UNIFIED SCREW THREADS (UNC/UNF/UNEF) Thread size chart
- UNIFIED SCREW THREADS (UNC/UNF/UNEF)The UTS (Unified Thread Standard) is a widely accepted definition for a standard thread form that comes along with allowances, tolerances and labels for screw threads that are most commonly used within the United States and Canada.
Currently, the UTS is under the control of ASME/ANSI of the United States. UTS is used as the main standard for bolts, nuts and various other fasteners used here. Although it contains the same profile as the ISO MTS, the difference is that its basic dimensions are chosen to be an inch fraction rather than a millimetre value.
1.What is the UNIFIED SCREW THREADS parameter?
The Unified Screw Threads have the designations of DPSC. These designations are as follows:
- Diameter
- Pitch
- Series
- Class
The designations are described in detail below:
1.Diameter
The Nomnal Diameter is measured in Inch Fraction. The diameters that are ¼” and above are measured in inch fractions. For instance, ¼”, ¾” or 1 ¼”. The diameters that are below ¼” are given with a series of numbers that range from #0 to #12. Every number is assigned to a single arbitrary diameter.
Instead of using fractions, diameters may also be indicated using the relevant decimal value. For instance, instead of ¼”, 0.250 and instead of 7/16”, 0.4375 can be used. The diameter that is described by each ‘number’ from #0 to #12 is given in the below table.
2. Pitch
The Pitch is given in TPI. For instance, a ¼-20 is in fact a thread with a pitch of 20 TPI. Instead of this, the pitch can also be denoted using distance. In this method, ¼-0.05P is a thread with a pitch of 0.05” which is equivalent to 20 TPI.
3.Series
Most of the time, the series of UST would be UNC (coarse pitch), UNF (fine pitch) or UNEF (extra fine pitch). The ASTM B1.1 also has given definitions for several constant pitch series. These are identified by ##-UN. For instance, the 12-UN or 8-UN remains the same for the complete diameter range within this series. Although this method is in use, it is very rare.
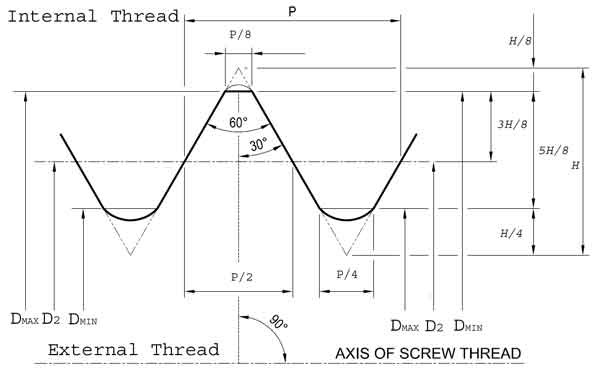
List of symbols used in charts and formulas of Unified Inch Threads
| Symbol | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Basic Parameters - Diameters and Pitch | |
| D | Major (Basic) diameter of internal thread |
D1 | Minor diameter of internal thread |
| D2 | Pitch diameter of internal thread |
| D3 | Major diameter, rounded root, internal thread |
| d | Major (Basic) diameter of external thread |
| d1 | Minor diameter of external thread |
| d2 | Pitch diameter of external thread |
| d3 | Major diameter, rounded root, internal thread |
| n | Number of threds per Inch (TPI) |
| P | Pitch (Distance) |
| L | Lead |
| Height Parameters | |
| H | Height of fundamental triangle |
| hs | Thread height - External thread |
| has | Thread addendum - External thread |
| hn | Thread height - Internal thread |
| han | Thread addendum - Internal thread |
| Length Parameters | |
| LE | Length of thread engagement |
| Lts | Length of complete external thread |
| Ltn | Length of complete internal thread |
| Allowance, Deviation, and Tolerances | |
| TD1 | Tolerance for D1 |
| TD2 | Tolerance for D2 |
| Td | Tolerance for d |
| Td2 | Tolerance for d2 |
| es | Allowance for external thread |
| Root / Creast Parameters | |
| Fcs | Flat crest width of external thread |
| Frs | Flat root width of external thread |
| Fcs | Flat crest width of internal thread |
| Fcs | Flat root width of internal thread |
4.Class
The class is defined using a code with two characters. The first character contains a digit between 1 and 3. The designations are 1 = Tight fit, 2 = Medium Fit and 3 = Loose Fit. The second character is a letter from the English alphabet. According to his, A = External thread and B = Internal thread.
