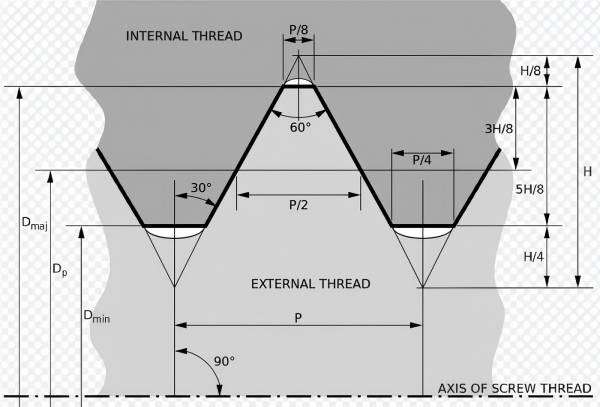
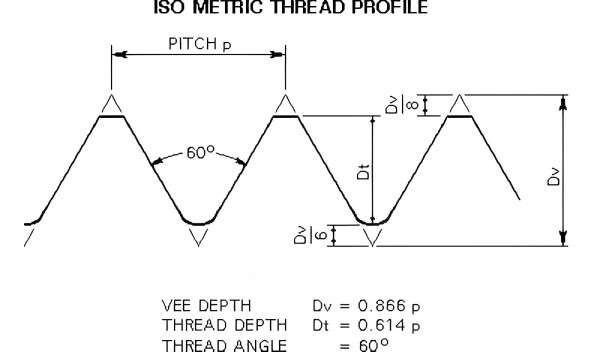
Metric Thread Chart
Introduction
As much as we are talking of mechanical engineering, construction, or even electronics, threads are some of the most crucial things used to join parts. Even though individuals do not spend considerable time on threads daily, they can be used for most of the applied devices and equipment.
Among many other threads, the metric threads are far and away the most popular and widely used worldwide, especially in industries such as automotive, electronics, and manufacturing.
If you are a hobbyist, an engineer, or a DIY enthusiast, it greatly helps to understand the different types of threads, how to measure and choose the proper metric thread size, and how to create such threads while working on your projects.
1. What Are the Types of Threads?
As for the threads, some basic types have different applications in various fields. Hence, this knowledge is essential in manufacturing, automotive, and construction. Now, look into some of the most accepted thread types used today.
● Acme Thread
Acme thread is applied in almost all applications where the transmission of motion or force is needed, such as lead screws and lifting gadgetry. This type of external thread offers high strength and durability due to its trapezoidal shape. This makes it perfect for use under high system load conditions.
● Square Thread
Like the Acme thread, the square thread is also used for power transmission in heavy machinery. It has a square-shaped profile that allows for efficient power transfer. Like the Acme thread, the square thread is typically an external thread.
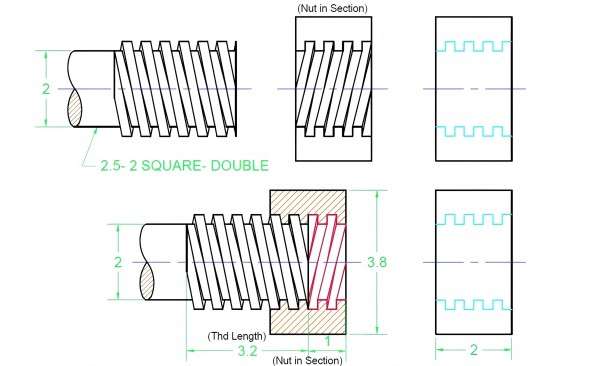
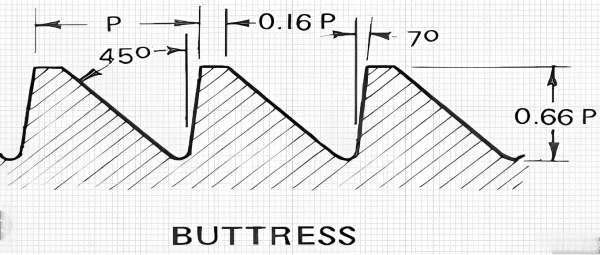
● Buttress Thread
This is a thread that is commonly used in situations requiring one-way pressure. For instance, it is found in screw jacks and high-load applications. Buttress threads feature a strong, one-sided thread design, which helps them withstand extreme forces.
