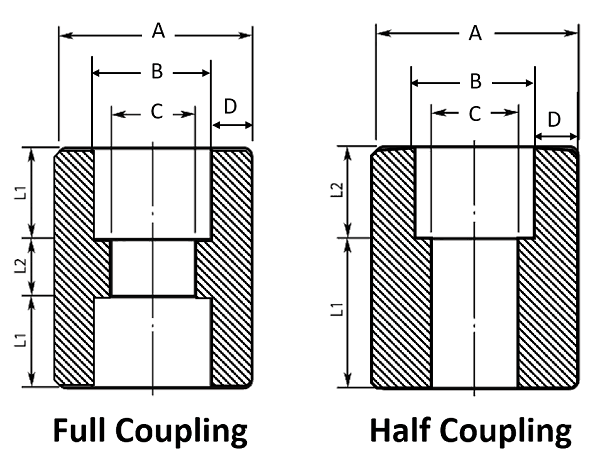
Full Coupling vs Half Coupling
Introduction:
Couplings are one of the essential fittings used to connect two ends of a pipe in plumbing and piping systems. These fittings provide a close, leak-proof connection to allow flow of liquids or gasses smoothly and uninterrupted. Two broadly used types of pipe coupling are full coupling and half coupling. The different types are designed with different use cases based on the sort of connection you need.
Selecting the correct sort of coupling assists to improve the strength and performance of the pipeline. The operation of both half couplings and full coupling are same; however, the design, installation process, and applications are apparently different. In this article, we will explore the differences between full coupling vs half coupling.
1.What is Full Couplings?
The full coupling connects pipes of the same diameter and the same material to form a continuous pipeline. It's composed of a cylindrical piece that fits over or screws into the ends of the pipe, providing considerable solid attachment.
Full couplings have different types and many applications, making them versatile. The internal threads of the threaded full couplings are of same type, which is on exterior of the pipes. It is commonly used in metal pipe systems and it is a robust, removable joint.
Slip-on couplings are inserted into the pipe ends and bonded or fixed with a mechanism. Revolutionized manufactured piping and equipment uses compression couplings as an alternative to traditional joining with welding, soldering, or threading.
The proper coupling size is important for piping assembly to be able to work properly. Couplings need to be used with similarly sized pipe to form a tight, leak proof seal. A coupling's size varies with the pipe and the material.
A coupling dimensions chart would help in choosing the right size as they list down the standard sizes against their corresponding pipe diameters. A proper match ensures that the coupling seals tightly, preventing leaks and the potential complete failure of your setup.
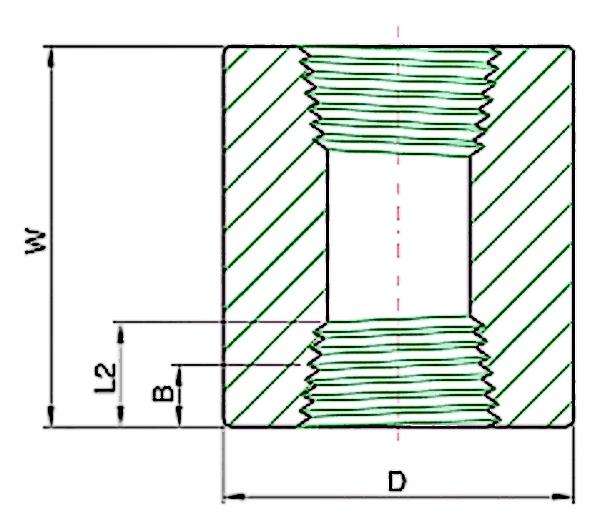
What Does a Full Coupling Do?
A full coupling is essential for all piping systems since they are used to connect a pipe with the same diameter and manufacturing material. It allows damaged pipeline segments to be repaired and extended by joining together and sealing two pipes. Full couplings are employed to connect two pipes to allow the free flow of fluid through the joint without the risk of obstruction.
Couplings usually attach two pieces of pipe and, in turn, prevent leaks by providing an even, continuous connection. For fully coupled systems, this is usually a permanent or strong enough link for high pressure systems. This allows for a continuous pipeline to flow, regardless of whether it is a completely new installation or a repair.
