Square Tube Weight Chart: A Detailed Overview
Introduction
Square Tubing has an important basic construction, manufacturing, and engineering load, as its strength and its widespread application make its weight of crucial importance in structural design, transportation planning safety, and overall application.
This blog covers square tube weight, how useful a square tube weight chart is, what other materials are used, and square tube applications.
1. What Are Square Tubes Weight?
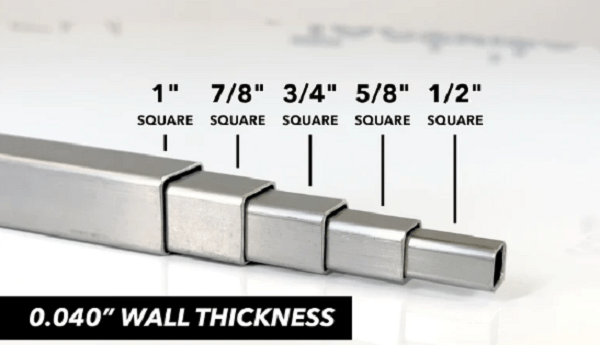
First of all, let's get to know what a square tube is, to then know the square tube's weight. Square tubes are hollow bars with equal lengths on all four sides. Round pipes or rectangular tubes cannot define these.
Weight signifies mass and is mainly expressed in pounds per foot or kilograms per foot, depending on the specific area. The weight of a square tube is hence determined by its external side length and wall thickness, along with the density of the material used in fabricating it.
As an example, a 2-inch by 2-inch steel square tube having a wall thickness of 0.25 inches would weigh more than one having its walls 0.125 inches thick, seeing that there is more material within.
The calculation of weight for a square tube is extremely simple in the form of a uniform cross-section of a hollow tube multiplied by a density of material and multiplied further by length. However, this could be very tedious for manual calculations on all sizes and materials, and this is where reference to standards comes in very handy.
The weight of square tubes is essential for structural integrity and logistics. Engineers need it to ensure that their frameworks are designed to withstand in-service loads without buckling.
Fabrication uses measures such as estimating shipping costs or how much material they would require for their job. Simply put, it is the metric most directly linking theory in design to reality in the field.

2. What Is the Square Tube Weight Chart?
A square tube weight chart is a tabular instrument that summarizes the weights of square tubes according to several different sizes and wall thicknesses, usually categorized by material type. Also known as a square tube weight table, it spares users from repetitively calculating values, as these are all precomputed for their convenience.
Specific charts take it a step further with metric measurements to accommodate the international standard. These tables are obtained in industry circles, either via manufacturers, engineering handbooks, or organizations, including the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC), to protect their accuracy and reliability.
Indisputably, a square tube weight table is not only a matter of convenience while working, but it also provides a rapid means of comparison among materials chosen, verifying compliance to aspects of the design and assisting with cost estimates that link weight and material volume.
In fact, the usefulness of these charts extends even deeper for professionals responsible for large projects or repetitive activities, thus adding value in terms of planning and execution time.
| Diameter (in) |
Wall Thickness(in) |
Steel (Ibs/ft) |
Aluminum (Ibs/ft) |
Titanium (Ibs/ft) |
| 2.00 | 0.120 | 2.42 | 0.82 | 1.38 |
| 1.75 | 0.250 | 4.01 | 1.36 | 2.29 |
| 1.75 | 0.120 | 2.09 | 0.71 | 1.19 |
| 1.75 | 0.095 | 1.68 | 0.57 | 0.96 |
| 1.50 | 0.250 | 3.35 | 1.13 | 1.91 |
| 1.50 | 0.120 | 1.77 | 0.60 | 1.01 |
| 1.50 | 0.095 | 1.43 | 0.48 | 0.82 |
| 1.50 | 0.065 | 1.00 | 0.34 | 0.57 |
| 1.25 | 0.120 | 1.45 | 0.49 | 0.83 |
| 1.25 | 0.095 | 1.17 | 0.40 | 0.67 |
| 1.25 | 0.065 | 0.82 | 0.28 | 0.47 |
| 1.00 | 0.120 | 1.13 | 0.38 | 0.64 |
| 1.00 | 0.065 | 0.65 | 0.22 | 0.37 |
| 0.75 | 0.100 | 0.70 | 0.24 | 0.40 |
| 0.75 | 0.065 | 0.48 | 0.16 | 0.27 |
3. What Materials Are Used to Construct Square Tubes?
Square tubes are manufactured from a variety of materials, each of them being chosen for its specific properties that could be suitable for particular applications. Steel is mainly used because it is very strong and durable.
Most carbon steel square tubes are either hot-rolled or cold-formed. The hot-formed square tube steel is the preferred vendor because of its low price and good weldability; these square tubes should be either painted or galvanized to prevent corrosion. Stainless steel has a percentage of chromium and has excellent resistance against corrosion; hence selected for use in very humid surroundings.
Two essential engineering materials are aluminum and steel. Complementing these properties will be the very light and corrosion-resistant properties of aluminum, shining with benefit because, at times, aluminum square tubing weighs even over 50 percent less than steel tubing.