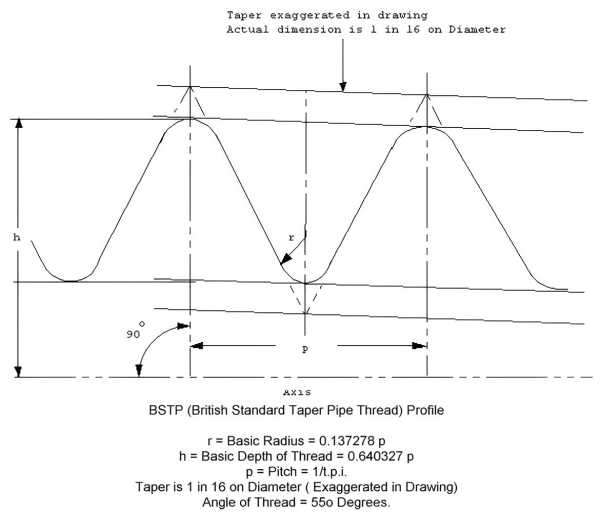
● British Standard Pipe (BSPT)
This type of thread is used in pipe fitting, particularly in the UK and countries that follow British standards. It is commonly used for sealing and preventing leakage in plumbing applications. Imperial threads are often used with BSPT, as the thread specifications follow the British imperial system.
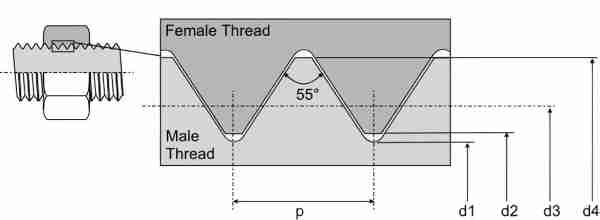
● British Standard Whitworth (BSW)
The British Standard Whitworth thread is an older standard still used in many mechanical and construction projects. Its profile differs from the BSPT, with a different thread angle and pitch.
● Metric Thread
Ultimately, the metric thread is widely used worldwide, in Europe and Asia. The outstanding deviation in the metric thread is that, unlike the other threads like BSPT or BSW, it is all in millimeters. Different applications vary but include the automotive and, of course, electronics.
Knowing such types of threads is advisable, especially when it is time to determine which type to apply to a particular need.
2. What Is the Metric Thread Size Chart?
When you begin working with metric threads, it is necessary to know the correct size. The metric thread size table normally depends on the diameter of the thread and the pitch, which is the distance between each thread.
ISO Metric Thread
The ISO metric thread is the world's most commonly used thread standard. It follows a simple system of designations, where the diameter is measured in millimeters, and the pitch is the distance between threads, also in millimeters, simplifying choosing the appropriate thread size.
Here is an example of the metric thread size chart:
- M5 x 0.8
- M6 x 1
- M10 x 1.5
Here, the "M" stands for a metric thread. The number following M represents the diameter (in millimeters), and the second number is the pitch. Although threads per inch (TPI) can be used, the usual practice in the metric system is the millimeter-based pitch.
Thread Pitch Formula
The thread pitch formula helps you calculate the distance between threads. Designing and selecting the right metric thread for your application is essential. In the formula, you use the diameter and pitch to determine the right fit.
| Thread Size | Major Diameter (mm) | Minor Diameter (mm) | Thread Pitch (mm) | (mm)Pitch Diameter (mm) |
(mmTapping Drill Diameter (mm)) |
(mClearance Hole Diameter (mm)m) |
| M1 | 1 | 0.729 | 0.25 | 0.838 | 0.75 | 1.3 |
| M1.1 | 1.1 | 0.829 | 0.25 | 0.938 | 0.85 | 1.4 |
| M1.2 | 1.2 | 0.929 | 0.25 | 1.038 | 0.95 | 1.5 |
| M1.4 | 1.4 | 1.075 | 0.3 | 1.205 | 1.1 | 1.8 |
| M1.6 | 1.6 | 1.221 | 0.35 | 1.373 | 1.25 | 2 |
| M1.8 | 1.8 | 1.421 | 0.35 | 1.573 | 1.45 | 2.3 |
| M2 | 2 | 1.567 | 0.4 | 1.74 | 1.6 | 2.6 |
| M2.2 | 2.2 | 1.713 | 0.45 | 1.908 | 1.75 | 2.9 |
| M2.5 | 2.5 | 2.013 | 0.45 | 2.208 | 2.05 | 3.1 |
| M3 | 3 | 2.459 | 0.5 | 2.675 | 2.5 | 3.6 |
| M3.5 | 3.5 | 2.85 | 0.6 | 3.11 | 2.9 | 4.2 |
| M4 | 4 | 3.242 | 0.7 | 3.545 | 3.3 | 4.8 |
| M4.5 | 4.5 | 3.688 | 0.75 | 4.013 | 3.8 | 5.3 |
| M5 | 5 | 4.134 | 0.8 | 4.48 | 4.2 | 5.8 |
| M6 | 6 | 4.917 | 1 | 5.35 | 5 | 7 |
| M7 | 7 | 5.917 | 1 | 6.35 | 6 | 8 |
| M8 | 8 | 6.647 | 1.25 | 7.188 | 6.8 | 10 |
| M9 | 9 | 7.647 | 1.25 | 8.188 | 7.8 | 11 |
| M10 | 10 | 8.376 | 1.5 | 9.026 | 8.5 | 12 |
| M11 | 11 | 9.376 | 1.5 | 10.026 | 9.5 | 13.5 |
| M12 | 12 | 10.106 | 1.75 | 10.863 | 10.2 | 15 |
| M14 | 14 | 11.835 | 2 | 12.701 | 12 | 17 |
| M16 | 16 | 13.835 | 2 | 14.701 | 14 | 19 |
| M18 | 18 | 15.394 | 2.5 | 16.376 | 15.5 | 22 |
| M20 | 20 | 17.294 | 2.5 | 18.376 | 17.5 | 24 |
| M22 | 22 | 19.294 | 2.5 | 20.376 | 19.5 | 26 |
| M24 | 24 | 20.752 | 3 | 22.051 | 21 | 28 |
| M27 | 27 | 23.752 | 3 | 25.051 | 24 | 33 |
| M30 | 30 | 26.211 | 3.5 | 27.727 | 26.5 | 35 |
| M33 | 33 | 29.211 | 3.5 | 30.727 | 29.5 | 38 |
| M36 | 36 | 31.67 | 4 | 33.402 | 32 | 41 |
| M39 | 39 | 34.67 | 4 | 36.402 | 35 | 44 |
| M42 | 42 | 37.129 | 4.5 | 39.077 | 37.5 | 47 |
| M45 | 45 | 40.129 | 4.5 | 42.077 | 40.5 | 50 |
| M48 | 48 | 42.857 | 5 | 44.752 | 43 | 53 |
| M52 | 52 | 46.587 | 5 | 48.752 | 47 | 57 |
| M56 | 56 | 50.046 | 5.5 | 52.428 | 50.5 | 61 |
| M60 | 60 | 54.046 | 5.5 | 56.428 | 54.5 | 65 |
| M64 | 64 | 57.505 | 6 | 60.103 | 58 | 69 |
| M68 | 68 | 61.505 | 6 | 64.103 | 62 | 73 |
3. What Is a Different Metric Thread?
Different metric thread variations are based on the application and thread profile. Understanding their differences will help you choose the best thread for your needs.
Metric Internal Thread Dimensions
An internal thread is cut inside a material and creates threaded holes. The metric internal thread dimensions are specified similarly to external threads, but the process differs. Internal threads are often used for nuts or threaded holes that require a bolt.
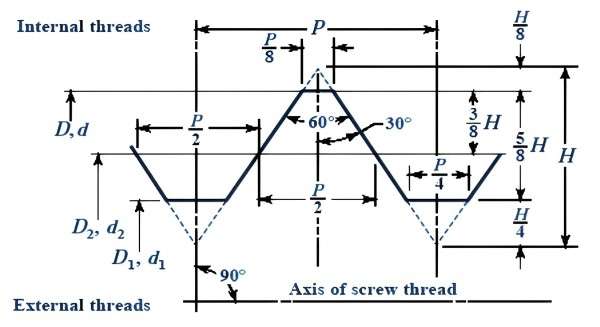
Male and Female Threads
In metric threads, there are male and female threads. Male threads are the external threads that fit into the internal female threads. Together, they allow for a strong connection in various applications.
Male Thread: This is the continuous part of the thread that juts out, as in the case of a bolt.
Female Thread: This component normally forms a hole and serves as a residence for the male thread, as with a nut.

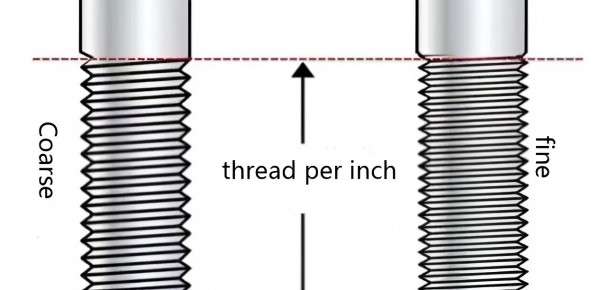
Coarse and Fine Threads
The distinction between coarse thread and fine thread refers to the thread pitch. The coarse threads have a larger pitch and are easier to manufacture, which makes them suitable for quick assembly. Fine threads, on the contrary, have a smaller pitch and are more useful when accuracy is required, as well as when there is a need for higher strength.
4. What Is The Application Of The Metric Thread?
The unique quality of metric threads is that they are widely used in various industries; their average usability and precision make them apt for most applications. Some of these applications are as follows:
Automotive
Metric threads become crucial for the automotive section's engine, transmission, and suspension parts. The efficacious adaptation of the metric thread means that manufacturers can use the same fasteners.

Electronics
Some everyday applications of metric threads in electronics are within computers, mobile phones, and any electronic gadgets. Fine threads are often applied in them due to their interference fittings and stability.

Manufacturing
Metric threads are important in manufacturing as they ensure certain strength connections that can be tight without possibly coming apart or losing a part. It provides fast construction through metric threads for machinery or tool applications.
5.How To Make Metric Thread?
There are two primary methods for making metric threads: cutting and extruding.
Cutting Metric Thread
Cutting metric thread involves using a die or a tap to carve the threads into a material. This method is precise for creating metric threads, especially when working with metal or hard materials.
Extruding Thread
An extruding thread is formed continuously using a die-forced-through material such as plastic. This process is usually called mass production of threaded elements, as it reduces effort compared to cutting.
Conclusion
Metric threads must be understood and classified into their types, sizes, and uses before entering the manufacturing, automotive, or electronic industries. Understanding these concepts is crucial to understanding whether the person will encounter external versus internal thread, coarse versus fine thread, or need to decide on the right metric thread size.
The next time you end up dealing with a metric thread, you can expect to have more insight into what to look for and how best to select your metric thread.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related Products
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and working details to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 159 27 555863

Want the best price & newest metal working machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Armpro's monthly newsletter,we're free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable working solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Tapping Machine: The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Electric Tapping Machines:the Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Drilling Machine: The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- Drilling milling Machine:The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024
- CNC Tapping Machine :The Complete Buying Guide in 2024
- Pipe chafering Machine:The Complete Importing Guide in 2024
- Radial drilling Machine:The Complete Buying Guide in 2024
- Thread rolling Machine:The Complete Buying Guide In 2024
- Pillar Drilling Machine:The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2024