Full couplings give a more reliable connection than other coupling types. They are used in both residential plumbing and industrial applications due to their stress resistant nature. A properly installed full coupling will ensure that your system is working reliably and efficiently for years to come.
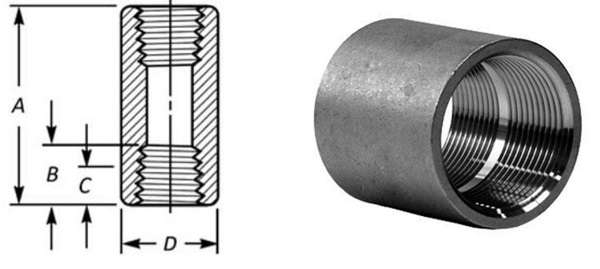
Uses and Applications of Full Couplings
Full couplings are used in many different plumbing and piping systems. It is utilized to connect two same dimensions and material tubing for smooth flow. Below are a few examples of full coupling applications and uses:
- Straight Line Connections:Extend or repair pipelines while eliminating leakage and become stable connection points in water supply systems
- Worn out Pipes Repairing:Damage pipes or corroded pipes get repaired in a way that you don't need to get them replaced totally, saving time and cost.
- Industrial Use:Used in widespread piping systems, also recommended for high-pressure conditions such as those found in chemical plants and oil refineries.
- Gas Lines and High-Pressure Systems:Provides couplings for gas lines and high-pressure systems, preventing potential hazards and leaks.
- HVAC systems:Provide a secure joint against extreme temperature and natural elements for refrigerants and air supply lines and for water.
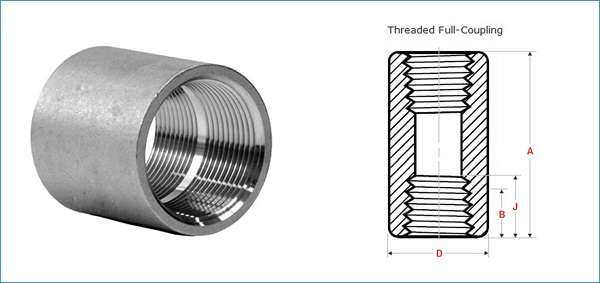
2.What is Half Coupling?
Half couplings attach one end of a pipe to another element, such as a valve, tank, or equipment. This is an all-purpose fitting for use in applications where only a single connection point is needed.
Half coupling in piping is commonly used for connecting branches or attaching pipes to larger components. The open end of a half coupling can be threaded, welded, or socketed, depending on its use. This fitting saves material and space while providing a reliable connection.
Coupling dimensions chart is essential when choosing a half coupling. This chart shows standard sizes, diameters, and specifications. Getting the correct sizes is an essential part of getting a secure, tight, no-leak connection.

Uses of Half Couplings
- Branch Connections:These connections are used to connect a pipe intermediate to a main pipe or a larger component in the system.
- Tank or Vessel Connections:Most often used to connect pipes to tanks, valves, or other equipment.
- Compact Systems:Practical for tight spaces where full couplings are not practical or not required.
- High Pressure Applications: Perfect for high pressure systems and connections that need to withstand significantly more pressure but still flowing perfectly.
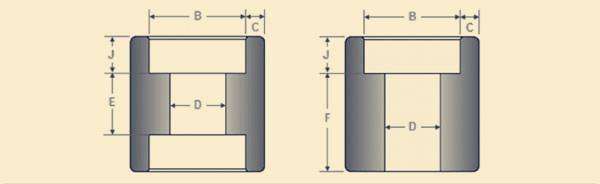
| COUPLING | ||||||||||
| DN | Nom. Pipe Size |
Center to End Coupling W |
Center to End Cap
P |
Outside Diameter D |
End Wall ThicknesS G Min. |
Length of Thread
Min. (1) |
||||
| 300086000 | 3000 | 6000 | 3000 | 6000 | 3000 | 6000 | B | L2 | ||
| 6 | 1/8" | 32 | 19 | 16 | 4.8 | 6.4 | 6.7 | |||
| 8 | 1/4" | 35 | 25 | 27 | 19 | 25 | 4.8 | 6.4 | 8.1 | 10.2 |
| 10 | 3/8" | 38 | 25 | 27 | 22 | 32 | 4.8 | 6.4 | 9.1 | 10.4 |
| 15 | 1/2" | 48 | 32 | 33 | 28 | 38 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 10.9 | 13.6 |
| 20 | 3/4" | 51 | 37 | 38 | 35 | 44 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 12.7 | 13.9 |
| 25 | 1" | 60 | 41 | 43 | 44 | 57 | 9.7 | 11.2 | 14.7 | 17.3 |
| 32 | 1-1/4" | 67 | 44 | 46 | 57 | 64 | 9.7 | 11.2 | 17.0 | 18.0 |
| 40 | 1-1/2 | 79 | 44 | 48 | 64 | 76 | 11.2 | 12.7 | 17.8 | 18.4 |
| 50 | 2" | 86 | 48 | 51 | 76 | 92 | 12.7 | 15.7 | 19.0 | 19.2 |
| 65 | 2-1/2" | 92 | 60 | 64 | 92 | 108 | 15.7 | 19.0 | 23.6 | 28.9 |
| 80 | 3" | 108 | 65 | 68 | 108 | 127 | 19.0 | 22.4 | 25.9 | 30.5 |
| 100 | 4" | 121 | 68 | 75 | 140 | 159 | 22.4 | 28.4 | 27.7 | 33.0 |
3.Key Differences Between Full Coupling and Half Coupling
Moreover, full couplings and half couplings are the most widely used fittings in piping, serving different purposes. Here are the key differences:
Design and Structure
Full coupling connects two similar diameter pipes. That connection is terminated to both ends so as to protect the connection. Simply put, half coupling connects single pipe. The other end is left open to be directly connected to some kind of structure (tank, equipment).
Application
The basic job of a full coupling is to join two pipes in a direct manner. This is the same stuff used to repair pipelines. Half coupling is more common on branch connections. It is most effective for tying pipes to larges objects like vessels and valves.
Material Usage
A full coupling uses more material because it covers pipe end to pipe end. That’s especially tough on high-pressure systems. A half coupling, however, is made with less material. This also makes it a cost-effective solution for targeted use cases.
Coupling Dimensions
Since full couplings join two pipes, they are generally larger. They need to be chosen according to a chart of the coupling sizes. Since they are smaller in size, half couplings can be used in congested areas and complex piping systems. They are usually more convenient due to their reduced size.
Connection Type
Full coupling allow for the uninterrupted flow of fluid through two different pipes of similar sizes. Perfect for the pipeline extensions. In contrast, a half coupling connects one pipe end. Therefore, it is more suitable for systems that use branch connections or equipment fitments.
| DN | Nom. Pipe Size |
Center to End Coupling W |
Center to End Cap
P |
Outside Diameter D |
End Wall ThicknesS G Min. |
Length of Thread
Min. (1) |
||||
| 300086000 | 3000 | 6000 | 3000 | 6000 | 3000 | 6000 | B | L2 | ||
| 6 | 1/8" | 32 | 19 | 16 | 4.8 | 6.4 | 6.7 | |||
| 8 | 1/4" | 35 | 25 | 27 | 19 | 25 | 4.8 | 6.4 | 8.1 | 10.2 |
| 10 | 3/8" | 38 | 25 | 27 | 22 | 32 | 4.8 | 6.4 | 9.1 | 10.4 |
| 15 | 1/2" | 48 | 32 | 33 | 28 | 38 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 10.9 | 13.6 |
| 20 | 3/4" | 51 | 37 | 38 | 35 | 44 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 12.7 | 13.9 |
| 25 | 1" | 60 | 41 | 43 | 44 | 57 | 9.7 | 11.2 | 14.7 | 17.3 |
| 32 | 1-1/4" | 67 | 44 | 46 | 57 | 64 | 9.7 | 11.2 | 17.0 | 18.0 |
| 40 | 1-1/2 | 79 | 44 | 48 | 64 | 76 | 11.2 | 12.7 | 17.8 | 18.4 |
| 50 | 2" | 86 | 48 | 51 | 76 | 92 | 12.7 | 15.7 | 19.0 | 19.2 |
| 65 | 2-1/2" | 92 | 60 | 64 | 92 | 108 | 15.7 | 19.0 | 23.6 | 28.9 |
| 80 | 3" | 108 | 65 | 68 | 108 | 127 | 19.0 | 22.4 | 25.9 | 30.5 |
| 100 | 4" | 121 | 68 | 75 | 140 | 159 | 22.4 | 28.4 | 27.7 | 33.0 |
4.Materials Used in Full and Half Couplings
Material selection is crucial for couplings (full and half) to ensure durability, strength, and compatibility with piping systems. They're available in numerous materials to fit the different needs of industrial and domestic applications.
Carbon Steel
Typical materials used in full and half couplings are carbon steel. It is known for its maximum strength & endurance. This kind of material is usually found in industrial applications, like oil refineries, chemical plants, and high-pressure systems. It is dirt resistant and can be used in high cleaning applications.
Stainless Steel
It is an excellent material for systems transferring, corrosive substances, including water and chemicals. These products are sanitary and, therefore, more suitable for food and pharmaceutical uses.
Brass
Brass is commonly used in plumbing as it’s ductile and corrosion-resistant. Best for low-pressure systems & home use. Full and half couplings are found in brass at both ends for water supply and gas line applications.
Alloy Steel
High temp, high pressure systems use alloy steel. It has strength and capacity to survive severe weather. Alloy steel full and half couplings are basic in power plants and mechanical pipelines.
Copper
Another popular residential plumbing material is copper. It is famous for its abrasive resistance and strength. Hot and cold water piping systems are much better with copper couplings that resist heat induced stress.
5.How to Choose Half Couplings or Full Couplings for Your Application
Half coupling or full coupling are used to get the reliable performance from piping systems. Here are a few important considerations to think about when making your choice:
Application Requirements
It is important to understand the need of your piping system. To connect two pipes with similar outer diameters, a full coupling connection is the best choice. A half coupling is used for branch connections or for connecting pipes to equipment notes such as tanks or valves.
Pipe Size and Compatibility
Verify a coupling dimensions chart to make sure the coupling will fit on the pipeline diameter. Ensure the coupling size matches the dimensions of the pipe to avoid leaks or ineffective connections.
Pressure and Temperature Ratings
For the purpose of ensuring a robust design, pressure, and temperature factors for larger coupling loadings can be accommodated from full couplings. Although more resistant and robust, half couplings are more appropriate for moderate pressure and temperature applications.

Material Selection
Choose a material to meet the needs of the system and the materials to be transported. Corrosive environments are well-suited for stainless steel, while PVC adapts to lower-pressure water situations. The material of coupling affect the coupling life time and strength.
Space Constraints
Assess your piping system for adequate spacing. Half coupling is small and helpful in tight spaces and complex design. A full coupling, however, occupies more space according to its dimensions.
Installation Type
Think about the connection type: threaded, welded, or socketed. Threaded couplings facilitate installation and removal; welded couplings create a stronger, permanent connection.
Cost Efficiency
Take into account the project budget and material cost. Half couplings also use less material, making them cheaper in some applications. But in challenging conditions, a full coupling could spare you more use for your money over the long run.

Conclusion
Understanding the different couplings is vital for the design and maintenance of efficient piping systems. They serve different functions, from joining pipes to adding branches.
The selection of couplings depends on application, material, and space limitation. Even if the coupling is full or half, an intelligent decision will increase the reliability of the system. Use a coupling dimensions chart to choose the right one for each situation for an optimal result.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related Products
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and working details to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 159 27 555863

Want the best price & newest metal working machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Armpro's monthly newsletter,we're free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable working solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Tapping Machine: The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2021
- Electric Tapping Machines:the Ultimate Buying Guide in 2021
- Drilling Machine: The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2021
- Grinding Machine:The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2021
- Metal Band Saw Machine :The Complete Buying Guide in 2021
- Pneumatic Tapping Machine:The Complete Importing Guide in 2021
- Bench Tapping Machine:The Complete Buying Guide in 2021
- CNC Tapping Machine:The Complete Buying Guide In 2021
- Magnetic Base Drill Machine:The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2021
- Drilling And Tapping Machine:The Complete Buying Guide in 2021