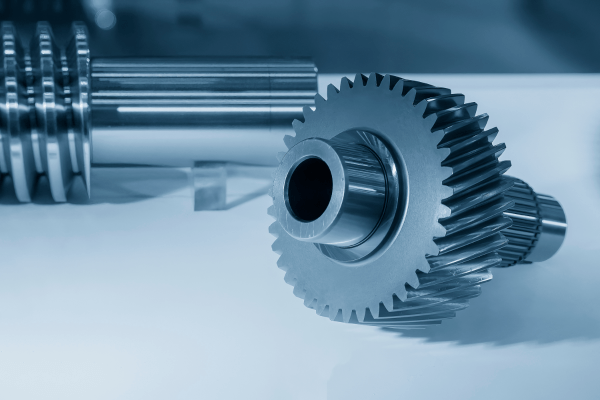
Helical Gear vs. Spur Gear: Comprehensive analysis of performance, efficiency, and noise levels in various applications.
Introduction

Gears are mechanical components employed in every conceivable piece of equipment since they act as transmitting power apparatus.
There are numerous kinds of gears, two of which are helical gears and spur gears, to name but a few, but they are distinguished by their functions or drawbacks.
This article aims to provide a comparison of helical gears and spur gears, including performance, efficiency, and noise level comparisons.
This information is important in determining the type of gear suitable for a certain application to improve the performance of the machines involved.
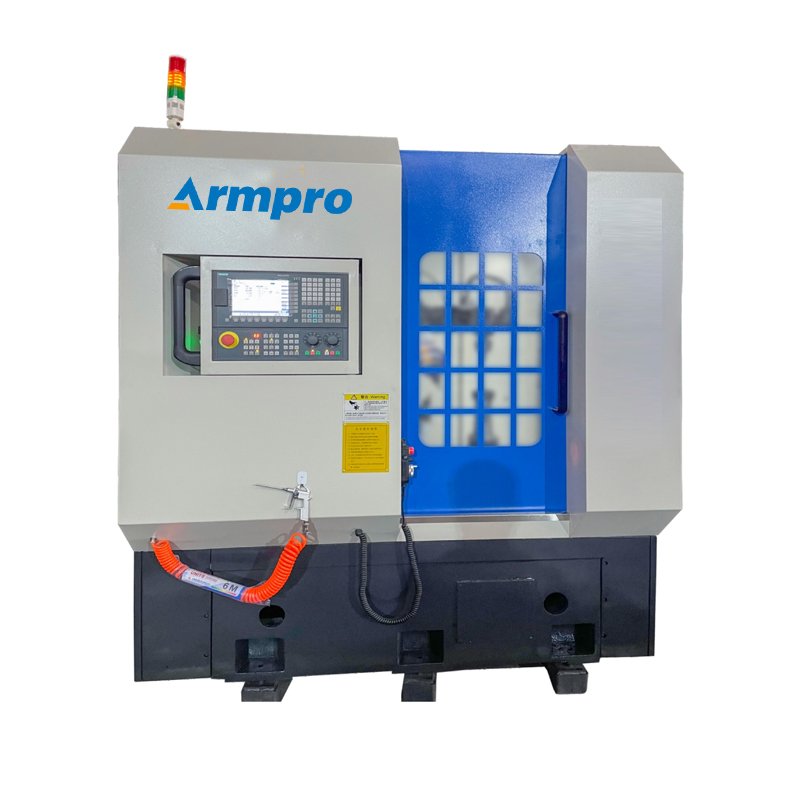
Of course, if you are looking for a gear chamfering machine ,you can contact us Armpro, our gear chamfering machine can do chamfering on both Spur Gears and Helical Gears easily
1. Understanding Gears
What Are Gears?
Gears are mechanical members comprising teeth projecting from two concentric circles – the carried shafts.
These changes in speed force and direction of motion are vital members used in power transmission in many different classifications of machines and mechanical or industrial operations.
Role in Mechanical Systems
Gears are utilized to convey energy between mechanical systems within transport such as automobiles, industry, and home apparatus. They enable change of motion by an amount of control that is valuable in attaining a desired performance using a specific mechanical structure.
Types of Gears
Spur Gears

- Straight teeth aligned with shaft axis for movement transmission.
- Plain design with high ratios, but may cause noise due to shear action.
Helical Gears
- Possess straight with involute profiles that enter into contact gradually this means that, as compared to spur gears, helical gears are smoother and quieter.
- Suitable in coupling both parallel and non-parallel shafts thus being suitable for any high-speed procedures.
Other Gear Types
Bevel Gears:
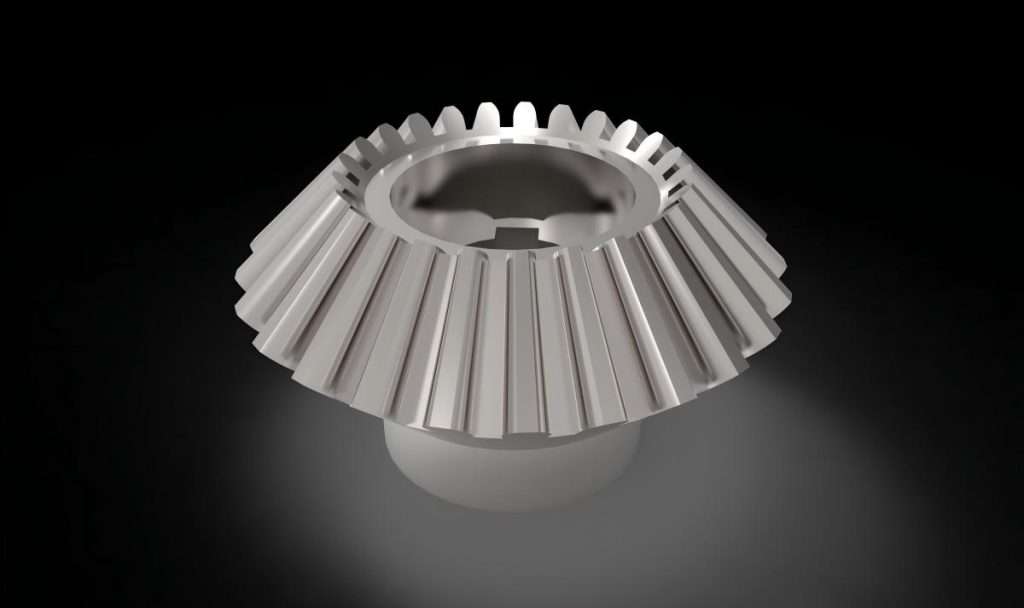

To transmit motion between two intersecting shafts that are commonly used in the differential system.
Worm Gears:

Offer high speed decreasing ability and are applied in sectors demanding high torque and restricted space offered.
2. Helical Gears
Design and Structure
Gear helix angle
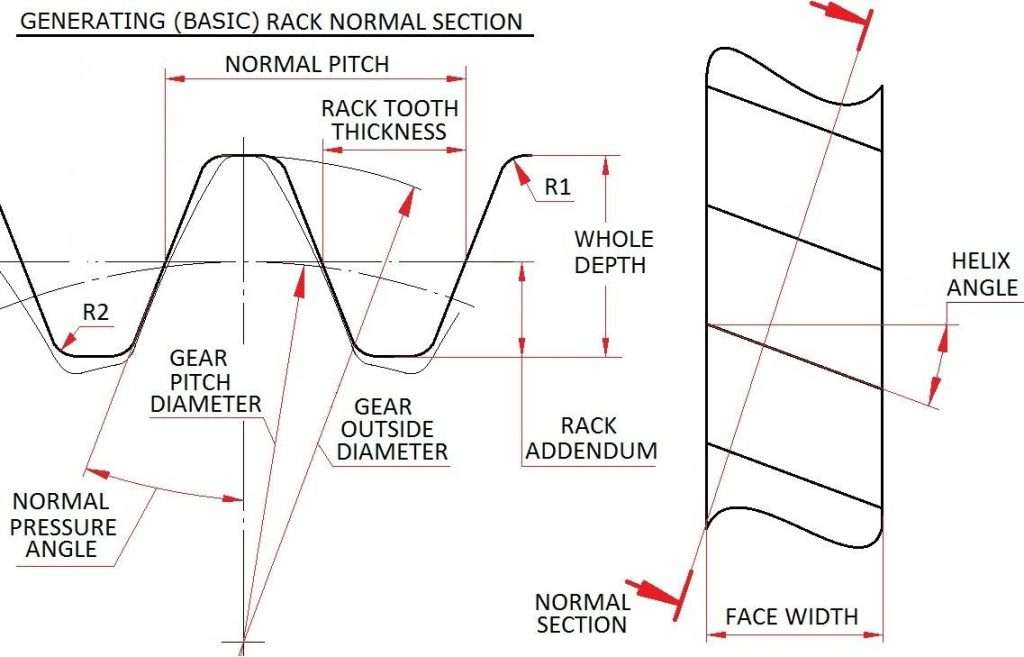
- Teeth in helical gears are parallel and cut at an angle to the longitudinal direction, resulting in a large contact area that distributes load among multiple teeth.
Helix Angle Impact
- The position of the teeth which is specified by the helix angle defines the surface finish and load-carrying capacity of the gears.
- The advantage is that higher helix angles can improve smoothness but these also have the advantage of increased axial force which has to be controlled.
Performance Characteristics
High Load Capacity

- They are also capable of transmitting larger amounts of load as compared with spur gears because of this the helical gears are applicable where high loads have to be tackled.
- A load is spread out over several teeth so that they wear evenly and to increase gear longevity.
Smooth and Quiet Operation
- The teeth are set at an angle and as such the gears roll into engagement, at which point the gear train is smoother and there is less vibration and backlash than with straight-cut gears.
- This characteristic makes the helical gears appropriate in precision machines in addition to those machines that require a constant rate.
Efficiency
Efficiency in Various Applications
- The performance of generating helical gears is excellent; real gear efficiency can rise to 0. 97-0. 98 in fully lubricated applications.
- Although possess a slightly lower gear ratio than spur gears due to the sliding action of the teeth they offer excellent performance in high-speed continuous operations.
Noise Levels
Noise Reduction Through Gradual Engagement
- The cutter teeth have a negative rake angle which means that they enter the workpiece gradually thereby minimizing shock and vibration at the point of the cutter teeth and workpiece interface.
- This smoother engagement leads to a reduction in noise level and hence helical gears are preferred where noise is a critical factor; automobiles and industries.
Applications
Automotive Transmissions
- It has extensive use in car gearboxes to give smooth and noiseless shifts and performs well even at high speeds.
Industrial Machinery
- Used in conveyors, compressors, and mixers among other equipment that requires efficient power transmission.
Aerospace industry
- Used in applications like aircraft systems because of high load capability with acceptable levels of noise and efficiency.
Robotics and Automation
- Best used in environments that call for reduced motion and super high loads as with the case in robotic joints and actuators.
3. Spur Gears
Design and Structure
Straight Teeth Design
- Spur gearsare defined by having straight, parallel-tooth patterns that run along the length of the axis of the gear.
- This basic structure makes it convenient to transfer power between two parallel shafts.
Gear Geometry
- The direct line is favored as the tooth profile for a bending connection, thus offering a strong joined between meshing gears.
- Spur gears also vary in terms of size and pitch; thus they may be applied in numerous mechanical systems.
Performance Characteristics
Simplicity and Direct Power Transmission
- In the configuration, spur gears are quite simple and therefore their production and integration are not complicated at all.
- They provide efficient power transmission with less mechanical system interference, thus being suitable for simple use.
Load Handling
- Though they can transmit larger loads than helical gears, spur gears don’t offer as much loading capacity because the dropping of loads is not as efficient.
Efficiency
High Efficiency in Optimal Conditions
- Spur gears are known to exhibit high gear efficiency frequently touching 95-99% when in optimal working condition with a good lubricant.
- This efficiencycan be attributed to their simplicity and no sliding friction, and therefore they can be applied widely in many mechanical procedures.
Efficiency in Various Scenarios
- It works best in areas where speed reduction is not essential and where large torque is to be transmitted at low speeds.
Noise Levels
Noise Production from Straight Teeth
- Most of the noise and vibrations occur during the initial contact of the straight teeth during their interaction or meshing than in the helical gears.
- This characteristic can be a disadvantage in applications where noise production is not desirable.
Applications
Machinery and Equipment
- Often used in industrial machines conveyors lathes, partly because of their simplicity and also a high degree of efficiency.
Automotive Applications
- Used in automotive differentials and gearboxes where simple power transmitting takes place.
Pumps and Compressors
- Being used in positive displacement pumps and air compressors where there is a need to ensure proper movement transfer.
Robotics
- Applicable in directly powering robot apparatuses for basic movement applications.
4. Pros and Cons

Helical Gears:

Pros:
- Smooth Operation:
The inclined teeth ensure progressive meshing which makes it easier for the gears and makes little noise operation when compared to spur gears.
- Higher Load Capacity:
Helical gears can handle more weight due to their larger contact surface and high-quality materials, making them suitable for harsher service conditions.
- Quieter Operation:
It also cuts shock and vibration allowing the machinery to operate at a quieter volume which is critical in areas where sound is a concern.
Cons:
- More Complex Design:
The design of the helical teeth is more elaborate than that of the spur gears as this may make the manufacturing and installation of the gears more challenging.
- Higher Manufacturing Cost:
The design and manufacturing processes of helical gears are relatively complex, and as a result, the manufacturing cost of helical gears is typically higher than that of spur gears.
- Axial Thrust:
Helical gears generate thrust along the axial direction and hence need more support in the actual assembly.
Spur Gears

Pros
- Simplicity:
Due to simple construction, they can be produced and assembled in large quantities with reduced complexity of gear assemblies.
- Cost-Effectiveness:
Less in cost than helical gears, spur gears prove to be more economical for most use, and therefore preferred.
- High Efficiency in Specific Applications:
They have relatively higher efficiency in provisions where high speed is necessary together with little torque utilization.
Cons:
- Noisier Operation:
Animation is also increased by contact of the straight teeth that may cause noises and vibrations especially where this is discouraged.
- Lower Load Capacity:
Spur gears involve less load-carrying capacity compared to helical gears resulted due to less effective force distribution.
- Less Smooth Engagement:
The sudden interlocking of teeth may result in oscillatory movements and early attrition of teeth surfaces.
5. Choosing the Right Gear for Your Application
Application Requirements
- Load Capacity
Determine to what extent the gear will be required to bear the load. You get helical gears for higher load applications while the spur gears are adequate for lower loads.
- Speed
Identify the speed at which the application will be operational. Spur gears work satisfactorily at high speeds while helical gears work satisfactorily in situations where there are smooth transitions at different speeds.
- Noise Tolerance
Think of how much amount of noise the application will be able to handle. For situations, where low noise is desirable, then helical gears are preferable because of their low noise expected from the initial engagement.
Cost Considerations
- Initial Investment
How do you determine the initial costs of both types of gear? Spur gears are generally cheaper in relation to their cutter and manufacturing methods as compared to helical gears.
- Long-Term Costs
Think about the maintenance and replacement costs that might be attached to the company. While their price could be somewhat higher initially, they could provide greater service life and better performance in the applications that require it.
Maintenance and Longevity
- Maintenance Needs
Consider the requirements of maintenance for every type of gear. Spur gears need less maintenance compared to helical gears for this reason that the latter has more complications in its design arising from the axial thrust it generates.
- Expected Lifespan
Consider the expected service life of gears in the application you are designing. Helical gears will last longer in high-load, high-speed applications than spur gears in the same application.
Conclusion
In conclusion, helical gear and spur gear estimations depend on the application.
For high-reliability and precision applications, helical gears improve smoothness, load-bearing capacity, and noise.
Spur gears are cheaper and easier to make, but they are noisy and can carry less load than helical gears.
They are more efficient for simple applications.
Considering the weights and speeds of the mechanical systems, noise level, and cost will determine the best gear type.
If you have any question please contact us, we Armpro will give you solution on gear manufacturing solution on Gear Cutting machine, Gear hobbing machine, Gear chamfering machine,
Don't forget to share this post!
Related Products
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and working details to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 159 27 555863

Want the best price & newest metal working machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?
Sign up for Armpro's monthly newsletter,we're free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable working solutions!