In addition to the above designations, some additional parameters are given as well. They are:
- Direction: the suffix -LH should be added to a left-handed thread. Always the default direction of the thread would be right-handed, which means a screw would be right-handed unless specified so.
- The number of starts: Every thread has a single start by default; which results in an equal number of lead and pitch on the thread. The lead is indicated along with a thread that has multiple starts.
2. What is the UNIFIED SCREW THREADS size chart?
After considering all the given designations, it is clear that there is a wide range of screw threads to choose from. This is especially important when we choose the right type of screw thread based on the purpose, we need to use them. The size chart that is used to identify the screw threads based on the relevant applications is given below.
The size chart is calibrated based on the major diameter, threads per inch, tap drill size and the pitch of the screw thread. The below-given chart can be used to choose the right unified screw thread that you will need for your task.
The table below shows the types of screw threads, sizes, and specifications of Unified Coarse (UNC) threads.
| Thread | Major Diameter | Thread Per Inch | Pitch Diameter | Minor Diameter Male Thread | Minor Diameter Female Thread |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0730 | 64 | 0.0629 | 0.0544 | 0.0561 |
| 2 | 0.0860 | 56 | 0.0744 | 0.0648 | 0.0667 |
| 3 | 0.0990 | 48 | 0.0855 | 0.0741 | 0.0764 |
| 4 | 0.1120 | 40 | 0.0958 | 0.0822 | 0.0849 |
| 5 | 0.1250 | 40 | 0.1088 | 0.0952 | 0.0979 |
| 6 | 0.1380 | 32 | 0.1177 | 0.1008 | 0.1042 |
| 8 | 0.1640 | 32 | 0.1437 | 0.1268 | 0.1302 |
| 10 | 0.1900 | 24 | 0.1629 | 0.1404 | 0.1449 |
| 12 | 0.2160 | 24 | 0.1889 | 0.1664 | 0.1709 |
| 1/4 | 0.2500 | 20 | 0.2175 | 0.1905 | 0.1959 |
| 5/16 | 0.3125 | 18 | 0.2764 | 0.2464 | 0.2524 |
| 3/8 | 0.3750 | 16 | 0.3344 | 0.3005 | 0.3073 |
| 7/16 | 0.4375 | 14 | 0.3911 | 0.3525 | 0.3602 |
| 1/2 | 0.5000 | 13 | 0.4500 | 0.4084 | 0.4167 |
| 9/16 | 0.5625 | 12 | 0.5084 | 0.4633 | 0.4723 |
| 5/8 | 0.6250 | 11 | 0.5660 | 0.5168 | 0.5266 |
| 3/4 | 0.7500 | 10 | 0.6850 | 0.6309 | 0.6417 |
| 7/8 | 0.8750 | 9 | 0.8028 | 0.7427 | 0.7547 |
| 1 | 1.0000 | 8 | 0.9188 | 0.8512 | 0.8647 |
| 1-1/8 | 1.1250 | 7 | 1.0322 | 0.9549 | 0.9704 |
| 1 1/4 | 1.2500 | 7 | 1.1572 | 1.0799 | 1.0954 |
| 1-3/8 | 1.3750 | 6 | 1.2667 | 1.1766 | 1.1946 |
| 1 1/2 | 1.5000 | 6 | 1.3917 | 1.3016 | 1.3196 |
| 1 3/4 | 1.7500 | 5 | 1.6201 | 1.5119 | 1.5335 |
| 2 | 2.0000 | 4.5 | 1.8557 | 1.7353 | 1.7594 |
| 2 1/4 | 2.2500 | 4.5 | 2.1057 | 1.9853 | 2.0094 |
| 2 1/2 | 2.5000 | 4 | 2.3376 | 2.2023 | 2.2294 |
| 2 3/4 | 2.7500 | 4 | 2.5876 | 2.4523 | 2.4794 |
| 3 | 3.0000 | 4 | 2.8376 | 2.7023 | 2.7294 |
| 3 1/4 | 3.2500 | 4 | 3.0876 | 2.9523 | 2.9794 |
| 3 1/2 | 3.5000 | 4 | 3.3376 | 3.2023 | 3.2294 |
| 3 3/4 | 3.7500 | 4 | 3.5876 | 3.4523 | 3.4794 |
| 4 | 4.0000 | 4 | 3.8376 | 3.7023 | 3.7294 |
The table below shows the types of screw threads, sizes, and specifications of Unified Fine (UNF) threads.