These applications are typically those that require less mass so that other resources are conserved, with a tiny compromise on strength, thus disposing of themselves with aluminum as a material in heavily loaded conditions.
Others would include brass and copper, undeniably not more commonly found than the initial two. Brass square tubes resist corrosion very well and have an attractive finish; hence, they are suited for decoration or low-stress applications.
Copper conducts heat very well, but it has limitations for structural use because of its price and softness. A significant factor in the material selection for fabrication will be the weight of the square tube because steel weighs 490 pounds per cubic foot, whereas aluminum weighs about 169 pounds per cubic foot.

4. What Is a Square Tube Used For?
Somewhere, there is a fusion or blend of structural efficiency and aesthetic versatility that square tubes can serve any industry. For any construction work, square tubes will form the backbone of frames for buildings, bridges, and towers, taking advantage of their regular shape for columns, beams, and bracings that carry loads.
Though the hollow shape provides strength, it does so with the least possible excessive weight, thus maximizing material utilization in the case of high-rise buildings and industrial structures.
They are also used in the construction of machine frames, conveyors, and storage racks in manufacturing. Their flat surfaces facilitate welding and bolting, which is a significant consideration for any application requiring stability and precision.
Applications in the automotive sector include parts for chassis, while such uses for square tubes include very much cage reinforcement, as well as for trailer frames where strength-to-weight ratio is a consideration for safety, as well as fuel efficiency.

Square tubes find attractive applications for clean lines and strength in form and function for modern-day home construction-so much so that even in furniture applications such as chairs and shelving units, square tubes seem to have found their way.
That speaks more for the robustness and construction simplicity that square tubing has to offer when it comes to framing a greenhouse or making a livestock pen. Indeed, for these applications, the weight of the square tube itself considerably affects their load capacities, transportability, and in some ways in which these structures can be put in place.
Aerospace is one specialized user of the tubes, so the aluminum square tubes can be used to build lightweight structures that counteract gravity; in marine settings, there is a high degree of benefit for the use of stainless steel square tubes.
It is this proper mate material on the right side with the proper geometry that brings the variability of square tubes for various applications in heavy engineering or those that are light fabrication.

Conclusion
A square tube weight chart practically stands as the viability link-after what square tubing weight is to its practical application. The square tube weight chart values weights with respect to sizes and materials, thus saving the engineers/builders and fabricators further complications with calculations and letting them come to a decision quickly. The square tube weight table provides a link from engineering data to a real-world result concerning accuracy in design and speed in execution.
Guiding construction, manufacturing, and much more, square tube materials like steel, aluminum, and brass define their weight and strain potential for different types of jobs, ranging from heavy to light. Hence, the application of a square tube is well exemplified.
Simply put, it arms professionals with insights to maximize their projects-building a skyscraper, or framing custom work. With calculated weights and practicality, square tubes continue to be some of the building blocks of modern engineering, proving how even the simplest geometries can hold great power when understood and applied suitably.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related Products
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and working details to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 159 27 555863

Want the best price & newest metal working machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?
Sign up for Armpro's monthly newsletter,we're free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable working solutions!