Why Armpre Machinery is Trusted
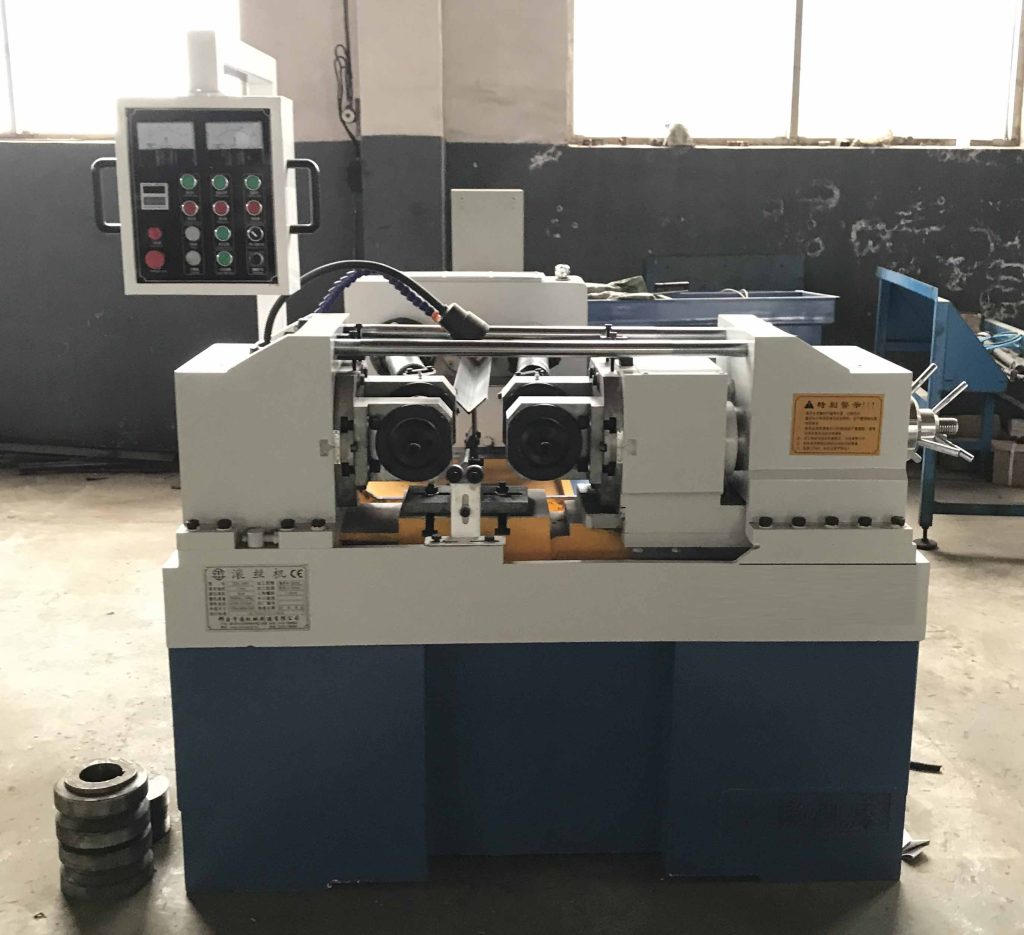
Welcome to Visist Our Hydraulic Thread Rolling MachineFactory
Welcome customers from any country come to visit us, we can show you the Hydraulic Thread Rolling Machine workshop, and show the Hydraulic Thread Rolling Machine production site.
The Buyer's Guide
Hydraulic thread rolling machine, thread roller :The Complete Buying Guide In 2024
Your Complete Buying Guide for Thread Rolling Machines in 2024
Thread rolling is an efficient and cost-effective method for producing threads, as it can be done quickly and with minimal material waste. Apart from that, it also helps in strengthening the surface with more precise accuracy and minimizes material waste.
Did you know that more screw threads are produced each year than any other machine element? While there are many methods for threading in manufacturing such as casting, rolling, chasing, die-cutting, etc., not all of them are widely used anymore in the industry. As the industry has been getting more and more competitive over the years while available resources are also slowly depleting, a majority of manufacturers have opted for Die-cutting and Thread Rolling methods to maximize their production efficiency. Out of the pair, the Thread Rolling method stands out due to its low-cost high-quality finish, and a lot of industrialists are transitioning into incorporating this method even more.
Let us dig deeper to uncover more about Thread Rolling and how it stands out from the rest of the methods alongside its advantages and disadvantages in this ultimate buying guide to Thread Rolling Machines.
What is Thread Rolling?

Thread Rolling is the process of forming threads on a metal stock by displacing the metal surface. The Thread Rolling process involves pressing a hardened tool, called a die, onto the surface of a workpiece to create the threads. It does not remove any excess metal from the piece like chips or shavings but simply uses more hardened steel to mold threads on a more ductile metal piece. This method does not severe the integrity of the metal form but simply elongates and reforms it to make it even stronger. Thread Rolling is typically used to produce threads on rods or bars, and it is capable of producing threads with high accuracy and surface finish.

It is a known fact that cold working helps strengthen most materials including metals alongside their fatigue resistance and hardness. Thread rolling is such a method that grants a ton of benefits for the manufacturers using this method. Apart from putting out a way stronger product, it also does the job with minimum wastage and the best-looking surface finish. In hindsight, Thread Rolling is a process of forming threads rather than cutting or carving them out like in older traditional methods and is way more accurate and economic.
What are the Differences Between Thread Rolling and Thread Cutting?

Thread Rolling is a Thread forming method that does not cut or shave the surface to make threads but reforms and molds threads on it with applied pressure. It is a cold forging method meaning that squeezes the metal to form threads below its recrystallization temperature. It is not exactly a new technology and has been around for a very long time. However, the recent advancement in technology and the industry allowed this method to be precise and cost-effective for mass manufacturing only recently.

On the other hand, Thread Cutting involves using a cutting tool to remove material from the workpiece to create the threads. It is a subtractive method that outputs a considerable amount of chips or shavings in the process. This can be done with a single-point tool on a lathe or with a multi-point tool on a screw machine. Thread cutting is typically used to produce threads on bolts, screws, and other fasteners, and it is capable of producing threads with a wide range of thread profiles and pitches. Unlike the rolling method, Thread Cutting allows for the production of threads on a wider range of materials.
So to summarize the differences; thread rolling is a more efficient and cost-effective process than thread cutting, but thread cutting is more versatile and can be used on a wider range of metals.

What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Thread Rolling?
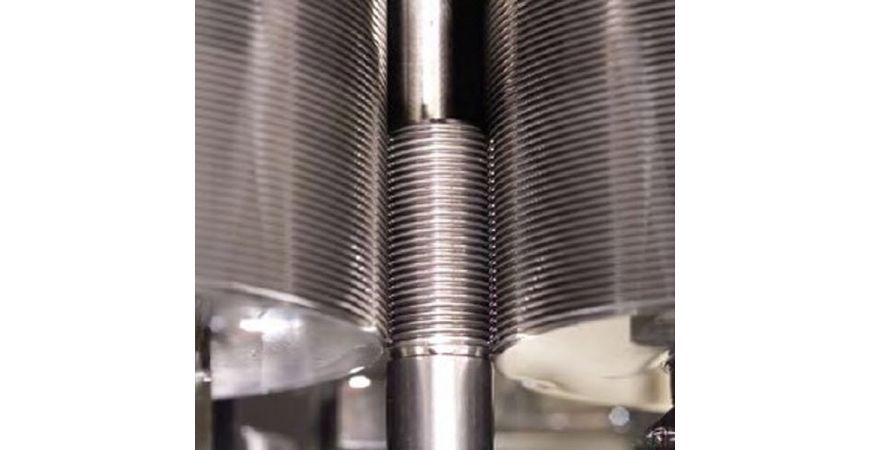

Now that we have gone over what Thread Rolling is and how it generally functions, let us look into how this method holds up in mass manufacturing. Here are some advantages and disadvantages of the Thread Rolling method.
Advantages:
- High production rates: Thread rolling is a fast process, and it is capable of producing a large number of threads in a short period of time. This makes it suitable for the mass production of threads.
- High tensile strength: Threads produced using the thread rolling tend to have high tensile strength, as the process work hardens the material and imparts a pattern on the surface that increases the strength of the threads.
- Good surface finish: Thread rolling produces threads with a smooth and uniform surface finish, as the die imparts a pattern on the surface of the workpiece that helps to eliminate surface defects.
- Suitable for a wide range of materials: Thread rolling can be used to produce threads on a wide variety of materials, including steel, aluminum, brass, and plastic.
- No wastage: The thread rolling process doesn’t put out any shavings or chips like in subtractive methods, meaning the production of threads using this method is more economically efficient.
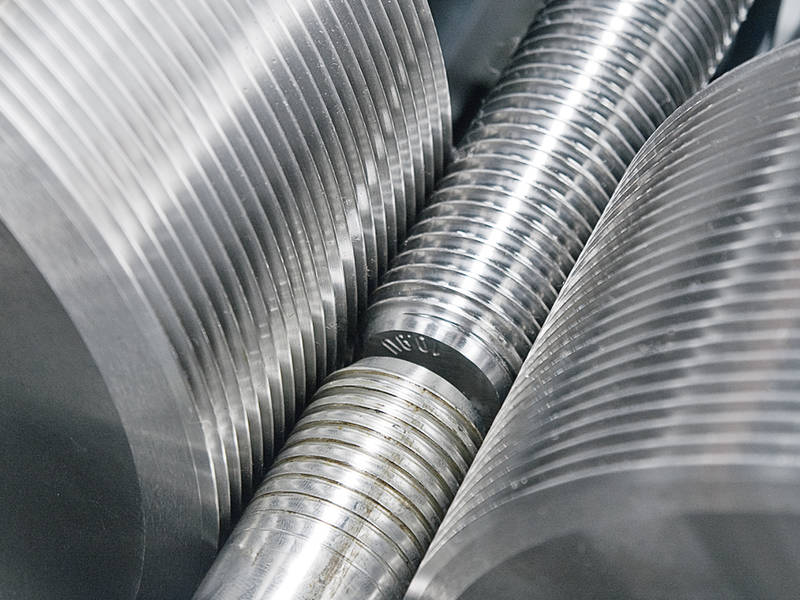

Disadvantages:
- Limited to cylindrical shapes: Thread rolling is only suitable for producing threads on cylindrical shapes. It cannot be used to produce threads on non-cylindrical shapes or on tapered threads.
- Limited to certain thread sizes: Thread rolling is only suitable for producing threads within a certain size range. If the threads being produced are outside of this range, another method may be more appropriate.
- Limited to certain thread pitches: Thread rolling is only suitable for producing threads with certain pitches, or thread spacing. If the desired pitch is outside of this range, another method may be more appropriate.
- Initial tooling costs: Setting up a thread rolling process can be expensive, as it requires specialized equipment and dies. This can make it less cost-effective for low-volume orders.
- Limited to ductile metals: Even though the thread rolling method can be used on a wide range of metals, they are limited to more ductile ones, meaning another method may be more appropriate for harder metals.
What are Main Factors to be Considered in the Thread Rolling Process?

Thread Rolling is a superior method in thread manufacturing. However, due to its specialized process, there are a few factors to be considered in order to utilize this method:
- Type of material: The type of material being used will affect the type of thread rolling process and the tools used. Essentially, the material used needs to be more ductile than the dies of the tool used.
- Thread pitch: The pitch of the thread, or the distance between threads, will be determined by the size and shape of the tools used in the thread rolling process.
- Thread tolerance: The desired tolerance of the finished thread will be determined by the precision of the tools and the process used.
- Surface finish: The desired surface finish of the finished thread will be affected by the type of thread rolling process used and the tools used. Higher-quality tools and dies give out the best results.
- Thread strength: The strength requirements of the finished thread will be determined by the type of thread rolling process used and the precision of the tools used. Some high-quality machines are capable of giving stronger threads compared to others.
- Production volume: The volume of threads being produced will affect the type of thread rolling process and the tools used. While some are more efficient at the process, some take time and are more precise.
- Equipment and tooling: The availability and capabilities of the equipment and tools used in the thread rolling process will also need to be considered.
What are the Different Types of Thread Rolling Machines?

There are 2 main Thread Rolling methods: Infeed Rolling and Through-feed (Thrufeed) Rolling. While almost all industrial thread rolling machines use these 2 methods, they differ when it comes to their use cases.
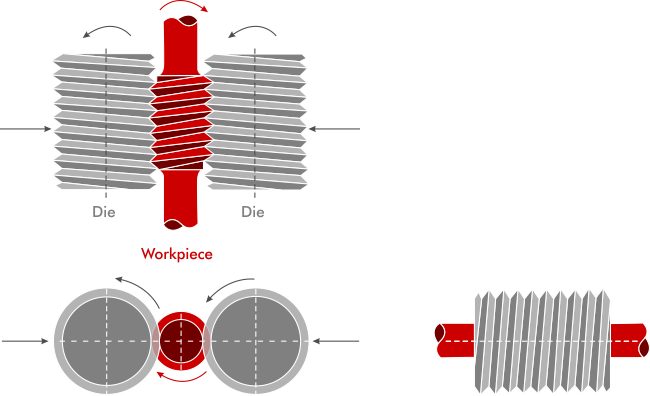
Infeed rolling method uses circular dies where the thread angle is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. This method is also commonly referred to as the plunge method. The workpiece and the dies are placed parallel in this method and move in synchronization to form the threads. The main advantage of this method is the speed of the process, which makes it ideal for mass production. And machines that use this method come with 2 or 3 dies according to the specifications. However, the rolling is limited to the maximum length of the dies meaning that it is typically used for shorter threads and for parts with more complex shapes or profiles.
Infeed Rolling with Circular dies
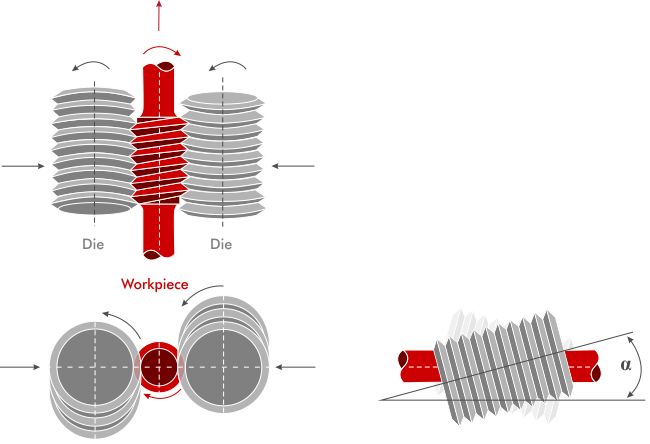
Thrufeed rolling method, on the other hand, is a continuous process where the part is fed through the machine, and the die rolls along the entire length of the part in a single pass. This method is more efficient in creating longer threads or larger quantities of parts. The dies in this process are usually placed at an angle the tilted Helix angle helps in the continuation of the rolling process, allowing for longer workpieces. Even though this method excels in managing much longer workpieces, it is typically limited to parts with simple shapes and profiles. The machines that use this method come with either Groove dies or Lead Corrected dies to fit the requirement of the work.
Throughfeed rolling with Groove Dies
So in retrospection, both infeed rolling and thrufeed rolling can produce high-quality threads with good surface finish and dimensional accuracy. The choice between the two methods will depend on the specific requirements of the part and the thread being produced.
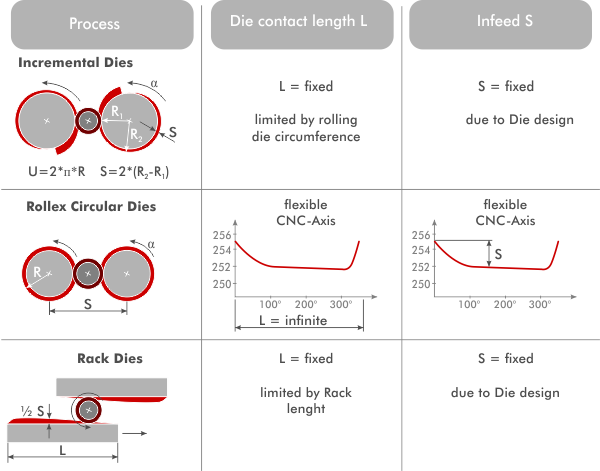
Typical rollable Dimensions
Infeed rolling
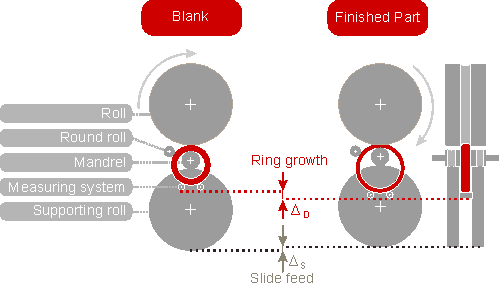
Ring Rolling Process
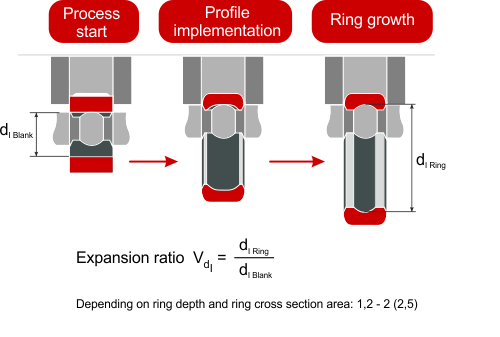
What are the Key Factors to Consider When Purchasing Thread Rolling Machine?

Thread rolling has a couple of special methods that cater to different scenarios and workpieces as mentioned above. So it is important to consider your requirements before proceeding with a Thread Rolling machine. There are several key factors to consider when purchasing a thread rolling machine for manufacturing threads:
- Type of machine: There are several types of thread rolling machines available, including two-die machines, three-die machines, and multiple-die machines. The type of machine you choose will depend on the size and complexity of the parts you will be producing and the types of threads you need to create.
- Production capacity: Consider the production capacity of the machine and whether it will meet your current and future needs. You may also want to consider the speed at which the machine can produce threads and whether it can handle the required volume of production.
- Quality: The quality of the threads produced by the machine is an important consideration. Look for a machine that produces threads with good dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
- Ease of use: Consider the ease of use of the machine, including the complexity of setup and changeover, as well as the level of training required to operate it.
- Maintenance: Look for a machine that is easy to maintain and has a good track record for reliability. You may also want to consider the availability of spare parts and technical support from the manufacturer.
- Cost: The cost of the machine is an important consideration, but it should not be the only factor. Look for a machine that offers good value for money and meets your production and quality requirements.
What Type of Materials Can Be Used in a Thread Rolling Machine?
Thread Rolling machines use hardened dies to press against the surface of the workpiece and form the threads. These dies are typically made of high-strength materials such as tool steel or tungsten carbide, which are able to withstand the high forces and wear associated with the thread rolling process. So metals such as steel, aluminum, brass, and copper are the ideal materials that can be used in common Thread Rolling processes due to their less intimidating properties when compared to the dies.
Other materials, such as plastics, can also be rolled to create threads, although the process is generally more limited and the materials may need to be treated or modified in some way to make them suitable for rolling. In general, the suitability of a material for thread rolling will depend on its strength, ductility, and other mechanical properties, as well as the type of thread being produced and the specific requirements of the application.
What are the Applications of Thread Rolling Machines?
Thread Rolling is exclusively used to create threads on cylindrical parts and their application spreads across multiple industries. Thread rolling machines are an essential tool for the production of high-quality, accurately-dimensioned threads in a variety of industries. Some of the main applications of these machines include:
- Automotive: Thread rolling machines are used to produce a variety of parts for the automotive industry, including fasteners, engine components, and transmission parts.
- Aerospace: Thread rolling machines are used to produce parts for the aerospace industry, including fasteners, structural components, and aircraft engines.
- Construction: Thread rolling machines are used to produce fasteners and other parts for the construction industry, such as bolts, screws, and nails.
- Electrical and electronic: Thread rolling machines are used to produce parts for the electrical and electronic industries, including connectors, switches, and electrical boxes.
- Medical: Thread rolling machines are used to produce medical devices such as implants and surgical instruments.
- Industrial: Thread rolling machines are used in a variety of industrial applications, including the production of fasteners, pumps, valves, and other mechanical components.
What are the Different Types of Dies Used in Thread Rolling Machines?
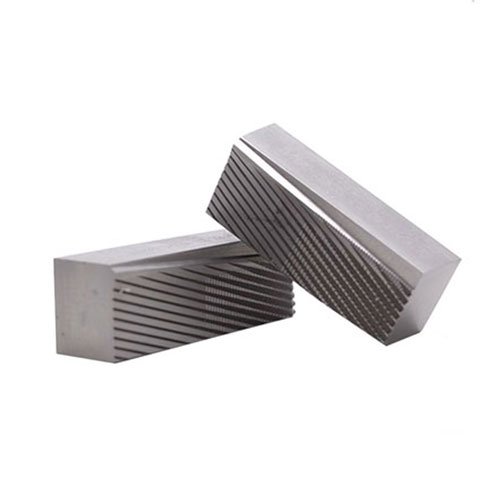
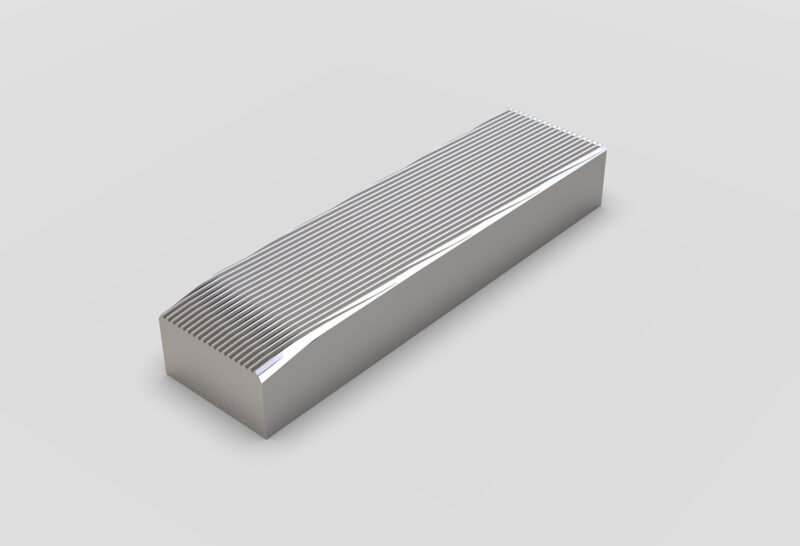




Thread rolling dies are usually made from high-strength materials such as tool steel or carbide, and are designed to withstand the high stresses and abrasive forces that are involved in the thread rolling process. There are several types of thread-rolling dies that are used in thread-rolling machines in the manufacturing of threads. These include:
- Straight dies: These are used to roll threads on straight or cylindrical parts. This is the most basic and the most common type of die found in the industry.
- Taper dies: These are used to roll threads on tapered parts, such as the ends of bolts or screws.
- Form dies: These are used to roll threads with special shapes or profiles, such as square or Acme threads.
- Knurling dies: Apart from general threads being forged into workpieces, Thread Rolling machines are also used to form patterns and grips on cylindrical workpieces. So these dies are used to roll a pattern of raised or indented lines onto a part, typically for the purpose of improving grip or aesthetics.
- Fluting dies: These are used to roll a pattern of shallow grooves onto a part, typically for the purpose of improving grip or aesthetics.
- Specialty dies: There are also a variety of specialized dies that are used for specific types of threads or applications, such as thread rolling dies for rolling threads on thin-walled parts or thread rolling dies for rolling threads on non-ferrous materials.
We hope that this guide clears all your general questions regarding Thread Rolling in general and assists you in deciding the perfect thread-rolling machine for your business/factory. If you are also looking for a Gear Chamfering Machine, check out our detailed guide on How Gear Chamfering Works and how you should decide on which machine to buy.




