| Thread | Major Diameter | Thread per Inch | Pitch Diameter | Minor Diameter Male Thread | Minor Diameter Female Thread |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.0600 | 80 | 0.0519 | 0.0451 | 0.0465 |
| 1 | 0.0730 | 72 | 0.0640 | 0.0565 | 0.0580 |
| 2 | 0.0860 | 64 | 0.0759 | 0.0674 | 0.0691 |
| 3 | 0.0990 | 56 | 0.0874 | 0.0778 | 0.0797 |
| 4 | 0.1120 | 48 | 0.0985 | 0.0871 | 0.0894 |
| 5 | 0.1250 | 44 | 0.1102 | 0.0979 | 0.1004 |
| 6 | 0.1380 | 40 | 0.1218 | 0.1082 | 0.1109 |
| 8 | 0.1640 | 36 | 0.1460 | 0.1309 | 0.1339 |
| 10 | 0.1900 | 32 | 0.1697 | 0.1528 | 0.1562 |
| 12 | 0.2160 | 28 | 0.1928 | 0.1734 | 0.1773 |
| 1/4 | 0.2500 | 28 | 0.2268 | 0.2074 | 0.2113 |
| 5/16 | 0.3125 | 24 | 0.2854 | 0.2629 | 0.2674 |
| 3/8 | 0.3750 | 24 | 0.3479 | 0.3254 | 0.3299 |
| 7/16 | 0.4375 | 20 | 0.4050 | 0.3780 | 0.3834 |
| 1/2 | 0.5000 | 20 | 0.4675 | 0.4405 | 0.4459 |
| 9/16 | 0.5625 | 18 | 0.5264 | 0.4964 | 0.5024 |
| 5/8 | 0.6250 | 18 | 0.5889 | 0.5589 | 0.5649 |
| 3/4 | 0.7500 | 16 | 0.7094 | 0.6763 | 0.6823 |
| 7/8 | 0.8750 | 14 | 0.8286 | 0.7900 | 0.7977 |
| 1 | 1.0000 | 12 | 0.9459 | 0.9001 | 0.9098 |
| 1 1/8 | 1.1250 | 12 | 1.0709 | 1.0258 | 1.0348 |
| 1 1/4 | 1.2500 | 12 | 1.1959 | 1.1508 | 1.1598 |
| 1 3/8 | 1.3750 | 12 | 1.3209 | 1.2758 | 1.2848 |
| 1 1/2 | 1.5000 | 12 | 1.4459 | 1.4008 | 1.4098 |
The table below is the types of threads specifications of Unified Extra Fine (UNEF) threads.
| Thread | Major Diameter | Thread Per Inch | Pitch Diameter | Minor Diameter Male Thread | Minor Diameter Female Thread |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. 12 | 0.2160 | 32 | 0.1957 | 0.1788 | 0.1822 |
| 1/4 | 0.2500 | 32 | 0.2297 | 0.2128 | 0.2162 |
| 5/16 | 0.3125 | 32 | 0.2922 | 0.2753 | 0.2787 |
| 3/8 | 0.3750 | 32 | 0.3547 | 0.3378 | 0.3412 |
| 7/16 | 0.4375 | 28 | 0.4143 | 0.3949 | 0.3988 |
| 1/2 | 0.5000 | 28 | 0.4768 | 0.4574 | 0.4613 |
| 9/16 | 0.5625 | 24 | 0.5354 | 0.5129 | 0.5174 |
| 5/8 | 0.6250 | 24 | 0.5979 | 0.5754 | 0.5799 |
| 11/16 | 0.6875 | 24 | 0.6604 | 0.6379 | 0.6424 |
| 3/4 | 0.7500 | 20 | 0.7175 | 0.6905 | 0.6959 |
| 13/16 | 0.8125 | 20 | 0.7800 | 0.7530 | 0.7584 |
| 7/8 | 0.8750 | 20 | 0.8425 | 0.8155 | 0.8209 |
| 15/16 | 0.9375 | 20 | 0.9050 | 0.8780 | 0.8834 |
| 1 | 1.0000 | 20 | 0.9675 | 0.9405 | 0.9459 |
| 1 1/16 | 1.0625 | 18 | 1.0264 | 0.9964 | 1.0024 |
| 1 1/8 | 1.1250 | 18 | 1.0889 | 1.0589 | 1.0649 |
| 1 3/16 | 1.1875 | 18 | 1.1514 | 1.1214 | 1.1274 |
| 1 1/4 | 1.2500 | 18 | 1.2139 | 1.1839 | 1.1899 |
| 1 5/16 | 1.3125 | 18 | 1.2764 | 1.2464 | 1.2524 |
| 1 3/8 | 1.3750 | 18 | 1.3389 | 1.3089 | 1.3149 |
| 1 7/16 | 1.4375 | 18 | 1.4014 | 1.3714 | 1.3774 |
| 1 1/2 | 1.5000 | 18 | 1.4639 | 1.4339 | 1.4399 |
| 1 9/16 | 1.5625 | 18 | 1.5264 | 1.4964 | 1.5024 |
| 1 5/8 | 1.6250 | 18 | 1.5889 | 1.5589 | 1.5649 |
| 1 11/16 | 1.6875 | 18 | 1.6514 | 1.6214 | 1.6274 |
3. What is the application of the UNIFIED SCREW THREADS?
The unified screw thread is used in various applications. It has become prominent in a number of industries as well as domestic usage due to its ease of use. Three main basic applications can be identified for screw threads:
- Holding parts together
- Adjusting parts with reference to each other
- Transmitting power
Precisely, screw threads are used in a wide range of applications in many industries. Nuts and bolts, machine screws, plastic screws and wood screws are used as fasteners. Screw threads are also used for connecting thread pipes and hoses to each other as well as to caps and fixtures.
Screw threads are also used for the below functions. When all of these applications are considered, the screw thread has two main functions. They are:
- Converting rotary motion into linear motion
- Preventing linear motion without the corresponding rotation
- Gear reduction using worm drives.
The applications of screw threads are as follows:
- Moving objects linearly. This is done by converting rotary motion into linear motion similar to the leadscrew of a jack.
- Measuring and amplifying by correlating linear motion to rotary motion similar to a micrometer.
4. How to make UNIFIED SCREW THREADS?
Unified Screw threads have their own manufacturing process similar to other screw threads like ACME, Square and Buttress threads. The screw threads give a far more favorable touch in some instances which enhances its usage against the rest of them. The screw is basically a ridge wrapped around a cylinder or a cone, which is in the form of a helix. The two matched pair of threads that are external and internal are described as males and females. A screw that contains threads on the surface is considered as male and the screws that have threads on the internal surface are considered as female.
5. Conclusion
Basically, Screw threads have an increased number of threads per inch. This decreases the linear screw motion per turn compared to ACME, Square and Buttress threads. The screw threads also have an increased shaft diameter which increases the delivery strength. There are three variations in which screw threads are presented: they are coarse, fine and extra-fine variations.
The main advantage of using unified screw threads is that the increased number of threads per inch allows an increased linear force at the same amount of torque when square, ACME or buttress threads are compared.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related Products
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and working details to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 159 27 555863
Want the best price & newest metal working machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for Armpro's monthly newsletter,we're free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable working solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Tapping Machine: The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2021
- Electric Tapping Machines:the Ultimate Buying Guide in 2021
- Drilling Machine: The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2021
- Grinding Machine:The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2021
- Metal Band Saw Machine :The Complete Buying Guide in 2021
- Pneumatic Tapping Machine:The Complete Importing Guide in 2021
- Bench Tapping Machine:The Complete Buying Guide in 2021
- CNC Tapping Machine:The Complete Buying Guide In 2021
- Magnetic Base Drill Machine:The Ultimate Buying Guide in 2021
- Drilling And Tapping Machine:The Complete Buying Guide in 2021
Most Popular
Tell us your material or budget,we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours