NPT - American National Standard Taper Pipe Threads Size Chart
NPT was the result of the standard that was set by William Sellers in America, as a result of meeting the compatibility problems of having too many fastening mechanisms. He set the standard for nuts, bolts and screws which resulted in the NPT.
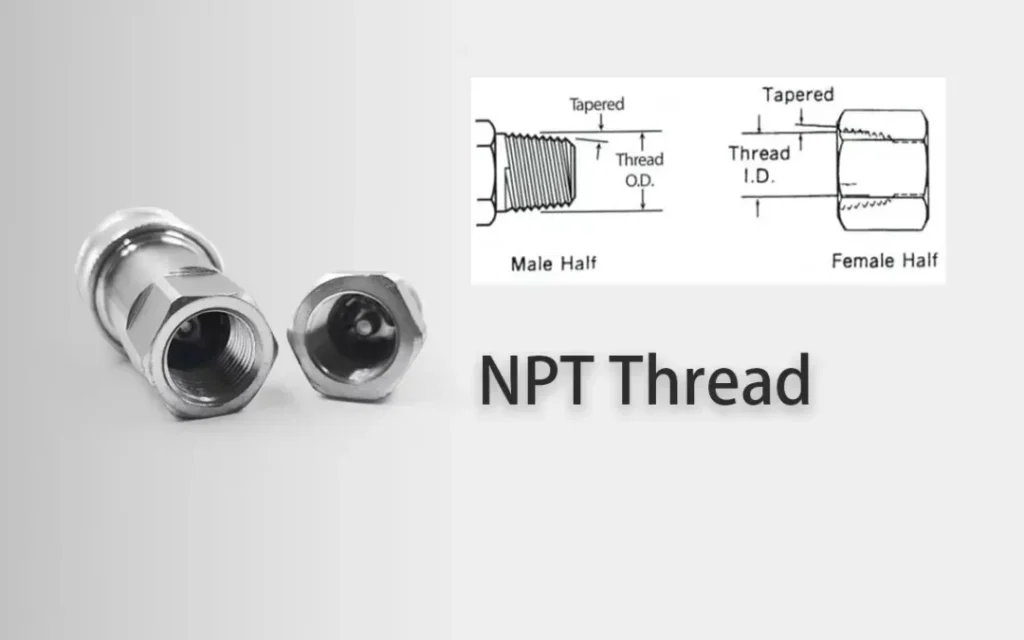
NPT, short for National Pipe Taper, refers to a standard for tapered threads,defined by ANSI B1.20.1, that are commonly used in the United States. NPT are used in many applications, especially for joining and sealing pipes and fittings. These threads are designed to create a tight and leak-resistant connection as they tighten and seal when threaded together.
NPT threads have a taper ratio of 1:16, which means the diameter of the threads decreases along the length of the pipe. This standard is used in a wide range of industries, particularly in applications like plumbing and fluid transportation.
National Pipe Taper or NPT threads are the most known and widely used pipe threads in terms of connection, where the pipe thread provides both the mechanical joint as well as the hydraulic seal. Most of the time, NPTs are sealed using Teflon tape or a specific jointing compound.
A compound used as a sealant or PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) tape must be used in order to make sure it is a leak-free seal. NPT threads are also known as MPT or Male Pipe Threads, MNP, or NPT (M) for external threads, and FPT or Female Pipe Threads, or NPT(F) for internal threads. However, FPT and MPT are not ANSI authorized designation standards.
1. What are the Characteristics of National Pipe Taper NPT threads

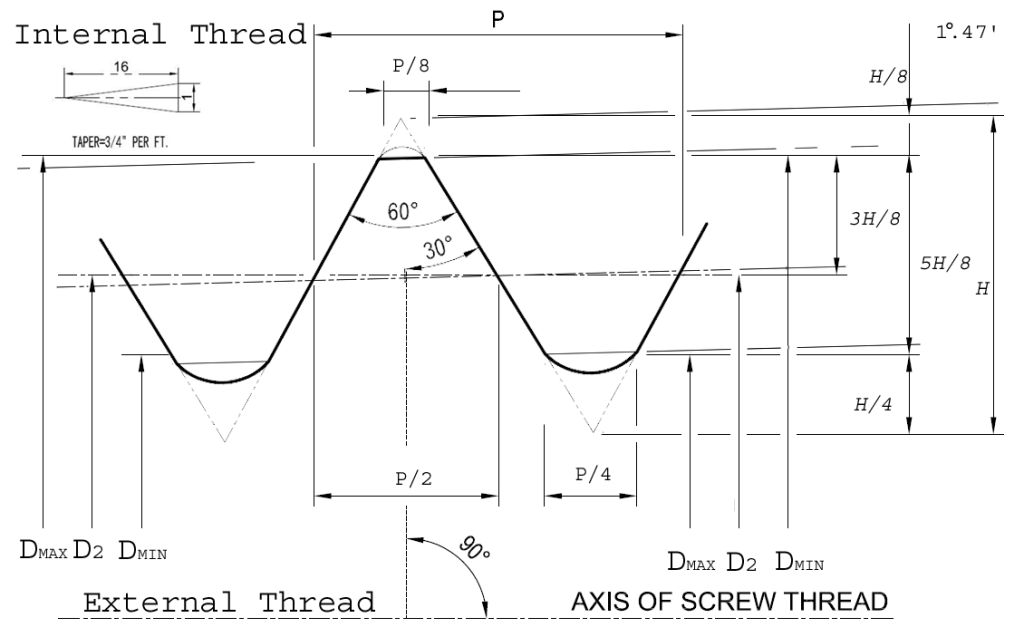
NPT that are also known as ANSI/ASME B1.20.1 Pipe Threads have some basic characteristics as follows:
- There is an angle of 1° 47' 24" (1,7899°) between the taper and the center axis.
- They contain a flat truncation of roots and crests.
- They possess a thread angle of 60°.
- Their pitch is measured in TPI (Threads per Inch).
NPTs are widely used in hydraulic circuits as leak-proof sealants. The pipe threads that are used in applications like hydraulic circuits can be mainly classified into two types as follows:
- Jointing threads: Jointing threads are NPTs that are used for joints where there is a requirement of pressure tight area by sealing on the threads and are taper external and parallel or taper internal. In this type of pipe threads, the sealing effect can be improved by using a jointing compound.
- Fastening threads: Fastening threads are pipe threads on which pressure tight joints are not made on the threads. In fastening threads, both threads are parallel and the sealing is affected by compression of a soft material or a flat gasket on the external thread.
2. What are Different sizes of National Pipe Taper
Pipe thread sizes are based on the inside diameter (ID) or flow size. If you find an LH added to the mentioned size the. The pipe has a left hand thread.
For instance, "½-14 NPT" marked on a pipe thread means that there is a diameter of ½ inch and 14 threads to each inch and that is made according to the NPT standard.
There are different types of pipe thread forms that are used in jointing fixtures. The most commonly used pipe thread forms are:
- NPT: American Standard Pipe Taper Thread
- NPSC: American Standard Straight Coupling Pipe Thread
- NPTR: American Standard Taper Railing Pipe Thread
- NPSM: American Standard Straight Mechanical Pipe Thread
- NPSL: American Standard Straight Lock Nut Pipe Thread
- NPTF: American Standard Pipe Thread Tapered (Dryseal)
- BSPP: British Standard Pipe Thread Parallel
- BSPT: British Standard Pipe Thread Tapered
3. What is the Size Chart of NPT- American National Standard Taper Pipe Threads
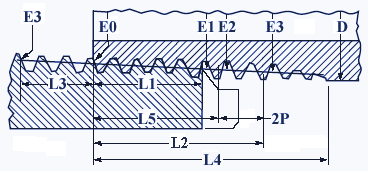
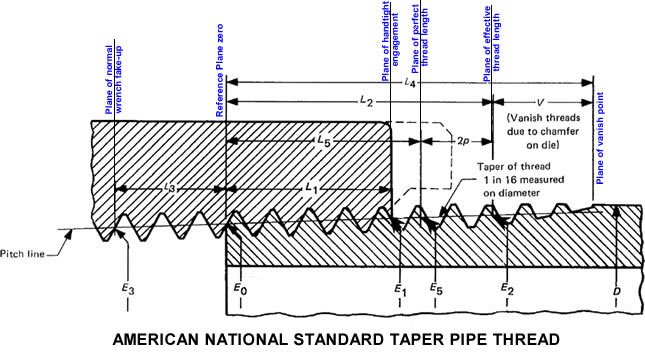
National Standard Pipe Taper Thread size charts contain data regarding both internal and external threads.
The tape rate of all the NPT threads is 1/16 which is measured by the change of diameter over the distance. Given below is a standard size chart that can be used for reference in order to find the most suitable national standard that will suit your needs.
| NPT Thread Chart | ||||||||||||
| Nom. Pipe Size | Outer Dia. of Pipe | TPI | Pitch of Thread | Ptich Dia. at Begining of External Thread | Handtight Engagement | Effective Thread, External | Overall Length, External Thread (L4) b | Basic Minor Dia. at Small End of Pipe a | ||||
| Length (L1) | Dia. (E1) |
Length (L2) | Dia. (E2) | |||||||||
| inch | Thd. | inch | Thd. | |||||||||
| 1/16 | 0.3125 | 27 | 0.03704 | 0.27118 | 0.160 | 4.32 | 0.28118 | 0.2611 | 7.05 | 0.28750 | 0.3896 | 0.2416 |
| 1/8 | 0.405 | 27 | 0.03704 | 0.36351 | 0.1615 | 4.36 | 0.37360 | 0.2639 | 7.12 | 0.38000 | 0.3924 | 0.3339 |
| 1/4 | 0.540 | 18 | 0.05556 | 0.47739 | 0.2278 | 4.10 | 0.49163 | 0.4018 | 7.23 | 0.50250 | 0.5946 | 0.4329 |
| 3/8 | 0.675 | 18 | 0.05556 | 0.61201 | 0.240 | 4.32 | 0.62701 | 0.4078 | 7.34 | 0.63750 | 0.6006 | 0.5676 |
| 1/2 | 0.840 | 14 | 0.07143 | 0.75843 | 0.320 | 4.48 | 0.77843 | 0.5337 | 7.47 | 0.79179 | 0.7815 | 0.7013 |
| 3/4 | 1.050 | 14 | 0.07143 | 0.96768 | 0.339 | 4.75 | 0.98887 | 0.5457 | 7.64 | 1.00179 | 0.7935 | 0.9105 |
| 1 | 1.315 | 11.5 | 0.08696 | 1.21363 | 0.400 | 4.60 | 1.23863 | 0.6828 | 7.85 | 1.25630 | 0.9845 | 1.1441 |
| 1 1/4 | 1.660 | 11.5 | 0.08686 | 1.55713 | 0.420 | 4.83 | 1.58338 | 0.7068 | 8.13 | 1.60130 | 1.0085 | 1.4876 |
| 1 1/2 | 1.900 | 11.5 | 0.08696 | 1.79609 | 0.420 | 4.83 | 1.82234 | 0.7235 | 8.32 | 1.84130 | 1.0252 | 1.7265 |
| Nom. Pipe Size | Outer Dia. of Pipe | TPI | Pitch of Thread | Ptich Dia. at Begining of External Thread | Handtight Engagement | Effective Thread, External | Overall Length, External Thread (L4) b | Basic Minor Dia. at Small End of Pipe a | ||||
| Length (L1) | Dia. (E1) |
Length (L2) | Dia. (E2) | |||||||||
| inch | Thd. | inch | Thd. | |||||||||
| 2 | 2.375 | 11.5 | 0.08696 | 2.26902 | 0.436 | 5.01 | 2.29627 | 0.7565 | 8.70 | 2.31630 | 1.0582 | 2.1995 |
| 2 1/2 | 2.875 | 8 | 0.12500 | 2.71953 | 0.682 | 5.46 | 2.76216 | 1.1375 | 9.10 | 2.79062 | 1.5712 | 2.6195 |
| 3 | 3.500 | 8 | 0.12500 | 3.34062 | 0.766 | 6.13 | 3.38850 | 1.20000 | 9.60 | 3.41562 | 1.6337 | 3.2406 |
| 3 1/2 | 4.000 | 8 | 0.12500 | 3.83750 | 0.821 | 6.57 | 3.88881 | 1.2500 | 10.00 | 3.91562 | 1.6837 | 3.7375 |
| 4 | 4.5000 | 8 | 0.12500 | 4.33438 | 0.844 | 6.75 | 4.38712 | 1.3000 | 10.40 | 4.41562 | 1.7337 | 4.2344 |
| 5 | 5.563 | 8 | 0.12500 | 5.39073 | 0.937 | 7.50 | 5.44929 | 1.4063 | 11.25 | 5.47862 | 1.8400 | 5.2907 |
| 6 | 6.625 | 8 | 0.12500 | 6.44609 | 0.958 | 7.66 | 6.50597 | 1.5125 | 12.10 | 6.54062 | 1.9462 | 6.3461 |
| 8 | 8.625 | 8 | 0.12500 | 8.43359 | 1.063 | 8.50 | 8.50003 | 1.7125 | 13.70 | 8.54062 | 2.1462 | 8.3336 |
| Nom. Pipe Size | Outer Dia. of Pipe | TPI | Pitch of Thread | Ptich Dia. at Begining of External Thread | Handtight Engagement | Effective Thread, External | Overall Length, External Thread (L4) b | Basic Minor Dia. at Small End of Pipe a | ||||
| Length (L1) | Dia. (E1) |
Length (L2) | Dia. (E2) | |||||||||
| inch | Thd. | inch | Thd. | |||||||||
| 10 | 10.750 | 8 | 0.12500 | 10.54531 | 1.210 | 9.68 | 10.62094 | 1.9250 | 15.40 | 10.66562 | 2.3587 | 10.4453 |
| 12 | 12.750 | 8 | 0.12500 | 12.53281 | 1.360 | 10.88 | 12.61781 | 2.1250 | 17.00 | 12.66562 | 2.5587 | 12.4328 |
| 14 O.D. | 14.000 | 8 | 0.12500 | 13.77500 | 1.562 | 12.50 | 13.87262 | 2.2500 | 18.00 | 13.91562 | 2.6837 | 13.6750 |
| 16 O.D. | 16.000 | 8 | 0.12500 | 15.76250 | 1.812 | 14.50 | 15.87575 | 2.4500 | 19.60 | 15.91562 | 2.8837 | 15.6625 |
| 18 O.D. | 18.000 | 8 | 0.12500 | 17.75000 | 2.000 | 16.00 | 17.87500 | 2.6500 | 21.20 | 17.91562 | 3.0837 | 17.6500 |
| 20 O.D. | 20.000 | 8 | 0.12500 | 19.73750 | 2.125 | 17.00 | 19.87031 | 2.8500 | 22.80 | 19.91562 | 3.2837 | 19.6375 |
| 24 O.D. | 24.000 | 8 | 0.12500 | 23.71250 | 2.375 | 19.00 | 23.86094 | 3.2500 | 26.00 | 23.91562 | 3.6837 | 23.6125 |
4. What is Applications of NPT (National Standard Taper Pipe Threads)
NPT pipes are used in a wide variety of applications ranging from electrical conduits to high-pressure piping that carry natural gas and chemically reactive and aggressive liquids.
Some applications that use NPT are as follows:
- Pneumatic systems
- Hydraulic systems
- Plumbing and fittings
- Fire protection systems
- Chemical industry
- Processing industry
- Agricultural industry
- Irrigation systems
- Control systems
- Air-conditioning systems
NPT threaded plastic fittings can be readily found as they are standard. However, there are distinct and specific installation and sealing recommendations for installations involving plastic Vs metals. Also, both thread types have installation methods that are different based on gauging the threads for conformance before true installation is complete.
Although these standards are manufactured in order to maintain the uniformity in fittings, tapered pipe threads can become unreliable over time. Due to the continued usage and repair, the threads can become damaged and susceptible to leakage. As a result of this, the area on the pipe where the crest and the root of the thread meet can form a spiral leak path. When this happens, no amount of tightening can make the joint leak proof.
To face this situation, a leak proofing sealant is used. Most of the time, Teflon based sealant is recommended and used on all plastic pipe threads. Most commonly, Teflon tape is wrapped in about two to three turns around the male thread before the final assembly.
Sometimes, liquid Teflon based sealants are also used in order to ensure a pressure tight seal. However, it is always important to ensure that sealants are applied with maximum care so as to prevent from introducing the sealant materials into the flow path of the system.
5. Conclusion
NPT or National Pipe Taper Thread Standard is the most commonly used standard for pipe threads throughout the United States and Canada.
NPT provides a reliable seal for pipes that are used for transportation of hydraulic fluid as well as other liquids, gases and steam. NPTs can be seen to be used in materials like PTFE, PVC, nylon bronze and cast iron, in addition to steel and brass. Among many other thread standards, NPT remains one of the most commonly used standards due to their versatile applications.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related Products
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and working details to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 159 27 555863
Want the best price & newest metal working machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Armpro's monthly newsletter,we're free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable working solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Tapping Machine: The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2021
- Electric Tapping Machines:the Ultimate Buying Guide in 2021
- Drilling Machine: The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2021
- Grinding Machine:The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2021
- Metal Band Saw Machine :The Complete Buying Guide in 2021
- Pneumatic Tapping Machine:The Complete Importing Guide in 2021
- Bench Tapping Machine:The Complete Buying Guide in 2021
- CNC Tapping Machine:The Complete Buying Guide In 2021
- Magnetic Base Drill Machine:The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2021
- Drilling And Tapping Machine:The Complete Buying Guide in 2021
Most Popular

Tell us your material or budget,we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours